
Contributions
Abstract: S290
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Transfusion medicine
Background
CAD is chronic autoimmune hemolytic anemia mediated by classical complement pathway activation. CAD patients also may experience profound fatigue (secondary to the anemia and chronic inflammation) (Weitz et al. Blood. 2020), anxiety, and depression (Patel et al. Blood. 2020). Sutimlimab (formerly BIVV009), a first-in-class humanized monoclonal G4 antibody, selectively inhibits C1s of the C1 complex, preventing classical pathway activation. In the single-arm CARDINAL study (NCT03347396), sutimlimab rapidly improved all patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in CAD patients and recent transfusion history. CADENZA (NCT03347422) is a randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled Phase 3 study to assess sutimlimab in CAD patients without history of recent transfusion.
Aims
To report the effects of sutimlimab versus PBO on QOL PROs from CADENZA Part A (initial 26-week treatment period).
Methods
Adult patients with confirmed CAD diagnosis, baseline hemoglobin ≤10 g/dL, total bilirubin above normal, ≥1 recent CAD-related symptom, and no recent transfusion were enrolled. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive sutimlimab (<75 kg, 6.5g; ≥75 kg, 7.5 g; N=22) or PBO (N=20) on Days 0 and 7, then biweekly infusions. A secondary objective is to evaluate QOL using the PROs, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue, Patient Global Impression of (fatigue) Severity (PGIS), Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC), EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L; index and visual analog scale [VAS] scores) questionnaire, and 12-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-12; physical and mental components). Treatment assessment time point (TAT) was the mean value for Weeks (W) 23, 25, and 26 for FACIT-Fatigue. FACIT-Fatigue was analyzed by a mixed model for repeated measures; W26 change from baseline for other PROs was analyzed by analysis of covariance with baseline as the covariate.
Results
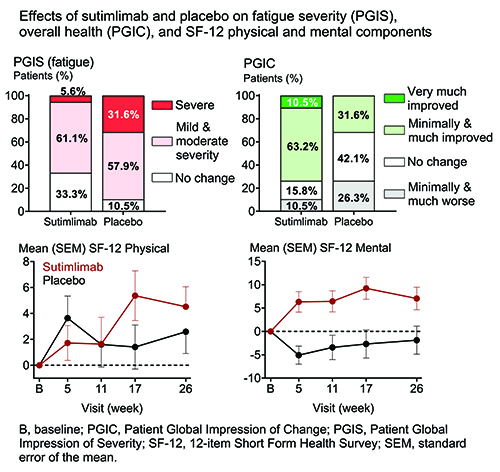
Baseline QOL (mean FACIT-Fatigue, 32.3) was comparable to other hemolytic anemias, such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (Schrezenmeier et al. Haematologica. 2014), and cancer (Escalente et al. Cancer Med. 2019). As early as W1, sutimlimab, but not PBO, elicited a clinically meaningful increase (≥5 points) in mean FACIT-Fatigue. At TAT, the least squares (LS) mean (standard error of the mean [SEM]) difference in FACIT-Fatigue between sutimlimab and PBO groups was 8.9 (2.5) (P<0.001). At W26, severe fatigue was present in 5.6% of patients in the sutimlimab group compared with 31.6% in PBO (PGIS; Figure). W26 overall health (PGIC) was assessed as “improved” by 73.7% of patients receiving sutimlimab compared with 31.6% on PBO (Figure). Strong trends were present for improved (higher) W26 SF-12 physical and mental scores in the sutimlimab group compared with PBO (LS mean [SEM] difference physical: 4.0 [2.1], P=0.064; mental: 6.1 [3.2], P=0.065) (Figure). A strong trend also existed for improved (higher) W26 EQ-5D-5L VAS in the sutimlimab versus PBO groups (LS mean [SEM] difference: 10.8 [5.3], P=0.052). W26 change in EQ-5D-5L index score was not different between groups.
