
Contributions
Abstract: PB1352
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
The frequency of spontaneous mutagenesis of tetranucleotide microsatellites (STR) in the human population is less than 0.3% for most of STR loci [https://strbase.nist.gov/str_fact.htm]. The frequency of these events during leukemia cell development could hardly be measured by means of testing clinical specimens. However, these data could be assessed by in vitro culturing and cloning experiments with common lymphoblastoid cell lines and could be useful for investigating possible associations of instability in certain chromosomal loci with the disease features in ALL.
Aims
To evaluate frequency of STR profile mutations during long term culturing of Jurkat and WIL2-S cell lines after cloning by limiting dilutions.
Methods
Jurkat is an immortalized T lymphocyte cell line originally obtained from the peripheral blood of T cell leukemia patient. WIL2-S is an immortalized B lymphoblast cell line derived from the spleen of the patient with hereditary spherocytosis. Cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium. Cells were cloned by the method of limiting dilutions; 21 individual clones of WIL2-S and 18 Jurkat clones were taken for STR profiling. Clone WIL2-S #11 was karyotyped, further cloned and 350 subclones were STR profiled. Jurkat1-B4 clones (with stable STR-profile comparing with STR-profile of Jurkat cell line) and Jurkat-O1 (Y loss and 12p13.2 LOH in relation to Jurkat cell line) were also karyotyped, further cloned and 180 subclones of Jurkat1-B4 and 381 subclones of Jurkat-O1 were STR profiled. STR-profiles were assessed by PCR with COrDIS Plus multiplex kit for amplification of 19 polymorphic STR-markers and amelogenin loci (Gordiz Ltd, Russia). The fragment analysis was performed on ABI 3130 Genetic Analyzer. The data processing was accomplished using GeneMapper v.4-0 software.
Results
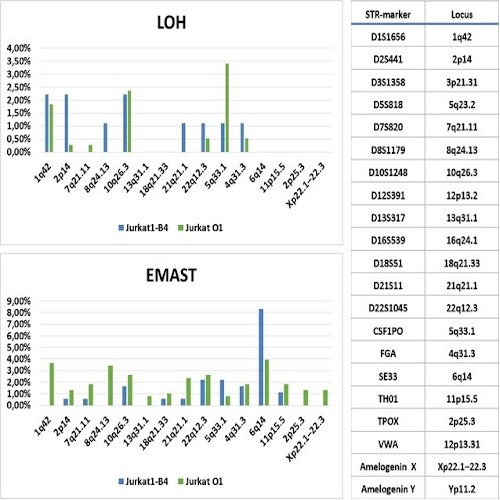
Out of 18 Jurkat clones, 7 have marker loss on Y-chromosome (amelogenin locus); 5 have LOH on 12p13.2 (3 of these clones also have amelogenin Y loss) one clone - LOH on 4q; one — on 5q33.1; and one - on 8q. Elevated Microsatellite Alteration at Selected Tetranucleotides (EMAST- change in the length of STR markers) was found in 10 clones. Only 4 clones retained exactly the same STR profile of initial Jurkat stock sample. Out of 21 WIL2-S clones, EMAST was found in 4 clones only. One clone lost the amelogenin Y marker. Out of 350 subclones of WIL2-S STR-stable clone #11, only two (0.57%) were found to lose the Y-chromosome amelogenin marker. One LOH at 10q26.3 was seen in one of 350 clones (0.29%) only. For Jurkat line LOH was seen in 26 from 180 Jurkat1-B4 subclones (14.4%) and in 35 from 381 Jurkat-O1 clones (9,1%). EMAST was found in 45 from 180 (25%) B4 and 111 from 381 O1 subclones (29%) respectively. While EMAST appears uniformely along different STR-markers, LOH frequency for distinct STR-loci differs and seems to be a feature of certain acute T-cell leukemia (See Fig.1 LOH and EMAST frequencies for different loci in Jurkat 1-B4 and Jurkat-O1 subclones. *STR loci at 3p21.31, 5q23.2, 16q24.1, 12p13.31 are homozygous in Jurkat cell line). Only 60% of Jurkat1-B4 and 64% Jurkat-O1 subclones were found STR-stable. No significant difference was found in mutation frequencies in stable initially Jurkat1-B4 and mutated Jurkat-O1 clones.
