
Contributions
Abstract: PB1728
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Mastocytosis are neoplastic diseases of the myeloid line. They are characterized by pathological increase and accumulation of mast cells in one or more organs, most frequently involving the skin, bone marrow, liver and gastrointestinal tract. They may present as cutaneous mastocytosis (CM), systemic mastocytosis (SM), and localized mast-cell tumors. An annual incidence of up to 0.89 cases per 100,000 inhabitants has been reported for SM. There is no clarity on the therapeutic strategies, and several experimental treatments are still underway. In Colombia, there are only case reports; and so far, there are no more extensive studies.
Aims
To characterize a series of 7 patients with mastocytosis (both cutaneous and systemic cases) describing their clinical manifestations, paraclinical behavior and response to the medical treatment established in a reference center in the city of Cali (Colombia, South America).
Methods
A descriptive study of a series of cases in which it was carried out an active search for patients with a diagnosis of mastocytosis, whether cutaneous or systemic, from the total number of consultations in the period between June 2004 and June 2019, in the hematology-oncology reference center (“mastocytosis”) in Cali. A total of 7 patients were found; their informed consent was obtained in accordance with the guidelines of the local ethics committee and the Helsinki act. Compliance with diagnostic criteria was verified according to existing WHO guidelines. The different sociodemographic, clinical, paraclinical and response to treatment variables were characterized, according to data from the clinical history. Qualitative variables were analyzed by frequencies and proportions, quantitative variables were measured by frequencies, averages and ranges.
Results
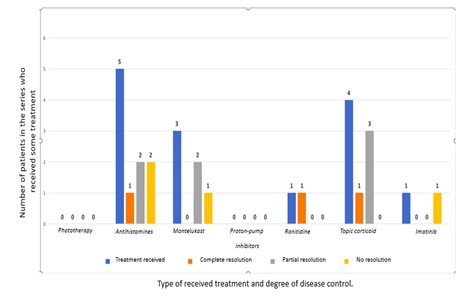
A total of 4 cases of CM and 3 cases of SM were identified. The most frequent clinical manifestations were skin lesions, which occurred in 100% of the patients; of these, the most frequent finding was hyper-pigmentary macules. 67% (2/3) of the SM patients presented gastrointestinal symptoms. Elevated serum tryptase (ST) levels were found in 67% (2/3) of MS patients. Both ST levels and the average absolute eosinophils values were higher in SM patients. The C-KIT mutation (D842B) was requested in only one patient (MC) in the series; this was positive. Only 28% (2/7) of the patients had complete resolution of symptoms with antihistamine treatment.
Conclusion
Regardless its presentations, mastocytosis is a rare disease, with little evidence to guide its diagnosis and management. A higher frequency of extracutaneous involvement, high levels of ST and eosinophils were found in SM patients; and in general, (there was) a very poor response to the established management in the two groups. The findings of this series are comparable to those reported in the world literature.
Keyword(s): Eosinophilia, Mastocytosis, Treatment
Abstract: PB1728
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Mastocytosis are neoplastic diseases of the myeloid line. They are characterized by pathological increase and accumulation of mast cells in one or more organs, most frequently involving the skin, bone marrow, liver and gastrointestinal tract. They may present as cutaneous mastocytosis (CM), systemic mastocytosis (SM), and localized mast-cell tumors. An annual incidence of up to 0.89 cases per 100,000 inhabitants has been reported for SM. There is no clarity on the therapeutic strategies, and several experimental treatments are still underway. In Colombia, there are only case reports; and so far, there are no more extensive studies.
Aims
To characterize a series of 7 patients with mastocytosis (both cutaneous and systemic cases) describing their clinical manifestations, paraclinical behavior and response to the medical treatment established in a reference center in the city of Cali (Colombia, South America).
Methods
A descriptive study of a series of cases in which it was carried out an active search for patients with a diagnosis of mastocytosis, whether cutaneous or systemic, from the total number of consultations in the period between June 2004 and June 2019, in the hematology-oncology reference center (“mastocytosis”) in Cali. A total of 7 patients were found; their informed consent was obtained in accordance with the guidelines of the local ethics committee and the Helsinki act. Compliance with diagnostic criteria was verified according to existing WHO guidelines. The different sociodemographic, clinical, paraclinical and response to treatment variables were characterized, according to data from the clinical history. Qualitative variables were analyzed by frequencies and proportions, quantitative variables were measured by frequencies, averages and ranges.
Results
A total of 4 cases of CM and 3 cases of SM were identified. The most frequent clinical manifestations were skin lesions, which occurred in 100% of the patients; of these, the most frequent finding was hyper-pigmentary macules. 67% (2/3) of the SM patients presented gastrointestinal symptoms. Elevated serum tryptase (ST) levels were found in 67% (2/3) of MS patients. Both ST levels and the average absolute eosinophils values were higher in SM patients. The C-KIT mutation (D842B) was requested in only one patient (MC) in the series; this was positive. Only 28% (2/7) of the patients had complete resolution of symptoms with antihistamine treatment.

Conclusion
Regardless its presentations, mastocytosis is a rare disease, with little evidence to guide its diagnosis and management. A higher frequency of extracutaneous involvement, high levels of ST and eosinophils were found in SM patients; and in general, (there was) a very poor response to the established management in the two groups. The findings of this series are comparable to those reported in the world literature.
Keyword(s): Eosinophilia, Mastocytosis, Treatment


