
Contributions
Abstract: PB2415
Type: Publication Only
Background
Recipients of allogeneic stem cells grafts have clonally expanded CD8+/CD28- and CD4+/CD28- T lymphocytes during the early period after SCT, this cellular dynamic is probably associated with the acquisition of a toxic phenotype who over produce granzime and perforin. This scenario predisposes to continuous inflammation, increase T cell cytotoxic, NK activity (NK Per+ Gran+) and favor the appearance of senescent lymphocytes. On the other hand, viruses are recognized as the predominant pathogens leading to pneumonia after allo SCT (lack data in auto SCT). The direct consequences of respiratory viral infection (RVI), subsequent cellular injury and altered host immunity could also initiate a cascade of immunologic events (T cell exhaustion, inflammation)
Aims
The present study aimed to evaluate the dynamics of T cell exhaustion profile CD4+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, CD8+/CD28- Per+/Gran+ NK Per+ Gran+ during the first 100 days after SCT recipients (autologous, allogenic and patients with RVI)
Methods
Informed consent was obtained from all the patients before blood samples were collected. In a prospective study, peripheral blood samples were obtained previous BMT and at day +100 post BMT from 34 patients (11 autologous, 23 allogenic). To evaluate the expression of CD4+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, CD8+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, flow cytometry analysis was performed: 100μL of PB was labeled, with a panel of 8 monoclonal antibodies: PERFORIN FITC, GRANZIME PE, CD4 PerCP, CD28 APC, CD8 APC-H7, CD16/56 V450 and CD45 V500.The molecular detection of RV were tested with the CLART® Pneumovir assay (Clinical Array Technology, Genomica, Spain) based on the principle of multiplex polymerase chain reaction and DNA microarray.Statistical analysis was performed with IBM SPSS v24
Results
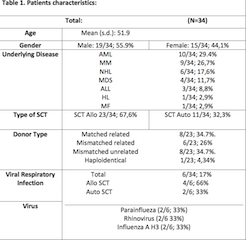
Thirty-four patients were evaluated from November 2016 to December 2017 at the University Hospital of La Princesa, Madrid Spain. The patients characteristics are shown in Table 1.The median percentages of baseline CD8+/CD28- cell line was 9,09% (range, 4,1-14,7) and the median percentages of CD8+/CD28-cell line at +100d were 29,2% (range, 13,3 -38,9). Likewise, significant differences were found (p = 0.001). We compared between the group of patients who had a RVI and the group without RVI: We found differences between patients with VRI and those who did not have VRI in the CD8+/CD28- +100d cell line, the median percentages of the RVI patients were 58.43% (range, 42.72-68.43) and the median percentages in the uninfected were 29.26% (range, 13.26-38.94) (p = 0.002). In the other cell lines, we did not find any statistically significant association.
Conclusion
In the present work, we show a dynamic change in the exhausted phenotype of T cell lymphocytes CD8+/CD28- throughout the SCT. There are a statistically significant differences when analyzing patients infected with RV vs non-infected patients (baseline vs + 100d). In agreement wtih previous reports, there was a marked increased od CD8+/CD28- cell fraction early after SCT. Exposure to certain VR in the first 100 days after TPH may contribute the appearance of populations of exhausted T lymphocytes CD8+/CD28- favoring a sustained inflammatory environment and probably works as a trigger in certain immunological complications (immune-disregulation). It is necessary to evaluate these patients over time and see their correlation with other clinico-epidemiological variables in the SCT (aGVHD, cGVHD, pulmonary functional tests, bronchiolitis obliterans, CMV reactivations).
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Bone marrow transplant, CD4+ T cells, CD8 T cells, T cell response
Abstract: PB2415
Type: Publication Only
Background
Recipients of allogeneic stem cells grafts have clonally expanded CD8+/CD28- and CD4+/CD28- T lymphocytes during the early period after SCT, this cellular dynamic is probably associated with the acquisition of a toxic phenotype who over produce granzime and perforin. This scenario predisposes to continuous inflammation, increase T cell cytotoxic, NK activity (NK Per+ Gran+) and favor the appearance of senescent lymphocytes. On the other hand, viruses are recognized as the predominant pathogens leading to pneumonia after allo SCT (lack data in auto SCT). The direct consequences of respiratory viral infection (RVI), subsequent cellular injury and altered host immunity could also initiate a cascade of immunologic events (T cell exhaustion, inflammation)
Aims
The present study aimed to evaluate the dynamics of T cell exhaustion profile CD4+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, CD8+/CD28- Per+/Gran+ NK Per+ Gran+ during the first 100 days after SCT recipients (autologous, allogenic and patients with RVI)
Methods
Informed consent was obtained from all the patients before blood samples were collected. In a prospective study, peripheral blood samples were obtained previous BMT and at day +100 post BMT from 34 patients (11 autologous, 23 allogenic). To evaluate the expression of CD4+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, CD8+/CD28- Per+/Gran+, flow cytometry analysis was performed: 100μL of PB was labeled, with a panel of 8 monoclonal antibodies: PERFORIN FITC, GRANZIME PE, CD4 PerCP, CD28 APC, CD8 APC-H7, CD16/56 V450 and CD45 V500.The molecular detection of RV were tested with the CLART® Pneumovir assay (Clinical Array Technology, Genomica, Spain) based on the principle of multiplex polymerase chain reaction and DNA microarray.Statistical analysis was performed with IBM SPSS v24
Results
Thirty-four patients were evaluated from November 2016 to December 2017 at the University Hospital of La Princesa, Madrid Spain. The patients characteristics are shown in Table 1.The median percentages of baseline CD8+/CD28- cell line was 9,09% (range, 4,1-14,7) and the median percentages of CD8+/CD28-cell line at +100d were 29,2% (range, 13,3 -38,9). Likewise, significant differences were found (p = 0.001). We compared between the group of patients who had a RVI and the group without RVI: We found differences between patients with VRI and those who did not have VRI in the CD8+/CD28- +100d cell line, the median percentages of the RVI patients were 58.43% (range, 42.72-68.43) and the median percentages in the uninfected were 29.26% (range, 13.26-38.94) (p = 0.002). In the other cell lines, we did not find any statistically significant association.

Conclusion
In the present work, we show a dynamic change in the exhausted phenotype of T cell lymphocytes CD8+/CD28- throughout the SCT. There are a statistically significant differences when analyzing patients infected with RV vs non-infected patients (baseline vs + 100d). In agreement wtih previous reports, there was a marked increased od CD8+/CD28- cell fraction early after SCT. Exposure to certain VR in the first 100 days after TPH may contribute the appearance of populations of exhausted T lymphocytes CD8+/CD28- favoring a sustained inflammatory environment and probably works as a trigger in certain immunological complications (immune-disregulation). It is necessary to evaluate these patients over time and see their correlation with other clinico-epidemiological variables in the SCT (aGVHD, cGVHD, pulmonary functional tests, bronchiolitis obliterans, CMV reactivations).
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Bone marrow transplant, CD4+ T cells, CD8 T cells, T cell response


