
Contributions
Abstract: S207
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Tislelizumab is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody with high affinity/specificity for programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). It was engineered to minimize binding to Fc-γ receptors on macrophages, thereby decreasing antibody-dependent phagocytosis, a potential mechanism of T-cell clearance and resistance to anti–PD-1 therapy. Tislelizumab therapy was highly active in autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT)-failed or ineligible patients with relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (R/R cHL; Leukemia. 2020;34:533). Here, we report results from up to 3 years of follow-up.
Aims
To evaluate efficacy and safety of tislelizumab monotherapy in patients with R/R cHL in a single-arm, multicenter phase 2 study (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03209973).
Methods
Patients were eligible for the study if they failed to achieve a response or progressed after ASCT or received ≥2 lines of prior systemic chemotherapy for cHL and were ineligible for ASCT. Patients with R/R cHL enrolled in this study received 200 mg tislelizumab administered intravenously every 3 weeks until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) assessed by an independent review committee per Lugano criteria (J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059). Secondary endpoints were progression-free survival, duration of response, complete response (CR) rate, and time to response per independent review committee, safety, and tolerability.
Results
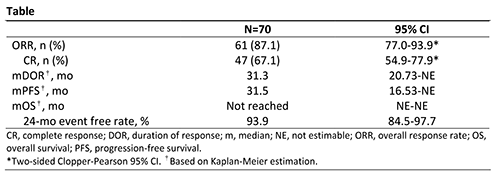
A total of 70 patients from 11 centers in China were enrolled and treated; patient characteristics have been previously reported. As of the data cutoff date (Nov 2, 2020), median follow-up was 33.8 months (range, 3.4-38.6). Patients still on treatment at the end of study (n=33; 47.1%) entered a long-term extension study. Efficacy data are presented in the Table. The ORR as assessed by IRC was 87.1%, and 67.1% of patients achieved CR. Among the 13 patients who received prior ASCT, 11 (84.6%) achieved CR. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs; ≥30%) were pyrexia (57.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (38.6%), hypothyroidism (37.1%), and increased weight (34.3%). Treatment-related grade ≥3 AEs (≥2 patients) were pneumonitis, hypertension, neutropenia, lipase increased, weight increased, and increased creatine phosphokinase (2.9% each). Immune-related AEs were reported in 32 patients (45.7%), with grade ≥3 AEs in 8 patients (11.4%): pneumonitis (n=4) and skin adverse reactions, nephritis, lipase increased, and blood creatine phosphokinase increased (n=1 each). AEs led to treatment discontinuation in 6 patients (8.6%).
Conclusion
Long-term follow-up data from patients with R/R cHL treated with tislelizumab further demonstrated the substantial therapeutic activity and continued progression-free survival benefit. There were no new safety concerns identified for long-term treatment with tislelizumab.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Refractory, Relapse
Abstract: S207
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Tislelizumab is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody with high affinity/specificity for programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). It was engineered to minimize binding to Fc-γ receptors on macrophages, thereby decreasing antibody-dependent phagocytosis, a potential mechanism of T-cell clearance and resistance to anti–PD-1 therapy. Tislelizumab therapy was highly active in autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT)-failed or ineligible patients with relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (R/R cHL; Leukemia. 2020;34:533). Here, we report results from up to 3 years of follow-up.
Aims
To evaluate efficacy and safety of tislelizumab monotherapy in patients with R/R cHL in a single-arm, multicenter phase 2 study (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03209973).
Methods
Patients were eligible for the study if they failed to achieve a response or progressed after ASCT or received ≥2 lines of prior systemic chemotherapy for cHL and were ineligible for ASCT. Patients with R/R cHL enrolled in this study received 200 mg tislelizumab administered intravenously every 3 weeks until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) assessed by an independent review committee per Lugano criteria (J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059). Secondary endpoints were progression-free survival, duration of response, complete response (CR) rate, and time to response per independent review committee, safety, and tolerability.
Results
A total of 70 patients from 11 centers in China were enrolled and treated; patient characteristics have been previously reported. As of the data cutoff date (Nov 2, 2020), median follow-up was 33.8 months (range, 3.4-38.6). Patients still on treatment at the end of study (n=33; 47.1%) entered a long-term extension study. Efficacy data are presented in the Table. The ORR as assessed by IRC was 87.1%, and 67.1% of patients achieved CR. Among the 13 patients who received prior ASCT, 11 (84.6%) achieved CR. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs; ≥30%) were pyrexia (57.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (38.6%), hypothyroidism (37.1%), and increased weight (34.3%). Treatment-related grade ≥3 AEs (≥2 patients) were pneumonitis, hypertension, neutropenia, lipase increased, weight increased, and increased creatine phosphokinase (2.9% each). Immune-related AEs were reported in 32 patients (45.7%), with grade ≥3 AEs in 8 patients (11.4%): pneumonitis (n=4) and skin adverse reactions, nephritis, lipase increased, and blood creatine phosphokinase increased (n=1 each). AEs led to treatment discontinuation in 6 patients (8.6%).

Conclusion
Long-term follow-up data from patients with R/R cHL treated with tislelizumab further demonstrated the substantial therapeutic activity and continued progression-free survival benefit. There were no new safety concerns identified for long-term treatment with tislelizumab.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Refractory, Relapse