Conclusion
Jurkat T lymphocyte leukemia cell line demonstrated a high level of spontaneous LOH in selected loci and EMAST spreading equally through genome. More detailed STR profile testing on extended samples of in vitro cultured cell clones might identify more detailed patterns of spontaneous chromosomal instability in lymphoblastoid cells.
Keyword(s): Leukemia cell line, LOH, STR-PCR
Abstract: PB1352
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Background
The frequency of spontaneous mutagenesis of tetranucleotide microsatellites (STR) in the human population is less than 0.3% for most of STR loci [https://strbase.nist.gov/str_fact.htm]. The frequency of these events during leukemia cell development could hardly be measured by means of testing clinical specimens. However, these data could be assessed by in vitro culturing and cloning experiments with common lymphoblastoid cell lines and could be useful for investigating possible associations of instability in certain chromosomal loci with the disease features in ALL.
Aims
To evaluate frequency of STR profile mutations during long term culturing of Jurkat and WIL2-S cell lines after cloning by limiting dilutions.
Methods
Jurkat is an immortalized T lymphocyte cell line originally obtained from the peripheral blood of T cell leukemia patient. WIL2-S is an immortalized B lymphoblast cell line derived from the spleen of the patient with hereditary spherocytosis. Cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium. Cells were cloned by the method of limiting dilutions; 21 individual clones of WIL2-S and 18 Jurkat clones were taken for STR profiling. Clone WIL2-S #11 was karyotyped, further cloned and 350 subclones were STR profiled. Jurkat1-B4 clones (with stable STR-profile comparing with STR-profile of Jurkat cell line) and Jurkat-O1 (Y loss and 12p13.2 LOH in relation to Jurkat cell line) were also karyotyped, further cloned and 180 subclones of Jurkat1-B4 and 381 subclones of Jurkat-O1 were STR profiled. STR-profiles were assessed by PCR with COrDIS Plus multiplex kit for amplification of 19 polymorphic STR-markers and amelogenin loci (Gordiz Ltd, Russia). The fragment analysis was performed on ABI 3130 Genetic Analyzer. The data processing was accomplished using GeneMapper v.4-0 software.
Results
Out of 18 Jurkat clones, 7 have marker loss on Y-chromosome (amelogenin locus); 5 have LOH on 12p13.2 (3 of these clones also have amelogenin Y loss) one clone - LOH on 4q; one — on 5q33.1; and one - on 8q. Elevated Microsatellite Alteration at Selected Tetranucleotides (EMAST- change in the length of STR markers) was found in 10 clones. Only 4 clones retained exactly the same STR profile of initial Jurkat stock sample. Out of 21 WIL2-S clones, EMAST was found in 4 clones only. One clone lost the amelogenin Y marker. Out of 350 subclones of WIL2-S STR-stable clone #11, only two (0.57%) were found to lose the Y-chromosome amelogenin marker. One LOH at 10q26.3 was seen in one of 350 clones (0.29%) only. For Jurkat line LOH was seen in 26 from 180 Jurkat1-B4 subclones (14.4%) and in 35 from 381 Jurkat-O1 clones (9,1%). EMAST was found in 45 from 180 (25%) B4 and 111 from 381 O1 subclones (29%) respectively. While EMAST appears uniformely along different STR-markers, LOH frequency for distinct STR-loci differs and seems to be a feature of certain acute T-cell leukemia (See Fig.1 LOH and EMAST frequencies for different loci in Jurkat 1-B4 and Jurkat-O1 subclones. *STR loci at 3p21.31, 5q23.2, 16q24.1, 12p13.31 are homozygous in Jurkat cell line). Only 60% of Jurkat1-B4 and 64% Jurkat-O1 subclones were found STR-stable. No significant difference was found in mutation frequencies in stable initially Jurkat1-B4 and mutated Jurkat-O1 clones.

Conclusion
Jurkat T lymphocyte leukemia cell line demonstrated a high level of spontaneous LOH in selected loci and EMAST spreading equally through genome. More detailed STR profile testing on extended samples of in vitro cultured cell clones might identify more detailed patterns of spontaneous chromosomal instability in lymphoblastoid cells.
Keyword(s): Leukemia cell line, LOH, STR-PCR


