
Contributions
Abstract: PB2063
Type: Publication Only
Background
Peripheral blood CD64 index contribute to diagnosing clinical bacterial infection and early sepsis , but some patients with hematologic malignancies in the process of CD64 index detection are interfered with abnormal cells, which caused mature neutrophils group-dividing difficult. Thus, it affects mature neutrophil CD64 index detection, leading to error or not detected. The application of CD64 index in blood system disease was affected.
Aims
This cohort study include the patients with hematologic malignancies who are in the process of CD64 index test interference and influence the test results by abnormal cells. The antibody of CD45, CD15, CD10 was added to the original kit, the neutrophilic granulocytes were more accurately divided in order to measuring the improved CD64 index.
Methods
Try to improve the detection method of CD64 index of patients with hematologic malignancies.Comparing the diagnostic efficacy of improved CD64 index, PCT and CRP for sepsis with non-improved.
Results
The CD64 index detection was performed on patients with malignant hematologic disease with suspicious infection in the hematology ward. Results of 60 samples were disturbed by abnormal cells during the detection process. the CD64 index was higher than that in the non-sepsis group (P < 0.0001). The improved CD64 index was better for sepsis diagnose than the before improved CD64 index, PCT and CRP.
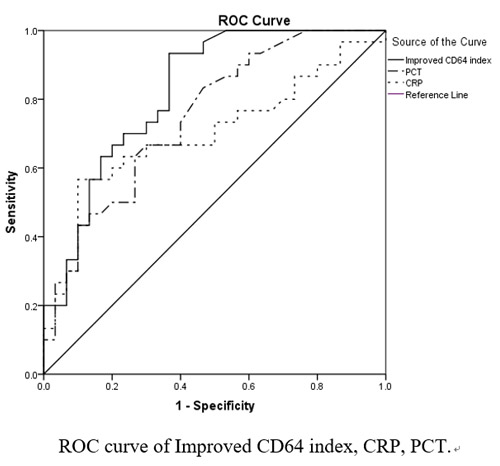
Conclusion
For patients with malignant hematopathy who are disturbed by abnormal cells during the detection of CD64 index, the detection rate and the accuracy of detection can be improved by adding antibody.
Session topic: 31. Infectious diseases, supportive care
Keyword(s): flow cytometry, Hematological malignancy, Sepsis
Abstract: PB2063
Type: Publication Only
Background
Peripheral blood CD64 index contribute to diagnosing clinical bacterial infection and early sepsis , but some patients with hematologic malignancies in the process of CD64 index detection are interfered with abnormal cells, which caused mature neutrophils group-dividing difficult. Thus, it affects mature neutrophil CD64 index detection, leading to error or not detected. The application of CD64 index in blood system disease was affected.
Aims
This cohort study include the patients with hematologic malignancies who are in the process of CD64 index test interference and influence the test results by abnormal cells. The antibody of CD45, CD15, CD10 was added to the original kit, the neutrophilic granulocytes were more accurately divided in order to measuring the improved CD64 index.
Methods
Try to improve the detection method of CD64 index of patients with hematologic malignancies.Comparing the diagnostic efficacy of improved CD64 index, PCT and CRP for sepsis with non-improved.
Results
The CD64 index detection was performed on patients with malignant hematologic disease with suspicious infection in the hematology ward. Results of 60 samples were disturbed by abnormal cells during the detection process. the CD64 index was higher than that in the non-sepsis group (P < 0.0001). The improved CD64 index was better for sepsis diagnose than the before improved CD64 index, PCT and CRP.

Conclusion
For patients with malignant hematopathy who are disturbed by abnormal cells during the detection of CD64 index, the detection rate and the accuracy of detection can be improved by adding antibody.
Session topic: 31. Infectious diseases, supportive care
Keyword(s): flow cytometry, Hematological malignancy, Sepsis


