
Contributions
Abstract: S236
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - GvHD
Background
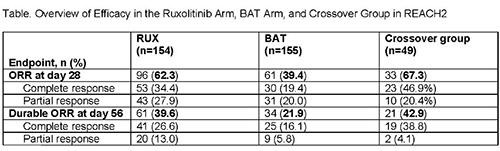
Historically, the long-term prognosis has been poor in patients (pts) with acute graft-vs-host disease (aGVHD) who fail initial treatment with steroids. REACH2 (NCT02913261; N=309) is a randomized, phase 3 trial investigating the efficacy and safety of the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib (RUX) vs best available therapy (BAT) in pts with steroid-refractory (SR) aGVHD. Pts treated with RUX had a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) at day 28 (primary endpoint) than pts treated with BAT (62.3%; complete response [CR], 34.4%; partial response [PR], 27.9% vs 39.4% [CR, 19.4%; PR, 20.0%]; P<0.001). Durable ORR at day 56 (key secondary endpoint) was also significantly higher with RUX (39.6% vs 21.9%; P<0.001). Pts randomized to BAT could cross over to RUX after day 28. We report safety and efficacy findings from the crossover group in REACH2.
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of RUX in pts who crossed over from BAT.
Methods
309 pts aged ≥12 years diagnosed with grade II-IV SR aGVHD were randomized 1:1 to receive RUX 10 mg bid (n=154) or investigator-selected BAT (n=155). All pts provided written informed consent. After day 28, pts in the BAT arm who did not meet the primary endpoint or lost response could cross over to RUX up to week 24.
Results
Overall, 49 pts (31.6%) crossed over to RUX treatment (data cutoff, January 6, 2020). At baseline, the median age in the crossover group was 54 years (range, 13-71 years) and 53.1% of pts were male; 38.8% and 61.2% of pts had grade II and grade III/IV disease, respectively. Overall, ATG (20.4%) and etanercept (20.4%) were the most common BATs; 12 pts (24.5%) were treated with ≥2 BATs. The median time to crossover was 34 days (range, 28-162 days). At data cutoff, 11 pts (22.4%) had completed the crossover treatment period (treatment up to crossover day 56), and 2 were still receiving RUX. 36 crossover pts (73.5%) discontinued RUX treatment, with the most common reasons for discontinuation being adverse events (AEs; 24.5%), death (16.3%), and lack of efficacy (12.2%). A total of 27 crossover pts (55.1%) entered long-term follow-up.
The ORR at day 28 after crossover was 67.3% (CR, 46.9%; PR, 20.4%; 95% CI, 52.5%–80.1%), and the durable ORR at day 56 after crossover was 42.9% (95% CI, 28.8%–57.8%), both consistent with observations in the RUX arm at the primary analysis (Table). The mean EQ-5D-5L health rating improved in pts who crossed over to RUX (crossover baseline, 51.5; crossover week 24, 80.2).
After crossover, the median duration of treatment with RUX was 61.0 days (range, 2.0-383.0 days). Most pts (93.9%) received RUX 20 mg daily. All 49 pts had a dose change, with 63.3% having a dose interruption; 61.2% had a dose change or interruption due to AEs. Dose re-escalation occurred in 38.8% of pts. The safety profile of RUX after crossover from BAT was consistent with that in the RUX arm, with the most common AEs (≥20%) being anemia (30.6%; grade ≥3, 18.4%), thrombocytopenia (30.6%; 26.5%), hypokalemia (22.4%; 8.2%), and neutropenia (20.4%; 20.4%). There were 19 deaths (38.8%), mainly due to aGVHD (n=8).
Conclusion
RUX led to high response rates in pts who crossed over from BAT to RUX. ORR and durable ORR were consistent with those seen with RUX during the randomized period. No new safety signals were observed in crossover pts. These findings support the use of RUX in pts with SR aGVHD who failed treatment with other systemic therapies.
Keyword(s): Acute graft-versus-host disease, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Ruxolitinib
Abstract: S236
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - GvHD
Background
Historically, the long-term prognosis has been poor in patients (pts) with acute graft-vs-host disease (aGVHD) who fail initial treatment with steroids. REACH2 (NCT02913261; N=309) is a randomized, phase 3 trial investigating the efficacy and safety of the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib (RUX) vs best available therapy (BAT) in pts with steroid-refractory (SR) aGVHD. Pts treated with RUX had a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) at day 28 (primary endpoint) than pts treated with BAT (62.3%; complete response [CR], 34.4%; partial response [PR], 27.9% vs 39.4% [CR, 19.4%; PR, 20.0%]; P<0.001). Durable ORR at day 56 (key secondary endpoint) was also significantly higher with RUX (39.6% vs 21.9%; P<0.001). Pts randomized to BAT could cross over to RUX after day 28. We report safety and efficacy findings from the crossover group in REACH2.
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of RUX in pts who crossed over from BAT.
Methods
309 pts aged ≥12 years diagnosed with grade II-IV SR aGVHD were randomized 1:1 to receive RUX 10 mg bid (n=154) or investigator-selected BAT (n=155). All pts provided written informed consent. After day 28, pts in the BAT arm who did not meet the primary endpoint or lost response could cross over to RUX up to week 24.
Results
Overall, 49 pts (31.6%) crossed over to RUX treatment (data cutoff, January 6, 2020). At baseline, the median age in the crossover group was 54 years (range, 13-71 years) and 53.1% of pts were male; 38.8% and 61.2% of pts had grade II and grade III/IV disease, respectively. Overall, ATG (20.4%) and etanercept (20.4%) were the most common BATs; 12 pts (24.5%) were treated with ≥2 BATs. The median time to crossover was 34 days (range, 28-162 days). At data cutoff, 11 pts (22.4%) had completed the crossover treatment period (treatment up to crossover day 56), and 2 were still receiving RUX. 36 crossover pts (73.5%) discontinued RUX treatment, with the most common reasons for discontinuation being adverse events (AEs; 24.5%), death (16.3%), and lack of efficacy (12.2%). A total of 27 crossover pts (55.1%) entered long-term follow-up.
The ORR at day 28 after crossover was 67.3% (CR, 46.9%; PR, 20.4%; 95% CI, 52.5%–80.1%), and the durable ORR at day 56 after crossover was 42.9% (95% CI, 28.8%–57.8%), both consistent with observations in the RUX arm at the primary analysis (Table). The mean EQ-5D-5L health rating improved in pts who crossed over to RUX (crossover baseline, 51.5; crossover week 24, 80.2).
After crossover, the median duration of treatment with RUX was 61.0 days (range, 2.0-383.0 days). Most pts (93.9%) received RUX 20 mg daily. All 49 pts had a dose change, with 63.3% having a dose interruption; 61.2% had a dose change or interruption due to AEs. Dose re-escalation occurred in 38.8% of pts. The safety profile of RUX after crossover from BAT was consistent with that in the RUX arm, with the most common AEs (≥20%) being anemia (30.6%; grade ≥3, 18.4%), thrombocytopenia (30.6%; 26.5%), hypokalemia (22.4%; 8.2%), and neutropenia (20.4%; 20.4%). There were 19 deaths (38.8%), mainly due to aGVHD (n=8).

Conclusion
RUX led to high response rates in pts who crossed over from BAT to RUX. ORR and durable ORR were consistent with those seen with RUX during the randomized period. No new safety signals were observed in crossover pts. These findings support the use of RUX in pts with SR aGVHD who failed treatment with other systemic therapies.
Keyword(s): Acute graft-versus-host disease, Janus Kinase inhibitor, Ruxolitinib


