
Contributions
Abstract: PB1448
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are curable in 50-60% of cases with frontline immunochemotherapy. Salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL is able to cure roughly 40-50% of patients, and includes high dose-chemotherapy plus autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) in chemosensitive fit patients, and chimeric antigen receptor T-cells (CAR-T), permitted only after ≥2 prior systemic regimes in patients with no major comorbidities. Therefore, there is an urgent need to investigate new salvage treatments for R/R DLBCL unresponsive or ineligible to ASCT or CAR-T. Rituximab plus bendamustine (RB) is active in R/R DLBCL with an overall response rate (ORR) ranged from 40 to 60% but usually of short duration. Copanlisib is an intravenous pan-class I PI3K inhibitor with predominant activity against PI3K-α and -δ isoforms, active as single agent in indolent lymphomas and DLBCL with ORR of 59% and 25%, respectively (NCT01660451) (NCT02391116). Most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events are transient hyperglycemia and transient hypertension. The association of copanlisib plus RB (Copa-RB) has been showed a safe treatment in R/R indolent lymphomas (NCT02626455).
Aims
To assess the efficacy and safety of Copa-RB followed by copanlisib maintenance in R/R DLBCL not eligible or relapsed after ASCT or CAR-T
Methods
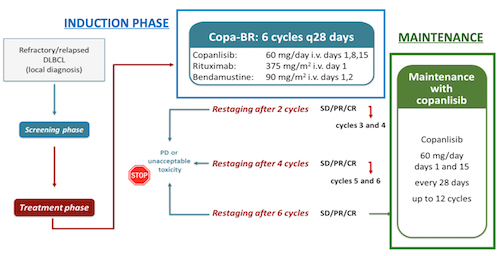
FIL Copa-RB is a multicentric open-label single arm, single stage, phase II trial. An estimated 81 patients will be enrolled, from 30 centers in Italy. Inclusion criteria are: patients aged 18 or older with histologically confirmed DLBCL (including de-novo DLBCL, DLBCL transformed by indolent lymphomas and high-grade lymphoma) R/R after 1 to 3 previous lines of therapy, considered not candidate or R/R to ASCT or CART, ECOG PS ≤ 2. Exclusion criteria include primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma histology, significant organ dysfunction, uncontrolled hypertension and hyperglycemia (HbA1c> 8.5%). Treatment consists of an induction phase with six 28-day cycles of copa-RB (copanlisib 60 mg intravenously on day (D) 1, D8 and D15, rituximab 375 mg/m2 on D1, bendamustine 90 mg/m2 on D1-D2) followed by a maintenance phase of twelve 28-day cycles of copanlisib 60 mg given on D1 and D15 (Fig.). The primary endpoint is progression free survival (PFS) defined as the time between the date of enrolment and the date of disease progression, relapse or death from any cause, whichever occurs earlier, with an expected improvement of 12-month PFS from 20% to 35%. Secondary endpoints include overall survival, ORR, complete response (CR) rate, duration of response and rate of response improvement during maintenance. Exploratory analysis will include correlation between outcome and cell of origin, MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 overexpression and rearrangements, and mutational analysis of selected genes possibly involved in predicting response to copanlisib. The expected study duration from first patient’s first visit to last patient’s last visit is approximately 4 years.
Results
The recruitment started in November 2020; at March 1st, 8/81 patients have been enrolled. Results for this study are not yet available.
Conclusion
The treatment of R/R DLBCL ineligible or unresponsive to ASCT or CAR-T is still an unmet clinical need and new treatment options are warranted. Copanlisib as single agent has been already shown a moderate activity in DLBCL and the association Copa-RB plus copanlisib maintenance could be a new strategy to improve the outcome of these patients. Biomarkers studies would further elucidate patients who are more likely to respond to this treatment.
Keyword(s): Chemotherapy, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Relapsed lymphoma
Abstract: PB1448
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Background
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are curable in 50-60% of cases with frontline immunochemotherapy. Salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL is able to cure roughly 40-50% of patients, and includes high dose-chemotherapy plus autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) in chemosensitive fit patients, and chimeric antigen receptor T-cells (CAR-T), permitted only after ≥2 prior systemic regimes in patients with no major comorbidities. Therefore, there is an urgent need to investigate new salvage treatments for R/R DLBCL unresponsive or ineligible to ASCT or CAR-T. Rituximab plus bendamustine (RB) is active in R/R DLBCL with an overall response rate (ORR) ranged from 40 to 60% but usually of short duration. Copanlisib is an intravenous pan-class I PI3K inhibitor with predominant activity against PI3K-α and -δ isoforms, active as single agent in indolent lymphomas and DLBCL with ORR of 59% and 25%, respectively (NCT01660451) (NCT02391116). Most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events are transient hyperglycemia and transient hypertension. The association of copanlisib plus RB (Copa-RB) has been showed a safe treatment in R/R indolent lymphomas (NCT02626455).
Aims
To assess the efficacy and safety of Copa-RB followed by copanlisib maintenance in R/R DLBCL not eligible or relapsed after ASCT or CAR-T
Methods
FIL Copa-RB is a multicentric open-label single arm, single stage, phase II trial. An estimated 81 patients will be enrolled, from 30 centers in Italy. Inclusion criteria are: patients aged 18 or older with histologically confirmed DLBCL (including de-novo DLBCL, DLBCL transformed by indolent lymphomas and high-grade lymphoma) R/R after 1 to 3 previous lines of therapy, considered not candidate or R/R to ASCT or CART, ECOG PS ≤ 2. Exclusion criteria include primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma histology, significant organ dysfunction, uncontrolled hypertension and hyperglycemia (HbA1c> 8.5%). Treatment consists of an induction phase with six 28-day cycles of copa-RB (copanlisib 60 mg intravenously on day (D) 1, D8 and D15, rituximab 375 mg/m2 on D1, bendamustine 90 mg/m2 on D1-D2) followed by a maintenance phase of twelve 28-day cycles of copanlisib 60 mg given on D1 and D15 (Fig.). The primary endpoint is progression free survival (PFS) defined as the time between the date of enrolment and the date of disease progression, relapse or death from any cause, whichever occurs earlier, with an expected improvement of 12-month PFS from 20% to 35%. Secondary endpoints include overall survival, ORR, complete response (CR) rate, duration of response and rate of response improvement during maintenance. Exploratory analysis will include correlation between outcome and cell of origin, MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 overexpression and rearrangements, and mutational analysis of selected genes possibly involved in predicting response to copanlisib. The expected study duration from first patient’s first visit to last patient’s last visit is approximately 4 years.
Results
The recruitment started in November 2020; at March 1st, 8/81 patients have been enrolled. Results for this study are not yet available.

Conclusion
The treatment of R/R DLBCL ineligible or unresponsive to ASCT or CAR-T is still an unmet clinical need and new treatment options are warranted. Copanlisib as single agent has been already shown a moderate activity in DLBCL and the association Copa-RB plus copanlisib maintenance could be a new strategy to improve the outcome of these patients. Biomarkers studies would further elucidate patients who are more likely to respond to this treatment.
Keyword(s): Chemotherapy, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Relapsed lymphoma


