
Contributions
Abstract: PB1836
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Transfusion medicine
Background
Patients with hematological disorders are at high risk of developing post-transfusion complications. The possibility of alloimmunization to red blood cell antigens grows with an increase in the number of transfusions.The incidence of alloantibodies in patients ofour hematology clinic is 1.8%. A register of blood donors typed for a wide range of transfusion-dangerous antigens was created to select compatible red blood cells.
Aims
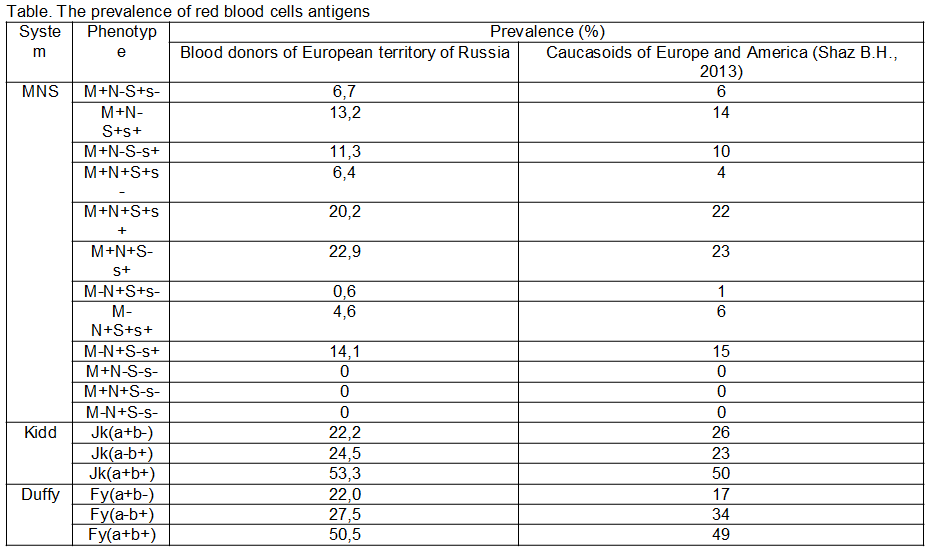
The aim was to study the prevalence of MNS, Kidd, Duffy blood group systems phenotypes in blood donors living inthe European part of Russian Federation and to compare with them in Caucasoids of Europe and America.
Methods
Immunohematological tests were carried out using equipment and reagents from BioRad (USA).
Results
The register currently includes 327 donors of blood components. The prevalence of phenotypes is shown in the table.
Conclusion
No significant difference was found in the prevalence of MNS, Kidd, Duffy phenotypes in blood donors living inthe European part of Russian Federation and with them in Caucasoids of Europe and America.
Keyword(s): Phenotype, Red blood cell, Transfusion
Abstract: PB1836
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Transfusion medicine
Background
Patients with hematological disorders are at high risk of developing post-transfusion complications. The possibility of alloimmunization to red blood cell antigens grows with an increase in the number of transfusions.The incidence of alloantibodies in patients ofour hematology clinic is 1.8%. A register of blood donors typed for a wide range of transfusion-dangerous antigens was created to select compatible red blood cells.
Aims
The aim was to study the prevalence of MNS, Kidd, Duffy blood group systems phenotypes in blood donors living inthe European part of Russian Federation and to compare with them in Caucasoids of Europe and America.
Methods
Immunohematological tests were carried out using equipment and reagents from BioRad (USA).
Results
The register currently includes 327 donors of blood components. The prevalence of phenotypes is shown in the table.

Conclusion
No significant difference was found in the prevalence of MNS, Kidd, Duffy phenotypes in blood donors living inthe European part of Russian Federation and with them in Caucasoids of Europe and America.
Keyword(s): Phenotype, Red blood cell, Transfusion


