
Contributions
Abstract: PB1819
Type: Publication Only
Background
Variety of diseases, haematological and non-haematological can affect the bone marrow primarily or secondarily, resulting in pancytopenia. But the incidence of pancytopenia with normal bone marrow was 3.38% to 10.5% in various international studies. Meanwhile, Sotos syndrome is an autosomal dominant childhood overgrowth syndrome with additional features of characteristic dysmorphisms, mild-to-severe learning disabilities (LD) and advanced bone age. As, in contrast, the duplication 5q35.2.q35.3 phenotype is characterized by growth delay, microcephaly and delayed bone age in some patients, it has been referred to as a reversed Sotos phenotype. However, there has been no report on the occurrence of pancytopenia as duplication 5q35.2.q35.3 phenotype.
Aims
We report the a 42-year-old male patient who has the microduplications of 5q35.2-q35.3 including NSD1 with unexplained pancytopenia was not improved by any treatment, but experienced no serious complications.
Methods
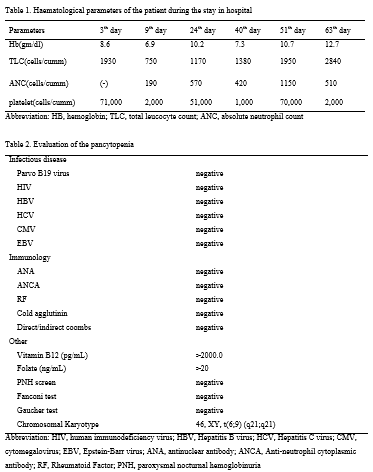
A 42-year-old male visited emergency room due to multiple trauma. He was diagnosed with mental retardation in the past. Physical examination was unremarkable except tenderness from bone fracture. Peripheral blood test showed leukocyte 3,510/mm3, neutrophil 190/mm3, hemoglobin 8.3 g/dL, hematocrit 25.0% and platelet 4,000/mm3. There was no relevant history of intake of any medications and exposure to radiation. And there were no other haematological parameters to lead pancytopenia. The finding of bone marrow biopsy was hypercellular marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis. The fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake increased in multiple lymph node, bone and spleen in positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET-CT) and lymph node biopsy was undergone in right axilla, but histologic finding was unremarkable. The chromosomal study in bone marrow showed 46 XY, t (6:9) (q21;q21) and the microarray revealed a gain of about 3.5 Mb at the 5q35.2q35.3 site including NSD1.
Results
Any treatments including vitamin and folic acid supplement, platelet transfusion, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, steroid and intravenous immunoglobulin had no effects in the patient. But there were no severe complications associated with pancytopenia during a follow-up of 3 months. And periodic pattern of deterioration and improvement appeared in pancytopenia, spontaneously.
Conclusion
Since it is rare for these distinctive feature of pancytopenia and chromosomal abnormality to coexist together, it is necessary to investigate the association. We describe the first case of 5q35.2q35.3 microduplication encompassing NSD1 with unexplained pancytopenia. Molecular cytogenetic testing in individuals with unexplained pancytopenia could led to the discovery of new phenotype of 5q35.2q35.3 microduplication syndromes.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chromosomal abnormality, Microarray analysis, Pancytopenia
Abstract: PB1819
Type: Publication Only
Background
Variety of diseases, haematological and non-haematological can affect the bone marrow primarily or secondarily, resulting in pancytopenia. But the incidence of pancytopenia with normal bone marrow was 3.38% to 10.5% in various international studies. Meanwhile, Sotos syndrome is an autosomal dominant childhood overgrowth syndrome with additional features of characteristic dysmorphisms, mild-to-severe learning disabilities (LD) and advanced bone age. As, in contrast, the duplication 5q35.2.q35.3 phenotype is characterized by growth delay, microcephaly and delayed bone age in some patients, it has been referred to as a reversed Sotos phenotype. However, there has been no report on the occurrence of pancytopenia as duplication 5q35.2.q35.3 phenotype.
Aims
We report the a 42-year-old male patient who has the microduplications of 5q35.2-q35.3 including NSD1 with unexplained pancytopenia was not improved by any treatment, but experienced no serious complications.
Methods
A 42-year-old male visited emergency room due to multiple trauma. He was diagnosed with mental retardation in the past. Physical examination was unremarkable except tenderness from bone fracture. Peripheral blood test showed leukocyte 3,510/mm3, neutrophil 190/mm3, hemoglobin 8.3 g/dL, hematocrit 25.0% and platelet 4,000/mm3. There was no relevant history of intake of any medications and exposure to radiation. And there were no other haematological parameters to lead pancytopenia. The finding of bone marrow biopsy was hypercellular marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis. The fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake increased in multiple lymph node, bone and spleen in positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET-CT) and lymph node biopsy was undergone in right axilla, but histologic finding was unremarkable. The chromosomal study in bone marrow showed 46 XY, t (6:9) (q21;q21) and the microarray revealed a gain of about 3.5 Mb at the 5q35.2q35.3 site including NSD1.
Results
Any treatments including vitamin and folic acid supplement, platelet transfusion, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, steroid and intravenous immunoglobulin had no effects in the patient. But there were no severe complications associated with pancytopenia during a follow-up of 3 months. And periodic pattern of deterioration and improvement appeared in pancytopenia, spontaneously.

Conclusion
Since it is rare for these distinctive feature of pancytopenia and chromosomal abnormality to coexist together, it is necessary to investigate the association. We describe the first case of 5q35.2q35.3 microduplication encompassing NSD1 with unexplained pancytopenia. Molecular cytogenetic testing in individuals with unexplained pancytopenia could led to the discovery of new phenotype of 5q35.2q35.3 microduplication syndromes.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chromosomal abnormality, Microarray analysis, Pancytopenia


