
Contributions
Abstract: PB2503
Type: Publication Only
Background
Hemoglobinopathies are the most common, potentially deadly monogenic disorders in the world. It is estimated that 7% of the world population are carriers. Global migration in the modern period has led to a continual spread of these anomalies so that they are rapidly becoming more common in the industrialized regions of Europe.
Aims
Description of the mutational spectrum of thalassemias and other hemoglobinopathies in a third hospital level
Methods
A cross-sectional study of patients diagnosed of hemoglobinopathies in a tertiary hospital. Period of study: January 2016- December 2017. Hemoglobin fractions were determined by capillary electrophoresis techniques Minicap® CDT (Sebia, Lisses, France). Molecular study was carried out in selected cases at the Hospital Clínico San Carlos in Madrid. The study of thalassemia was carried out on the most prevalent mutations by Gap-PCR and in those without detected mutation, genetic screening of the HBA1 / HBA2 or HBB genes was performed and the MLPA technique allowing the study of the exons of the HBB and HBA1 / HBA2 genes.
Results
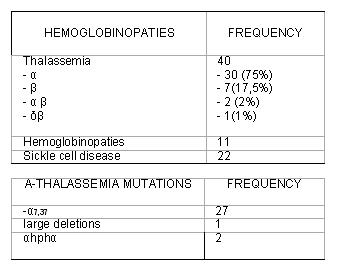
Based on this series of patients, α-thalassemia is identified as the most prevalent hemoglobinopathy in our patients and -α₃,₇deletion the most frequent deletion found in these patients. In our series prevalence demonstrates great variability, and the mutations expose big differences with respect to other prevalence studies. The study of these mutations is important for diagnosis, individual clinical prognosis and future planning of the management of possible complications and epidemiological records, these records being the way to develop future cohort studies and the possibility of comparison or integration with other registries because hemoglobin defects are of widely diverse genetic and clinical types, specialized laboratory analysis is needed to diagnose them correctly and provide a basis for proper therapeutic decisions.
Conclusion
Based on this series of patients, α-thalassemia is identified as the most prevalent hemoglobinopathy in our patients and -α₃,₇deletion the most frequent deletion found in these patients. In our series prevalence demonstrates great variability, and the mutations expose big differences with respect to other prevalence studies. The study of these mutations is important for diagnosis, individual clinical prognosis and future planning of the management of possible complications and epidemiological records, these records being the way to develop future cohort studies and the possibility of comparison or integration with other registries because hemoglobin defects are of widely diverse genetic and clinical types, specialized laboratory analysis is needed to diagnose them correctly and provide a basis for proper therapeutic decisions.
Session topic: 28. Thalassemias
Keyword(s): Hemoglobinopathy, mutation analysis, sickle cell disease, Thalassemia
Abstract: PB2503
Type: Publication Only
Background
Hemoglobinopathies are the most common, potentially deadly monogenic disorders in the world. It is estimated that 7% of the world population are carriers. Global migration in the modern period has led to a continual spread of these anomalies so that they are rapidly becoming more common in the industrialized regions of Europe.
Aims
Description of the mutational spectrum of thalassemias and other hemoglobinopathies in a third hospital level
Methods
A cross-sectional study of patients diagnosed of hemoglobinopathies in a tertiary hospital. Period of study: January 2016- December 2017. Hemoglobin fractions were determined by capillary electrophoresis techniques Minicap® CDT (Sebia, Lisses, France). Molecular study was carried out in selected cases at the Hospital Clínico San Carlos in Madrid. The study of thalassemia was carried out on the most prevalent mutations by Gap-PCR and in those without detected mutation, genetic screening of the HBA1 / HBA2 or HBB genes was performed and the MLPA technique allowing the study of the exons of the HBB and HBA1 / HBA2 genes.
Results
Based on this series of patients, α-thalassemia is identified as the most prevalent hemoglobinopathy in our patients and -α₃,₇deletion the most frequent deletion found in these patients. In our series prevalence demonstrates great variability, and the mutations expose big differences with respect to other prevalence studies. The study of these mutations is important for diagnosis, individual clinical prognosis and future planning of the management of possible complications and epidemiological records, these records being the way to develop future cohort studies and the possibility of comparison or integration with other registries because hemoglobin defects are of widely diverse genetic and clinical types, specialized laboratory analysis is needed to diagnose them correctly and provide a basis for proper therapeutic decisions.

Conclusion
Based on this series of patients, α-thalassemia is identified as the most prevalent hemoglobinopathy in our patients and -α₃,₇deletion the most frequent deletion found in these patients. In our series prevalence demonstrates great variability, and the mutations expose big differences with respect to other prevalence studies. The study of these mutations is important for diagnosis, individual clinical prognosis and future planning of the management of possible complications and epidemiological records, these records being the way to develop future cohort studies and the possibility of comparison or integration with other registries because hemoglobin defects are of widely diverse genetic and clinical types, specialized laboratory analysis is needed to diagnose them correctly and provide a basis for proper therapeutic decisions.
Session topic: 28. Thalassemias
Keyword(s): Hemoglobinopathy, mutation analysis, sickle cell disease, Thalassemia


