Contributions
Abstract: S187
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: New diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in multiple myeloma and AL amyloidosis
Background
IBER is an oral, novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) compound with marked synergistic tumoricidal and immune-stimulatory effects in combination with proteasome inhibitors (PIs) or anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies, preclinically and clinically. CC-220-MM-001 (NCT02773030) is an ongoing phase 1/2 study evaluating the maximum tolerated dose, recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D), safety, and preliminary efficacy of IBER with different treatment combinations in independent cohorts, in pts with RRMM.
Aims
To report results from the IBER+DARA+DEX (IberDd), IBER+BORT+DEX (IberVd), and IBER+CFZ+DEX (IberKd) cohorts of the CC-220-MM-001 study.
Methods
Eligible pts received ≥2 prior regimens in the IberDd and IberKd cohorts, and ≥1 prior regimen in the IberVd cohort, containing lenalidomide or pomalidomide, and a PI. All pts had progressed ≤60 days of their last MM therapy. Escalating oral doses of IBER were given on Day (D)1–21 of each 28-D cycle in the IberDd cohort and in the IberKd cohort with weekly CFZ, and on D1–14 of each 21-D cycle in the IberVd cohort. DEX was given weekly in all 3 cohorts.
Results
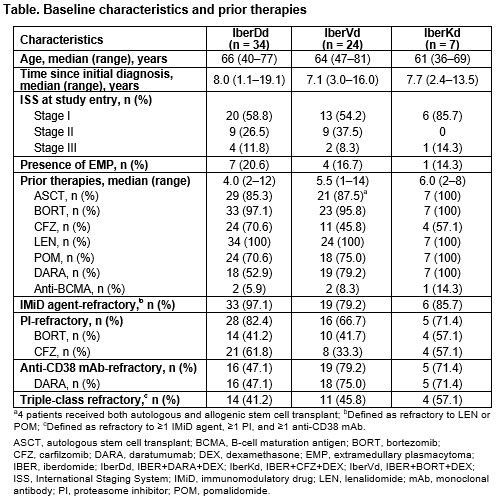
As of Dec 14, 2020, 34 pts had received IberDd, 24 pts IberVd, and 7 pts IberKd. Exposure to prior regimens was heterogeneous (Table), all pts were refractory to their last prior regimen, and median number of prior therapies was 4.0 (2–12), 5.5 (1–14), and 6.0 (2–8), with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively. IBER doses ranged from 1.0mg to 1.6mg. Median follow-up was 3.9 (0.1–20.7), 5.5 (1.2–18.0), and 5.1 (3.5–15.7) months, 15 (44%), 9 (38%), and 3 (43%) pts continue on treatment, and median cycles received was 4.0 (1–21), 7.5 (1–24), and 5.0 (3–16) with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively.
Most frequent hematologic grade (G) 3–4 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were neutropenia (63%), anemia (28%), leukopenia (28%), and lymphopenia (25%) with IberDd, neutropenia (29%) and thrombocytopenia (25%) with IberVd, and lymphopenia (57%) and neutropenia (43%) with IberKd. In all cohorts, neutropenia was managed with G-CSF. One pt (IberDd; 1.2mg) had G4 neutropenic sepsis. Occurrence of G3–4 non-hematologic TEAEs was low in all 3 cohorts. There were 12 (38%), 8 (33%), and 3 (43%) pts with ≥1 IBER dose reduction, with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively.
In the IberDd cohort, the overall response rate (ORR) was 41% (12/29 pts: 1 stringent complete response [sCR], 2 CRs, 2 very good partial responses [VGPRs], 7 partial responses [PRs]), the clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 52%, and disease control rate (DCR) was 86%. In the IberVd cohort, ORR was 58% (14/24 pts: 2 CRs, 5 VGPRs, 7 PRs), CBR was 67%, and DCR was 92%. Responses with IberDd and IberVd were observed in DARA- and BORT-refractory pts, respectively. In the IberKd cohort, ORR was 57% (4/7 pts: 1 sCR, 2 VGPRs, 1 PR), CBR was 57%, and DCR was 86%. Median time to response was 4.1 (4.0–12.0), 3.6 (3.0–13.1), and 4.1 (4.1–8.1) weeks, in the IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd cohorts, respectively. Median duration of response is 63.3 weeks in the IberVd cohort, and not reached in the IberDd and IberKd cohorts.
RP2D was determined at 1.6mg in the IberDd cohort, while dose evaluation continues in the IberVd and IberKd cohorts.
