
Contributions
Abstract: S226
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma - Translational research
Background
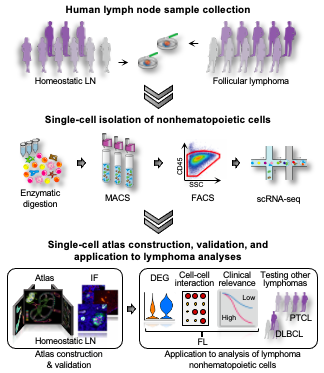
Activities of nonhematopoietic cells (NHCs) in lymphoma, including mesenchymal stromal cells and endothelial cells, reportedly underlie lymphomagenesis. However, understanding of lymphoma NHC activities have been hampered by unexplained NHC heterogeneity even in normal human lymph node (LN). Particularly, human LN blood endothelial cells (BECs) and non-endothelial stromal cells (NESCs) have not been analyzed at single-cell resolution.
Aims
We aimed to complete a transcriptome atlas of human NHCs in homeostatic LN (HLN) and lymphoma to reveal previously unrecognized heterogeneity. We also sought to reveal the single-cell landscape of stromal remodeling in lymphomas, particularly in follicular lymphoma (FL), to advance understanding of stromal contributions in lymphomagenesis.
Methods
We performed single-cell RNA sequencing of NHCs (>100,000 cells) extracted from human HLN (n=9), nodal FL (n=10), peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL; n=5), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL; n=3) samples. Data from HLN samples was mainly used for the construction of NHC atlas. Immunofluorescence (IF) staining was performed to validate the results of single-cell analysis and to explore the topological localizations of each NHC subcluster in the LN. Using the NHC atlas, we performed comprehensive comparative analysis with FL NHCs by differentially-expressed gene (DEG) and intercellular ligand-receptor analyses. We also investigated the prognostic impact of putative stroma-derived biomarkers using deposited microarray data of FL patients.
Results
Graph-based clustering analysis revealed that the transcriptional features of NHC subpopulations in HLN are highly conserved in FL NHCs. Unsupervised sub-clustering analysis of BECs, lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), and NESCs revealed 10, 8, and 12 subclusters, respectively, including some lacking mouse counterpart. IF staining successfully identified each NHC subcluster and its localization in the LN. In FL NHCs, the proportion of arterial BEC subclusters markedly increased relative to HLN, while the proportion of LECs decreased. In FL NESCs, the proportion of marginal reticular cells (MRCs) as well as follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) greatly increased. DEG analysis revealed that the greatest changes in gene expression occurs in NESC subclusters, particularly in MRCs, T-zone reticular cells (TRCs), perivascular stromal cells, and FDCs. Notably, in some NESC subclusters, we observed marked upregulation of genes relevant to solid cancers but previously not associated with lymphomagenesis (e.g. POSTN, EGFL6, and FAP). Combined interactome and DEG analysis revealed that interactions mediated through CXCL12 was unexpectedly upregulated only at stromal cells at adventitia. Additionally, the CCR7-CCL19 interaction was extended to non-TRC stromal cell subclusters. Also, the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis was highly activated in MRCs, indicating that MRCs as well as FDCs participate in FL expansion. Based, on these data, we identified putative stroma-derived biomarker LY6H, LOX, TDO2, and REM1 as promising prognostic predictors in FL. We finally confirmed that our NHC atlas is also useful to assess NHCs in more aggressive lymphomas including PTCL and DLBCL.
Conclusion
We constructed a comprehensive single-cell atlas of NHCs in human LN highly applicable to lymphoma NHC researches. Our study largely updates NHC taxonomy in LNs and provides a rich resource and deeper insights into lymphoma biology, a contribution that should advance lymphoma management and therapy.
Keyword(s): Endothelial cell, Follicular lymphoma, Lymphomagenesis, Stromal cell
Abstract: S226
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Lymphoma - Translational research
Background
Activities of nonhematopoietic cells (NHCs) in lymphoma, including mesenchymal stromal cells and endothelial cells, reportedly underlie lymphomagenesis. However, understanding of lymphoma NHC activities have been hampered by unexplained NHC heterogeneity even in normal human lymph node (LN). Particularly, human LN blood endothelial cells (BECs) and non-endothelial stromal cells (NESCs) have not been analyzed at single-cell resolution.
Aims
We aimed to complete a transcriptome atlas of human NHCs in homeostatic LN (HLN) and lymphoma to reveal previously unrecognized heterogeneity. We also sought to reveal the single-cell landscape of stromal remodeling in lymphomas, particularly in follicular lymphoma (FL), to advance understanding of stromal contributions in lymphomagenesis.
Methods
We performed single-cell RNA sequencing of NHCs (>100,000 cells) extracted from human HLN (n=9), nodal FL (n=10), peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL; n=5), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL; n=3) samples. Data from HLN samples was mainly used for the construction of NHC atlas. Immunofluorescence (IF) staining was performed to validate the results of single-cell analysis and to explore the topological localizations of each NHC subcluster in the LN. Using the NHC atlas, we performed comprehensive comparative analysis with FL NHCs by differentially-expressed gene (DEG) and intercellular ligand-receptor analyses. We also investigated the prognostic impact of putative stroma-derived biomarkers using deposited microarray data of FL patients.
Results
Graph-based clustering analysis revealed that the transcriptional features of NHC subpopulations in HLN are highly conserved in FL NHCs. Unsupervised sub-clustering analysis of BECs, lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), and NESCs revealed 10, 8, and 12 subclusters, respectively, including some lacking mouse counterpart. IF staining successfully identified each NHC subcluster and its localization in the LN. In FL NHCs, the proportion of arterial BEC subclusters markedly increased relative to HLN, while the proportion of LECs decreased. In FL NESCs, the proportion of marginal reticular cells (MRCs) as well as follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) greatly increased. DEG analysis revealed that the greatest changes in gene expression occurs in NESC subclusters, particularly in MRCs, T-zone reticular cells (TRCs), perivascular stromal cells, and FDCs. Notably, in some NESC subclusters, we observed marked upregulation of genes relevant to solid cancers but previously not associated with lymphomagenesis (e.g. POSTN, EGFL6, and FAP). Combined interactome and DEG analysis revealed that interactions mediated through CXCL12 was unexpectedly upregulated only at stromal cells at adventitia. Additionally, the CCR7-CCL19 interaction was extended to non-TRC stromal cell subclusters. Also, the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis was highly activated in MRCs, indicating that MRCs as well as FDCs participate in FL expansion. Based, on these data, we identified putative stroma-derived biomarker LY6H, LOX, TDO2, and REM1 as promising prognostic predictors in FL. We finally confirmed that our NHC atlas is also useful to assess NHCs in more aggressive lymphomas including PTCL and DLBCL.

Conclusion
We constructed a comprehensive single-cell atlas of NHCs in human LN highly applicable to lymphoma NHC researches. Our study largely updates NHC taxonomy in LNs and provides a rich resource and deeper insights into lymphoma biology, a contribution that should advance lymphoma management and therapy.
Keyword(s): Endothelial cell, Follicular lymphoma, Lymphomagenesis, Stromal cell


