
Contributions
Abstract: PB1509
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Chronic myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
: Chronic myeloid leukemia is a clonal disease of the bone marrow characterized by a genetic marker: the t (9; 22) translocation. This genetic event produces an oncoprotein (BCR-ABL1) with constitutive tyrosine kinase activity which, through the phosphorylation of adapter proteins, leads to an increase in proliferation and decrease in apoptosis of hematopoietic precursors.
Although this genetic translocation was believed to be the only responsible for the pathology, nowadays, other additional molecular events are being investigated. Such events could be an alteration in the expression of microRNAs since t (9; 22) generates genomic instability and consequently additional genetic alterations to BCR-ABL1. It is well known that miRNAs are dysregulated in many types of cancer and they are being studied as potential biomarkers. Moreover, dysregulation in miRNAs expression could be independent from the activity of the BCR-ABL1.
Aims
To evaluate the dependence of miRNAs expression from BCR-ABL1 activity in vitro
Methods
mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Ambion®) was used for RNA extraction from K562 CML cell line which was previously incubated with either imatinib 1000nM, 450nM and 200nM or nilotinib 120nM, 60nM and 30nM according to calculated IC50 using MTT assay. To confirm inhibition of the BCR-ABL1 pathway a western blot for phospho-CRKL was performed. For qPCR a protocol that is designed to specifically amplify and quantify miRNAs using stem-loop primers was used. The following miRNAs were evaluated: hsa-miR-196a-5p, hsa-miR-92b-3p, hsa-miR-126-5p, hsa-miR-125a-5p, hsa-miR-2355-5p, hsa-miR-10a-5p, hsa-miR-132-3p, hsa-let-7a-5p and hsa-miR-182-5p. This panel was based on previous experiments from our group which assessed miRNAs expression in CML patients (leukemic stem cells vs hematopoietic stem cells) by next generation sequencing. Statistical analysis was done with GraphPad v6.0. T-Student test was used to calculate statistical significance between samples.
Results
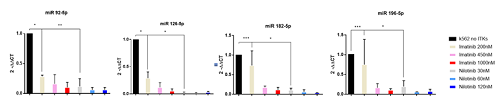
Imatinib at a concentration of 200nM did not inhibit p-CRKL by western blot. The expression of all miRNAs aforementioned but for miR2355 was downregulated after incubation for 48hs with both TKIs. This effect was more powerful with nilotinib than imatinib. When incubated with imatinib hsa-miR-126-5p, hsa-miR-182-5p hsa-miR-92b-5p and hsa-miR-196a-5p showed a dose dependent inhibition (Figure 1).
*p< 0,01 ** p< 0,05 ***p> 0,05
Conclusion
In K562 cell line, a down regulation of miRNA expression was observed when exposed to both drugs, with a dose-dependent effect confirmed for some miRNAs incubated with imatinib. More studies should be done to evaluate if this effect is also observed in vivo. Eventually, miRNAs could be used as a biomarker of response to TKIs in CML patients.
The fact that imatinib 200nM did not inhibited BCR-ABL1 but miR92 and miR 126 where still dowregulated could be explained by off target effect of TKIs.
Keyword(s): Cell line, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Imatinib, Molecular markers
Abstract: PB1509
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Chronic myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
: Chronic myeloid leukemia is a clonal disease of the bone marrow characterized by a genetic marker: the t (9; 22) translocation. This genetic event produces an oncoprotein (BCR-ABL1) with constitutive tyrosine kinase activity which, through the phosphorylation of adapter proteins, leads to an increase in proliferation and decrease in apoptosis of hematopoietic precursors.
Although this genetic translocation was believed to be the only responsible for the pathology, nowadays, other additional molecular events are being investigated. Such events could be an alteration in the expression of microRNAs since t (9; 22) generates genomic instability and consequently additional genetic alterations to BCR-ABL1. It is well known that miRNAs are dysregulated in many types of cancer and they are being studied as potential biomarkers. Moreover, dysregulation in miRNAs expression could be independent from the activity of the BCR-ABL1.
Aims
To evaluate the dependence of miRNAs expression from BCR-ABL1 activity in vitro
Methods
mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Ambion®) was used for RNA extraction from K562 CML cell line which was previously incubated with either imatinib 1000nM, 450nM and 200nM or nilotinib 120nM, 60nM and 30nM according to calculated IC50 using MTT assay. To confirm inhibition of the BCR-ABL1 pathway a western blot for phospho-CRKL was performed. For qPCR a protocol that is designed to specifically amplify and quantify miRNAs using stem-loop primers was used. The following miRNAs were evaluated: hsa-miR-196a-5p, hsa-miR-92b-3p, hsa-miR-126-5p, hsa-miR-125a-5p, hsa-miR-2355-5p, hsa-miR-10a-5p, hsa-miR-132-3p, hsa-let-7a-5p and hsa-miR-182-5p. This panel was based on previous experiments from our group which assessed miRNAs expression in CML patients (leukemic stem cells vs hematopoietic stem cells) by next generation sequencing. Statistical analysis was done with GraphPad v6.0. T-Student test was used to calculate statistical significance between samples.
Results
Imatinib at a concentration of 200nM did not inhibit p-CRKL by western blot. The expression of all miRNAs aforementioned but for miR2355 was downregulated after incubation for 48hs with both TKIs. This effect was more powerful with nilotinib than imatinib. When incubated with imatinib hsa-miR-126-5p, hsa-miR-182-5p hsa-miR-92b-5p and hsa-miR-196a-5p showed a dose dependent inhibition (Figure 1).
*p< 0,01 ** p< 0,05 ***p> 0,05

Conclusion
In K562 cell line, a down regulation of miRNA expression was observed when exposed to both drugs, with a dose-dependent effect confirmed for some miRNAs incubated with imatinib. More studies should be done to evaluate if this effect is also observed in vivo. Eventually, miRNAs could be used as a biomarker of response to TKIs in CML patients.
The fact that imatinib 200nM did not inhibited BCR-ABL1 but miR92 and miR 126 where still dowregulated could be explained by off target effect of TKIs.
Keyword(s): Cell line, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Imatinib, Molecular markers


