
Contributions
Abstract: PB1647
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Fragile elderly patients with multiple myeloma(MM) have poor efficacy and low survival rate due to many factors including complications, poor tolerance and compliance, high rate of treatment discontinuation.
Aims
This is a prospective multicenter non-randomized controlled study, design to compare efficacy and safety of ixazomib in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus ixazomib in combination with liposome doxorubicin and dexamethasone. (ClinicalTrials.gov number, chiCTR1900024917)
Methods
This multicenter trial was conducted in 13 hospitals. Inclusion criteria was patient age≥65 and IMWG geriatric scoring system (GA)≥2 points or Mayo geriatric vulnerability scoring system defined as vulnerable. No exclusion criteria. Scheme include: IAd regimen (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, liposome doxorubicin 40mg d1, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22); IRd regimen (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, lenalidomide 25mg d1-14, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22) 4 weeks a cycle. The assessment of response conducted post four 28-day cycles. The consolidation therapy of previous regimen recommended 2 cycles for ≥VGPR and 4 cycles for PR &MR. Id (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22) regimen maintenance initiated until progression. Primary endpoint is overall response rate (ORR). The secondary endpoints are progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), tolerability, toxicity, health-related Qol. This study is designed for 3 years, 120 patients in-total, 60 each group.
Results
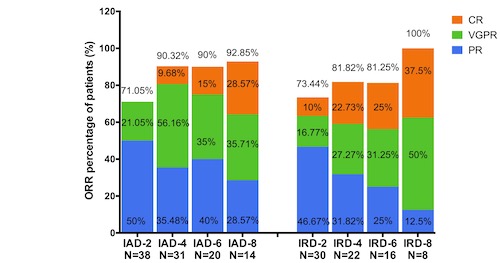
From Oct 2019 to Jan 2021, 79 cases were enrolled without intervention, 29.1%(23/79) of them were aged≥75. 15.2%(12/79) cases with renal insufficiency, including 9 severe renal failure (eGFR<30mL/min), 2 dialysis. 7 cases were complicated with paraplegia. Efficacy could be evaluated in 68 cases, 11 cases could not be evaluated, of them, 4 had not completed a cycle chemotherapy, 5 had given up, and 2 died in the 1st treatment course. Most if not all cases with renal failure, bedridden and thrombosis enter the IAd group. The total ORR was 82.35%, with 84.21% (32/38) in the IAd and 80.0% (24/30) in the IRd group, p>0.05. 53 cases (77.9%) completed 4 cycles (IAd group of 31, the IRd group 22); 22 cases (32.4%) completed 8 cycles (IAd group of 14, the IRd group 8).16 cases (23.5%) are in maintenance treatment (10 of IAd group, the IRd 6). The median follow-up period was 8 months (1-16m), the median PFS and OS were not achieved either, with OS of 85.7% at 12th months. According to IMWG risk stratification, OS in high-risk group was significantly shorter than that in standard risk group,14.0m vs not reached, respectively (p=0.022).
To date, 15 death occurred, including 4 early deaths within 60 days, 7 by disease progression, 3 individually gave up and 1 unexplained sudden death. During induction chemotherapy,11.8% (8/68) of cases experience hematology above grade 3, 11(16.2%) cases with pneumonia (8 of IAd and 3 of IRd), 13(19.1%) cases developed gastrointestinal AE above grade 3 (10 cases in the IAd group and 3 cases in the IRd group), among which 4 cases developed AE above grade 4.
Conclusion
The results showed in the interim observation, both three-drug combination regimen of ixazomib was effective, with overall response rate of 82.35% and 12-month OS of 85.7%. The adverse reactions were tolerable. As AE rate and the interim mortality rate are comparably high in fragile elderly MM patients, it is still a challenge for treatment. Drugs and regimens with low toxicity and high efficacy are needed to continuously explore.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Elderly, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor
Abstract: PB1647
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
Fragile elderly patients with multiple myeloma(MM) have poor efficacy and low survival rate due to many factors including complications, poor tolerance and compliance, high rate of treatment discontinuation.
Aims
This is a prospective multicenter non-randomized controlled study, design to compare efficacy and safety of ixazomib in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus ixazomib in combination with liposome doxorubicin and dexamethasone. (ClinicalTrials.gov number, chiCTR1900024917)
Methods
This multicenter trial was conducted in 13 hospitals. Inclusion criteria was patient age≥65 and IMWG geriatric scoring system (GA)≥2 points or Mayo geriatric vulnerability scoring system defined as vulnerable. No exclusion criteria. Scheme include: IAd regimen (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, liposome doxorubicin 40mg d1, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22); IRd regimen (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, lenalidomide 25mg d1-14, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22) 4 weeks a cycle. The assessment of response conducted post four 28-day cycles. The consolidation therapy of previous regimen recommended 2 cycles for ≥VGPR and 4 cycles for PR &MR. Id (Ixa 4mg d1,8,15, dexamethasone 20mg d1,8,15,22) regimen maintenance initiated until progression. Primary endpoint is overall response rate (ORR). The secondary endpoints are progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), tolerability, toxicity, health-related Qol. This study is designed for 3 years, 120 patients in-total, 60 each group.
Results
From Oct 2019 to Jan 2021, 79 cases were enrolled without intervention, 29.1%(23/79) of them were aged≥75. 15.2%(12/79) cases with renal insufficiency, including 9 severe renal failure (eGFR<30mL/min), 2 dialysis. 7 cases were complicated with paraplegia. Efficacy could be evaluated in 68 cases, 11 cases could not be evaluated, of them, 4 had not completed a cycle chemotherapy, 5 had given up, and 2 died in the 1st treatment course. Most if not all cases with renal failure, bedridden and thrombosis enter the IAd group. The total ORR was 82.35%, with 84.21% (32/38) in the IAd and 80.0% (24/30) in the IRd group, p>0.05. 53 cases (77.9%) completed 4 cycles (IAd group of 31, the IRd group 22); 22 cases (32.4%) completed 8 cycles (IAd group of 14, the IRd group 8).16 cases (23.5%) are in maintenance treatment (10 of IAd group, the IRd 6). The median follow-up period was 8 months (1-16m), the median PFS and OS were not achieved either, with OS of 85.7% at 12th months. According to IMWG risk stratification, OS in high-risk group was significantly shorter than that in standard risk group,14.0m vs not reached, respectively (p=0.022).
To date, 15 death occurred, including 4 early deaths within 60 days, 7 by disease progression, 3 individually gave up and 1 unexplained sudden death. During induction chemotherapy,11.8% (8/68) of cases experience hematology above grade 3, 11(16.2%) cases with pneumonia (8 of IAd and 3 of IRd), 13(19.1%) cases developed gastrointestinal AE above grade 3 (10 cases in the IAd group and 3 cases in the IRd group), among which 4 cases developed AE above grade 4.

Conclusion
The results showed in the interim observation, both three-drug combination regimen of ixazomib was effective, with overall response rate of 82.35% and 12-month OS of 85.7%. The adverse reactions were tolerable. As AE rate and the interim mortality rate are comparably high in fragile elderly MM patients, it is still a challenge for treatment. Drugs and regimens with low toxicity and high efficacy are needed to continuously explore.
Keyword(s): Clinical trial, Elderly, Multiple myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor


