
Contributions
Abstract: PB2429
Type: Publication Only
Background
Patients with acute leukemia (AL) who fail to achieve complete remission (CR) have a dismal prognosis. Only few of them can be rescue after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). We retrospectively applied the GITMO score for PIF AL patients, that divides patients in 3 different categories; low, intermediate and high risk (Todisco E, BMT 2017).
Aims
Retrospective GITMO score based analysis
Methods
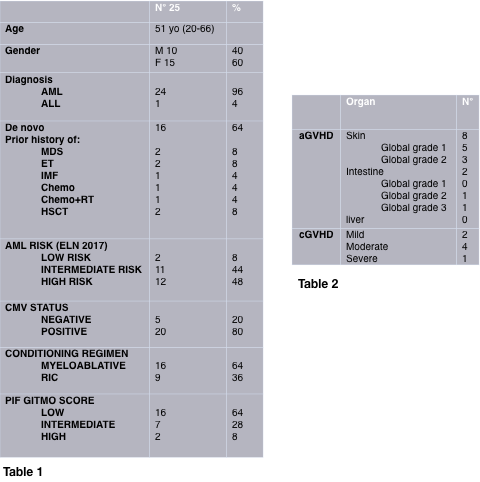
The study population included 25 patients with AL presented as primary induction failure (PIF) who had received an allogeneic HCT between 1 March 2014 and 30 September 2017 at our institution. Median age was 51 yo. Disease characteristics and prior history of hematological diseased and gender are summarized in Table 1. Patients received myeloablative (n=16) or reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens (n=9). Median time from diagnosis to transplant was 7 months, (range 0-9 months).
Results
Among PIF AL population 16 belong to low risk group; 7 to intermediate group and 2 to high risk group respectfully. 18 out of 25 were evaluable on +30 days from transplant: 16 patients achieved complete hematological remission (CHR), 2 patients shown refractory disease. 7 patients died within 2 months (range 0-4 months) from transplant due to multiorgan failure (2 pts), sepsis (3 pts) and engraftment failure (2pts). 12 out of 25 (35%) died due to TRM. Mean OS was 521 days, median OS was 331 days. Only 7 out of 25 patients (28%) are still alive without active disease, mean follow up was 337 days (79-1348 days). Among the three GITMO categories, the mean and median OS was 527 and 364 days, 581 and 341 days, and 262 days for low, intermediate and high risk group respectively (p=0.126). 8 patients experienced aGVHD and 7 patients cGVHD. All patients had received corticosteroids as frontline treatment. Those unresponsive were treated with second-line immunosuppressors. Mean time for developing GVHD was 2 and 4 months for aGVHD and cGVHD respectively. GVHD characteristic was shown in table 1. A trend to a better OS was shown in patients who developed aGVHD (p=0.380) and cGVHD (p=0.219). No impact was shown for CMV sierological status. (p=0,651). No impact was shown for myeloablative versus RIC regimens (p=0.983).
Conclusion
The clinical outcome of PIF AL patients is poor and only a minor proportion of patients is rescued by HSCT. GITMO score can be used to create a risk score that helps to identify patients who most likely benefit from the procedure. The availability of reliable prognostic factor is particularly important in the era of alternative donor, such as haploidentical source. The small sample size may prevent to assess more significant differences across the population.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Stem cell transplant
Abstract: PB2429
Type: Publication Only
Background
Patients with acute leukemia (AL) who fail to achieve complete remission (CR) have a dismal prognosis. Only few of them can be rescue after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). We retrospectively applied the GITMO score for PIF AL patients, that divides patients in 3 different categories; low, intermediate and high risk (Todisco E, BMT 2017).
Aims
Retrospective GITMO score based analysis
Methods
The study population included 25 patients with AL presented as primary induction failure (PIF) who had received an allogeneic HCT between 1 March 2014 and 30 September 2017 at our institution. Median age was 51 yo. Disease characteristics and prior history of hematological diseased and gender are summarized in Table 1. Patients received myeloablative (n=16) or reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens (n=9). Median time from diagnosis to transplant was 7 months, (range 0-9 months).
Results
Among PIF AL population 16 belong to low risk group; 7 to intermediate group and 2 to high risk group respectfully. 18 out of 25 were evaluable on +30 days from transplant: 16 patients achieved complete hematological remission (CHR), 2 patients shown refractory disease. 7 patients died within 2 months (range 0-4 months) from transplant due to multiorgan failure (2 pts), sepsis (3 pts) and engraftment failure (2pts). 12 out of 25 (35%) died due to TRM. Mean OS was 521 days, median OS was 331 days. Only 7 out of 25 patients (28%) are still alive without active disease, mean follow up was 337 days (79-1348 days). Among the three GITMO categories, the mean and median OS was 527 and 364 days, 581 and 341 days, and 262 days for low, intermediate and high risk group respectively (p=0.126). 8 patients experienced aGVHD and 7 patients cGVHD. All patients had received corticosteroids as frontline treatment. Those unresponsive were treated with second-line immunosuppressors. Mean time for developing GVHD was 2 and 4 months for aGVHD and cGVHD respectively. GVHD characteristic was shown in table 1. A trend to a better OS was shown in patients who developed aGVHD (p=0.380) and cGVHD (p=0.219). No impact was shown for CMV sierological status. (p=0,651). No impact was shown for myeloablative versus RIC regimens (p=0.983).

Conclusion
The clinical outcome of PIF AL patients is poor and only a minor proportion of patients is rescued by HSCT. GITMO score can be used to create a risk score that helps to identify patients who most likely benefit from the procedure. The availability of reliable prognostic factor is particularly important in the era of alternative donor, such as haploidentical source. The small sample size may prevent to assess more significant differences across the population.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Stem cell transplant


