
Contributions
Abstract: PB1679
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Multiple myeloma (MM) induces a hypercoagulability state which increases the occurrence of thrombotic events (TE). The common usage of immunmodulatory imide drugs (IMIDs) has had a relevant prognostic impact in patients with multiple myeloma, although a major risk of TE has been detected throughout the years. Besides, therapeutic strategies including high-dose corticosteroids, central venous catheters and comorbidities already present at the usual age of debut of the disease (such as diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, dyslipidemia or coexistence of previous neoplasms) also cast an increased risk of TE.
Aims
Describe the incidence of thrombotic events in MM patients treated with IMIDs in our hospital.
Methods
287 patients diagnosed from 2014 to 2021 were reviewed. Further risk factors, lines of therapy and antithrombotic prophylactic measures were also included.
Results
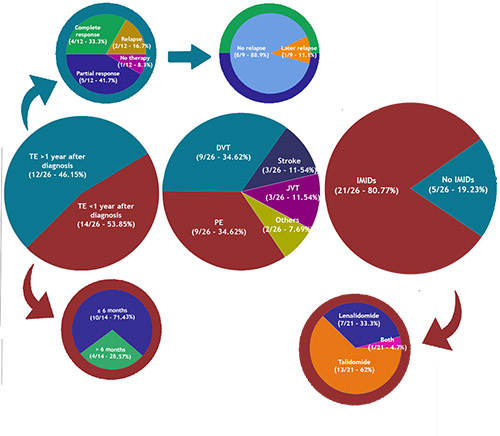
Of all the patients reviewed (287), 26 developed TE (9.06%). Out of these events, 14 occurred in the first year after the diagnosis (53.85%). Of all these cases, 19 (73.08%) featured more than one additional risk factor. Furthermore, 21 (80.77%) had received IMID-based therapies. Most common events were pulmonary embolism (9 - 34.62%), deep vein thrombosis (9 - 34.62%), strokes (3- 11.54%) and jugular venous thrombosis (3 - 11.54%) followed by other events (2 - 7.69%).
Conclusion
Prevalence of TE in MM patients in our institution is 9.06%, with a high proportion of them (80.77%) receiving IMID-based therapies and occurring in the first year after the diagnosis (53.85%).
Most of the events developed despite the usage of prophylactic antithrombotic measures, hence early high-risk prophylactic measures should be mandatory in MM patients treated with IMID-based therapies.
Keyword(s): Imids, Multiple myeloma, Thrombosis
Abstract: PB1679
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Multiple myeloma (MM) induces a hypercoagulability state which increases the occurrence of thrombotic events (TE). The common usage of immunmodulatory imide drugs (IMIDs) has had a relevant prognostic impact in patients with multiple myeloma, although a major risk of TE has been detected throughout the years. Besides, therapeutic strategies including high-dose corticosteroids, central venous catheters and comorbidities already present at the usual age of debut of the disease (such as diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, dyslipidemia or coexistence of previous neoplasms) also cast an increased risk of TE.
Aims
Describe the incidence of thrombotic events in MM patients treated with IMIDs in our hospital.
Methods
287 patients diagnosed from 2014 to 2021 were reviewed. Further risk factors, lines of therapy and antithrombotic prophylactic measures were also included.
Results
Of all the patients reviewed (287), 26 developed TE (9.06%). Out of these events, 14 occurred in the first year after the diagnosis (53.85%). Of all these cases, 19 (73.08%) featured more than one additional risk factor. Furthermore, 21 (80.77%) had received IMID-based therapies. Most common events were pulmonary embolism (9 - 34.62%), deep vein thrombosis (9 - 34.62%), strokes (3- 11.54%) and jugular venous thrombosis (3 - 11.54%) followed by other events (2 - 7.69%).

Conclusion
Prevalence of TE in MM patients in our institution is 9.06%, with a high proportion of them (80.77%) receiving IMID-based therapies and occurring in the first year after the diagnosis (53.85%).
Most of the events developed despite the usage of prophylactic antithrombotic measures, hence early high-risk prophylactic measures should be mandatory in MM patients treated with IMID-based therapies.
Keyword(s): Imids, Multiple myeloma, Thrombosis


