
Contributions
Abstract: PB2385
Type: Publication Only
Background
The care demands of children with chronic diseases can affect caregivers' health by imposing caregiving burden to them. In regard to caregiving burden of hemophilia, the levels of overload are high due to the frequent hospital dependence as well as the home management of bleeding. The development of inhibitors is related to a greater effect on the caregiver.
Aims
To analyze caregiving burden in hemophilia patients aged <25 years in a Reference Centre of Congenital Coagulopathies.
Methods
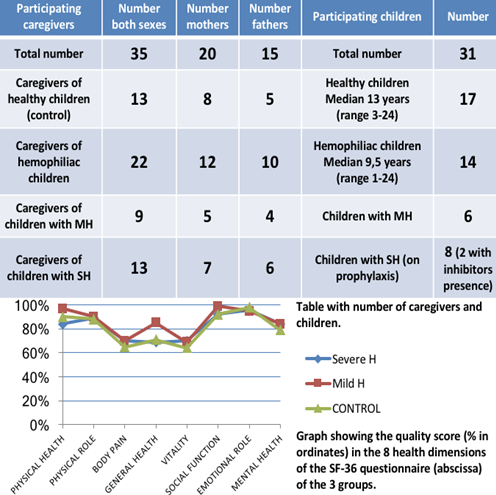
A questionnaire on health and quality of life for adults was given to both caregivers of hemophila patients <25 years of age controlled in our centre and a control group of caregivers of healthy children. The validated questionnaire used was the Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) of 36 items. This form includes 8 dimensions of health and quality of life: physical health, physical role, corporal pain, general health, vitality, social function, emotional role and mental health. The score is from 0% (worst quality) to 100% (best quality).
Results
The results of questionnaire of three groups of caregivers are shown in table and graph below:
1) Caregivers of children with severe hemophilia (SH)
2) Caregivers of children with mild hemophilia (MH)
3) Caregivers of healthy children (Control)
The groups were homogeneous in their demographic characteristics. No relevant differences were observed neither the 3 main groups nor among the parents of each group.
Conclusion
1. We have not found significant impact on the health related quality of life of caregivers of hemophilia children in relation to controls. 2. Mild clinical hemophilia profile, capable monitoring and compliance with the prophylaxis regimens have a positive impact on both health and quality of life of caregivers. 3. It is advisable to enlarge the sample size in futher studies to validate our results.
Session topic: 36. Quality of life, palliative care, ethics and health economics
Keyword(s): Hemophilia, Quality of Life
Abstract: PB2385
Type: Publication Only
Background
The care demands of children with chronic diseases can affect caregivers' health by imposing caregiving burden to them. In regard to caregiving burden of hemophilia, the levels of overload are high due to the frequent hospital dependence as well as the home management of bleeding. The development of inhibitors is related to a greater effect on the caregiver.
Aims
To analyze caregiving burden in hemophilia patients aged <25 years in a Reference Centre of Congenital Coagulopathies.
Methods
A questionnaire on health and quality of life for adults was given to both caregivers of hemophila patients <25 years of age controlled in our centre and a control group of caregivers of healthy children. The validated questionnaire used was the Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) of 36 items. This form includes 8 dimensions of health and quality of life: physical health, physical role, corporal pain, general health, vitality, social function, emotional role and mental health. The score is from 0% (worst quality) to 100% (best quality).
Results
The results of questionnaire of three groups of caregivers are shown in table and graph below:
1) Caregivers of children with severe hemophilia (SH)
2) Caregivers of children with mild hemophilia (MH)
3) Caregivers of healthy children (Control)
The groups were homogeneous in their demographic characteristics. No relevant differences were observed neither the 3 main groups nor among the parents of each group.

Conclusion
1. We have not found significant impact on the health related quality of life of caregivers of hemophilia children in relation to controls. 2. Mild clinical hemophilia profile, capable monitoring and compliance with the prophylaxis regimens have a positive impact on both health and quality of life of caregivers. 3. It is advisable to enlarge the sample size in futher studies to validate our results.
Session topic: 36. Quality of life, palliative care, ethics and health economics
Keyword(s): Hemophilia, Quality of Life


