
Contributions
Abstract: PB1782
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
Modern trends in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with high donor requirements (10/10 HLA-matching of donor and recipient, infectious status, young donor age) require new approaches to the operation of registries and donor centers. There are various strategies not only to attract more potential HSC donors, but also to increase the diversity of HLA phenotypes. The allele frequencies of the HLA system are specific for populations, which limits the number of different phenotypes that we obtain when typing new potential donors.
Aims
to analyze antigenic diversity in the population of siblings, patients and HSC donors of the registry.
Methods
The analysis included the results of HLA typing of 216 patients and 289 siblings, 27 885 phenotypes HSC donor of the registry of the Republic of Belarus.
Results
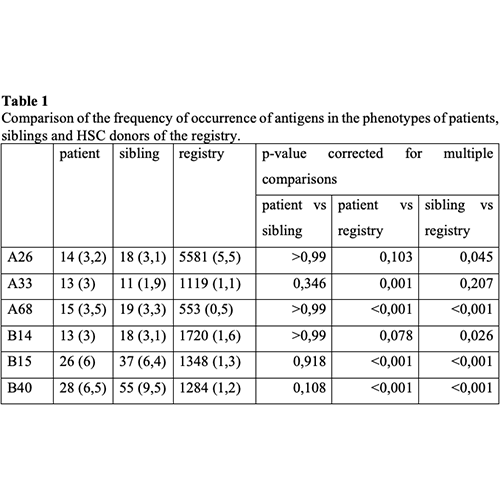
The results of the study of the frequency of occurrence of antigens in patients, siblings and HSC donors of the registry presented in Table 1.
Conclusion
Taking into account the results obtained, it can be concluded that there are differences in the phenotypes of related and unrelated HSC donors. The revealed differences in the frequency of occurrence of antigens suggest the formation of unique phenotypes that differ from the general population, the inclusion of which in the information base will increase the antigenic diversity of the main histocompatibility complex in the population of HSC donors of the registry, which will increase the number of suitable donor-recipient pairs.
Keyword(s): Donor, Hematopoietic stem cell, Sibling
Abstract: PB1782
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Background
Modern trends in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with high donor requirements (10/10 HLA-matching of donor and recipient, infectious status, young donor age) require new approaches to the operation of registries and donor centers. There are various strategies not only to attract more potential HSC donors, but also to increase the diversity of HLA phenotypes. The allele frequencies of the HLA system are specific for populations, which limits the number of different phenotypes that we obtain when typing new potential donors.
Aims
to analyze antigenic diversity in the population of siblings, patients and HSC donors of the registry.
Methods
The analysis included the results of HLA typing of 216 patients and 289 siblings, 27 885 phenotypes HSC donor of the registry of the Republic of Belarus.
Results
The results of the study of the frequency of occurrence of antigens in patients, siblings and HSC donors of the registry presented in Table 1.

Conclusion
Taking into account the results obtained, it can be concluded that there are differences in the phenotypes of related and unrelated HSC donors. The revealed differences in the frequency of occurrence of antigens suggest the formation of unique phenotypes that differ from the general population, the inclusion of which in the information base will increase the antigenic diversity of the main histocompatibility complex in the population of HSC donors of the registry, which will increase the number of suitable donor-recipient pairs.
Keyword(s): Donor, Hematopoietic stem cell, Sibling