Updated data will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion
In heavily pretreated pts with RRMM, IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd showed a manageable safety profile and promising efficacy including CRs, even among DARA- and BORT-refractory pts. The study is ongoing. These results support further development of IBER-based regimens in MM, including the initiation of phase 3 combination studies.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Immunomodulation, Multiple myeloma, Phase I/II
Abstract: S187
Type: Oral Presentation
Session title: New diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in multiple myeloma and AL amyloidosis
Background
IBER is an oral, novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) compound with marked synergistic tumoricidal and immune-stimulatory effects in combination with proteasome inhibitors (PIs) or anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies, preclinically and clinically. CC-220-MM-001 (NCT02773030) is an ongoing phase 1/2 study evaluating the maximum tolerated dose, recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D), safety, and preliminary efficacy of IBER with different treatment combinations in independent cohorts, in pts with RRMM.
Aims
To report results from the IBER+DARA+DEX (IberDd), IBER+BORT+DEX (IberVd), and IBER+CFZ+DEX (IberKd) cohorts of the CC-220-MM-001 study.
Methods
Eligible pts received ≥2 prior regimens in the IberDd and IberKd cohorts, and ≥1 prior regimen in the IberVd cohort, containing lenalidomide or pomalidomide, and a PI. All pts had progressed ≤60 days of their last MM therapy. Escalating oral doses of IBER were given on Day (D)1–21 of each 28-D cycle in the IberDd cohort and in the IberKd cohort with weekly CFZ, and on D1–14 of each 21-D cycle in the IberVd cohort. DEX was given weekly in all 3 cohorts.
Results
As of Dec 14, 2020, 34 pts had received IberDd, 24 pts IberVd, and 7 pts IberKd. Exposure to prior regimens was heterogeneous (Table), all pts were refractory to their last prior regimen, and median number of prior therapies was 4.0 (2–12), 5.5 (1–14), and 6.0 (2–8), with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively. IBER doses ranged from 1.0mg to 1.6mg. Median follow-up was 3.9 (0.1–20.7), 5.5 (1.2–18.0), and 5.1 (3.5–15.7) months, 15 (44%), 9 (38%), and 3 (43%) pts continue on treatment, and median cycles received was 4.0 (1–21), 7.5 (1–24), and 5.0 (3–16) with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively.
Most frequent hematologic grade (G) 3–4 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were neutropenia (63%), anemia (28%), leukopenia (28%), and lymphopenia (25%) with IberDd, neutropenia (29%) and thrombocytopenia (25%) with IberVd, and lymphopenia (57%) and neutropenia (43%) with IberKd. In all cohorts, neutropenia was managed with G-CSF. One pt (IberDd; 1.2mg) had G4 neutropenic sepsis. Occurrence of G3–4 non-hematologic TEAEs was low in all 3 cohorts. There were 12 (38%), 8 (33%), and 3 (43%) pts with ≥1 IBER dose reduction, with IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd, respectively.
In the IberDd cohort, the overall response rate (ORR) was 41% (12/29 pts: 1 stringent complete response [sCR], 2 CRs, 2 very good partial responses [VGPRs], 7 partial responses [PRs]), the clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 52%, and disease control rate (DCR) was 86%. In the IberVd cohort, ORR was 58% (14/24 pts: 2 CRs, 5 VGPRs, 7 PRs), CBR was 67%, and DCR was 92%. Responses with IberDd and IberVd were observed in DARA- and BORT-refractory pts, respectively. In the IberKd cohort, ORR was 57% (4/7 pts: 1 sCR, 2 VGPRs, 1 PR), CBR was 57%, and DCR was 86%. Median time to response was 4.1 (4.0–12.0), 3.6 (3.0–13.1), and 4.1 (4.1–8.1) weeks, in the IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd cohorts, respectively. Median duration of response is 63.3 weeks in the IberVd cohort, and not reached in the IberDd and IberKd cohorts.
RP2D was determined at 1.6mg in the IberDd cohort, while dose evaluation continues in the IberVd and IberKd cohorts.
Updated data will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion
In heavily pretreated pts with RRMM, IberDd, IberVd, and IberKd showed a manageable safety profile and promising efficacy including CRs, even among DARA- and BORT-refractory pts. The study is ongoing. These results support further development of IBER-based regimens in MM, including the initiation of phase 3 combination studies.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Immunomodulation, Multiple myeloma, Phase I/II