
Contributions
Abstract: PB1722
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) is a Philadelphia negative myeloproliferative neoplasia, which presents with persistent thrombocytosis, megakaryocytic hyperplasia in bone marrow and a tendency to both hemorrhagic and thrombotic complications. It predominates in female patients with a mean age of 60 years, with 15% being less than 40 years old.
Aims
The goal of our study was to describe our experience in patients with ET ≤ 40 years at diagnosis (dx).
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted based on the review of medical records of the adult patients diagnosed of TE in our centre from 2005 to 2020. Clinical and biological data were recorded.
Results
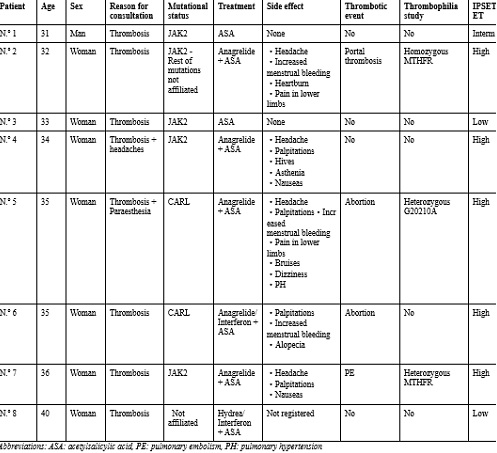
A total of 8 cases were detected (1 man and 7 women). in 38 total cases, which represents 21% (higher than that described in the literature). Mean age at dx: 34.5 [31-40] years.
- Reasons Consultation: Thrombocytosis + paresthesias (2), isolated thrombocytosis (5), thrombocytosis + headaches (1).
- Mutational status: CARL + (2), JAK-2 V617F + (4), not filiated (2).
- Thrombotic events (4/8): Abortion (2), PE (1), Portal Thrombosis (1).
- Thrombophilia study: MTHFR with increased Homocysteine (1), Gen 20210 Prothrombin (1). IPSET ET: High Risk (5), Low Risk (2), Intermediate (1).
- Treatment received: Hydrea + maintenance interferon (1/8), Anagrelide + antiplatelet (5/8), antiplatelet (ASA) (3/8), interferon due to pregnancy (1/8).
- Side effect: Heartburn + pain in lower limbs + headaches + heavy menstruation (1), hives + headaches + palpitations + asthenia + nausea (1), palpitations + dizziness + headaches + bruising + increased menstrual bleeding + pulmonary hypertension + pain in lower limbs (1), increased menstrual bleeding + alopecia + tachycardia (1) and nausea + headaches +palpitations (1).
- Intra-treatment thrombotic events (0/5).
- Treatment suspension (0/5).
- Evolution: Exitus due to breast neoplasia with metastases in a patient with previous Hydrea treatment (1/8).
Conclusion
- In our series 37.5% of the patients presented some thrombotic event / abortion as a precedent, the only etiology being ET 12.5%, given that the rest of the events were associated with prothrombotic mutations coinciding with the chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
- The common reason for consultation was thrombocytosis.
- Anagrelide therapy was acceptably tolerated, not being necessary to suspend treatment, and managed with dose adjustment.
- The most frequent side effects were: bleeding tendency, palpitations. The most serious side effect was pulmonary hypertension.
Keyword(s): Thrombocythemia, Thromboembolic events
Abstract: PB1722
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) is a Philadelphia negative myeloproliferative neoplasia, which presents with persistent thrombocytosis, megakaryocytic hyperplasia in bone marrow and a tendency to both hemorrhagic and thrombotic complications. It predominates in female patients with a mean age of 60 years, with 15% being less than 40 years old.
Aims
The goal of our study was to describe our experience in patients with ET ≤ 40 years at diagnosis (dx).
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted based on the review of medical records of the adult patients diagnosed of TE in our centre from 2005 to 2020. Clinical and biological data were recorded.
Results
A total of 8 cases were detected (1 man and 7 women). in 38 total cases, which represents 21% (higher than that described in the literature). Mean age at dx: 34.5 [31-40] years.
- Reasons Consultation: Thrombocytosis + paresthesias (2), isolated thrombocytosis (5), thrombocytosis + headaches (1).
- Mutational status: CARL + (2), JAK-2 V617F + (4), not filiated (2).
- Thrombotic events (4/8): Abortion (2), PE (1), Portal Thrombosis (1).
- Thrombophilia study: MTHFR with increased Homocysteine (1), Gen 20210 Prothrombin (1). IPSET ET: High Risk (5), Low Risk (2), Intermediate (1).
- Treatment received: Hydrea + maintenance interferon (1/8), Anagrelide + antiplatelet (5/8), antiplatelet (ASA) (3/8), interferon due to pregnancy (1/8).
- Side effect: Heartburn + pain in lower limbs + headaches + heavy menstruation (1), hives + headaches + palpitations + asthenia + nausea (1), palpitations + dizziness + headaches + bruising + increased menstrual bleeding + pulmonary hypertension + pain in lower limbs (1), increased menstrual bleeding + alopecia + tachycardia (1) and nausea + headaches +palpitations (1).
- Intra-treatment thrombotic events (0/5).
- Treatment suspension (0/5).
- Evolution: Exitus due to breast neoplasia with metastases in a patient with previous Hydrea treatment (1/8).

Conclusion
- In our series 37.5% of the patients presented some thrombotic event / abortion as a precedent, the only etiology being ET 12.5%, given that the rest of the events were associated with prothrombotic mutations coinciding with the chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
- The common reason for consultation was thrombocytosis.
- Anagrelide therapy was acceptably tolerated, not being necessary to suspend treatment, and managed with dose adjustment.
- The most frequent side effects were: bleeding tendency, palpitations. The most serious side effect was pulmonary hypertension.
Keyword(s): Thrombocythemia, Thromboembolic events


