
Contributions
Abstract: PB1636
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Multiple myeloma (MM) is malignant tumor with abnormal proliferation of bone marrow plasma cells. The existing clinical tools used to determine treatment response and minimal residual disease (MRD) are affected by focal distribution of myeloma cell in bone marrow and the quantity of sample. In our previous study, we demonstrated that the counts of CD138+microparticles (MPs) in BM showed to be a potential marker to monitor the load of MM. On this basis, we further investigated the feasibility of BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs to monitor MM load.
Aims
1.The number of MPs produced by a single myeloma cell.
2.If CD138+/BCMA+/CD319+MPs can monitor the load of multiple myeloma.
Methods
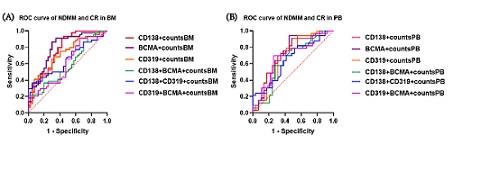
Peripheral blood and bone marrow of MM patients and healthy donors were collected. Microparticles were isolated by differential centrifugation, and MPs were immunolabeled and detected by flow cytometry (Cyto-FLEX). Mann-Whitney (U) test was conducted for the nonparametric data. New diagnosed MM (NDMM) patients and CR patients were compared, and ROC curves were used to identify cutoff points with optimal sensitivity and specificity concerning the counts of MPs in BM and PB.
Results
A single plasma cell produced more MPs than its own. Compared with CR patients and healthy donors, the counts of both BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs in NDMM patients were significantly increased; The counts of CD138+CD319+MPs in MM patients were higher than which in CR patients and healthy donors, The AUC of BCMA+ MP counts in bone marrow was the maximum (0.7966).
Conclusion
Our research showed that similar to CD138, the counts of BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs was also a powerful marker for monitoring MM cell, and the accuracy of monitoring MM using BCMA+MPs was higher than CD138; MM-MPs from the plasma provided support for a potential monitoring biomarker of MM.
Keyword(s): Flow cytometry, Microparticles, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: PB1636
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Biology & Translational Research
Background
Multiple myeloma (MM) is malignant tumor with abnormal proliferation of bone marrow plasma cells. The existing clinical tools used to determine treatment response and minimal residual disease (MRD) are affected by focal distribution of myeloma cell in bone marrow and the quantity of sample. In our previous study, we demonstrated that the counts of CD138+microparticles (MPs) in BM showed to be a potential marker to monitor the load of MM. On this basis, we further investigated the feasibility of BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs to monitor MM load.
Aims
1.The number of MPs produced by a single myeloma cell.
2.If CD138+/BCMA+/CD319+MPs can monitor the load of multiple myeloma.
Methods
Peripheral blood and bone marrow of MM patients and healthy donors were collected. Microparticles were isolated by differential centrifugation, and MPs were immunolabeled and detected by flow cytometry (Cyto-FLEX). Mann-Whitney (U) test was conducted for the nonparametric data. New diagnosed MM (NDMM) patients and CR patients were compared, and ROC curves were used to identify cutoff points with optimal sensitivity and specificity concerning the counts of MPs in BM and PB.
Results
A single plasma cell produced more MPs than its own. Compared with CR patients and healthy donors, the counts of both BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs in NDMM patients were significantly increased; The counts of CD138+CD319+MPs in MM patients were higher than which in CR patients and healthy donors, The AUC of BCMA+ MP counts in bone marrow was the maximum (0.7966).

Conclusion
Our research showed that similar to CD138, the counts of BCMA+MPs and CD319+MPs was also a powerful marker for monitoring MM cell, and the accuracy of monitoring MM using BCMA+MPs was higher than CD138; MM-MPs from the plasma provided support for a potential monitoring biomarker of MM.
Keyword(s): Flow cytometry, Microparticles, Multiple myeloma