Conclusion
Classical complement pathway inhibition by sutimlimab elicited a rapid, clinically meaningful and significant improvement in fatigue. Nearly three-quarters of patients on sutimlimab considered their overall health improved compared with approximately one-third on PBO. Improvements in some other PROs were also observed. In addition to the single-arm CARDINAL study, these PBO-controlled results support targeting the classical pathway via C1s inhibition in CAD.
Keyword(s): Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), Complement, Hemolysis, Quality of life
Abstract: S290
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Transfusion medicine
Background
CAD is chronic autoimmune hemolytic anemia mediated by classical complement pathway activation. CAD patients also may experience profound fatigue (secondary to the anemia and chronic inflammation) (Weitz et al. Blood. 2020), anxiety, and depression (Patel et al. Blood. 2020). Sutimlimab (formerly BIVV009), a first-in-class humanized monoclonal G4 antibody, selectively inhibits C1s of the C1 complex, preventing classical pathway activation. In the single-arm CARDINAL study (NCT03347396), sutimlimab rapidly improved all patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in CAD patients and recent transfusion history. CADENZA (NCT03347422) is a randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled Phase 3 study to assess sutimlimab in CAD patients without history of recent transfusion.
Aims
To report the effects of sutimlimab versus PBO on QOL PROs from CADENZA Part A (initial 26-week treatment period).
Methods
Adult patients with confirmed CAD diagnosis, baseline hemoglobin ≤10 g/dL, total bilirubin above normal, ≥1 recent CAD-related symptom, and no recent transfusion were enrolled. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive sutimlimab (<75 kg, 6.5g; ≥75 kg, 7.5 g; N=22) or PBO (N=20) on Days 0 and 7, then biweekly infusions. A secondary objective is to evaluate QOL using the PROs, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue, Patient Global Impression of (fatigue) Severity (PGIS), Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC), EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L; index and visual analog scale [VAS] scores) questionnaire, and 12-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-12; physical and mental components). Treatment assessment time point (TAT) was the mean value for Weeks (W) 23, 25, and 26 for FACIT-Fatigue. FACIT-Fatigue was analyzed by a mixed model for repeated measures; W26 change from baseline for other PROs was analyzed by analysis of covariance with baseline as the covariate.
Results
Baseline QOL (mean FACIT-Fatigue, 32.3) was comparable to other hemolytic anemias, such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (Schrezenmeier et al. Haematologica. 2014), and cancer (Escalente et al. Cancer Med. 2019). As early as W1, sutimlimab, but not PBO, elicited a clinically meaningful increase (≥5 points) in mean FACIT-Fatigue. At TAT, the least squares (LS) mean (standard error of the mean [SEM]) difference in FACIT-Fatigue between sutimlimab and PBO groups was 8.9 (2.5) (P<0.001). At W26, severe fatigue was present in 5.6% of patients in the sutimlimab group compared with 31.6% in PBO (PGIS; Figure). W26 overall health (PGIC) was assessed as “improved” by 73.7% of patients receiving sutimlimab compared with 31.6% on PBO (Figure). Strong trends were present for improved (higher) W26 SF-12 physical and mental scores in the sutimlimab group compared with PBO (LS mean [SEM] difference physical: 4.0 [2.1], P=0.064; mental: 6.1 [3.2], P=0.065) (Figure). A strong trend also existed for improved (higher) W26 EQ-5D-5L VAS in the sutimlimab versus PBO groups (LS mean [SEM] difference: 10.8 [5.3], P=0.052). W26 change in EQ-5D-5L index score was not different between groups.

Conclusion
Classical complement pathway inhibition by sutimlimab elicited a rapid, clinically meaningful and significant improvement in fatigue. Nearly three-quarters of patients on sutimlimab considered their overall health improved compared with approximately one-third on PBO. Improvements in some other PROs were also observed. In addition to the single-arm CARDINAL study, these PBO-controlled results support targeting the classical pathway via C1s inhibition in CAD.
Keyword(s): Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), Complement, Hemolysis, Quality of life


