
Contributions
Abstract: PB1775
Type: Publication Only
Background
R -CHOP still remains the standard of care for large B cell Lymphoma(LBCL) patients(pts) but it’s clearly unsatisfactory for about 30-40% of them, especially for pts characterized by high-risk molecular profile,carrying expression of MYC and BCL2 proteins (Double Expressor Lymphoma[DEL]) associated or not to the underlying translocation(Double Hit Lymphoma[DHL]).More intensive programs and in particular R-DA-EPOCH scheme obtained good results in retrospective studies. We report our prospective experience with this program.
Aims
to analyze the outcome in terms of response, Progression free survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), feasibility and toxicity of consecutive pts with Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma(DLBCL),High grade Lymphoma(HGL) or Primary mediastinal B cell Lymphoma(PMBCL) diagnosed in a single Italian hematological center and all treated with the R-DA-EPOCH, which was delivered either as an inpatient regimen or administered on an outpatient basis using ambulatory infusion pumps.
Methods
We reviewed chart data of 36 LBCL pts consecutively diagnosed from December 2014 to February 2018 at our center. For pts diagnosed since 2016 we introduced the new category of HGL according to WHO 2016.
Results
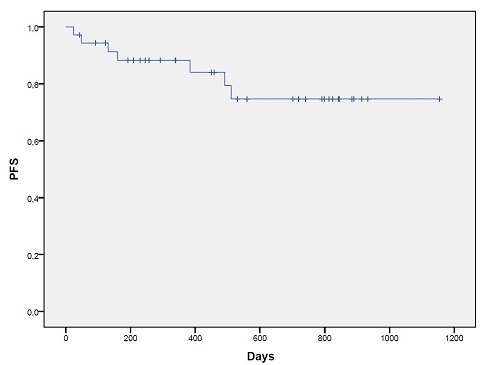
Median follow up of our pts is 533 days (42 -1154). Regarding pts characteristics 23/36 (63.9%) are male, 13/36 (36.1%) female. Response is available for 33/36 pts, 1 is waiting for restaging and 2 pts are still receiving therapy at time of analysis. Median age at diagnosis was 50 years(range 22-69). Considering histology 23/36 (63.9%) were DLBCL, 6/36(16.7%) HGL and 7/36 (19.4%) PMBCL. Median ki67% was 80% (range 50- >90). Regarding molecular profiles a total of 18/36 (50%) pts show bcl2 expression,28/36 (77,8%) are bcl6 and 7/36 (19,4%) myc positive. In our series 4/36(11,1%) pts were DEL (bcl2 and myc positive) but FISH data were available only for 2 pts and only 1 resulted DHL. Regarding the disease stage 17/36(47,2%) have IPI score 0-2 and 19/36 (52,8%) IPI score 3-5. Twenty out of 36 pts (55,6%) have an extra-nodal (EN) localization at diagnosis; 15/36 (41,7%) >1 EN localization. Of note 4/36 (11,1%) were HIV positive pts. Data regarding the feasibility of this approach are available for all pts: 28/36(77,8%) pts completed six planned cycles and 23/36(63,9%)received therapy on an outpatient basis (123 outpatient cycles administrated).Four pts didn’t complete 6 cycles because of disease progression. Dose escalation was possible in 23/36(63.9% [95% C.I. 57% - 85%]) pts, but rarely in pts >65 yrs (only in 2/36 [5,6%, 95% C.I. 1.7% - 17%]). The median dose level reached was 2 (range level -1 – 5). Grade4 neutropenia occurred in 36/36 (100%)pts, thrombocytopenia grade 4 in 8/36 pts (22,2%). A total of 15/36 (41,7%) pts had an infectious event and 10/36(27.8%) had therapy delay due to toxicities. Grade 3/4 non-hematological toxicities, especially neurotoxicity, were infrequent and manageable. We observed cardiotoxicity in 2/36 pts, which was related to tumor lysis syndrome and HIV infection. Among pts evaluable for response, 27/33(81,8%) obtained a complete remission (CR). A total of 6/36 pts died, all due to disease progression. PFS at 2 years was 74,7% (Figure 1). OS at 2 years 77%.
Conclusion
Our results confirm R-DA-EPOCH as a feasible program with promising response rate.This scheme allows to obtain CR in 81,8% of pts with an acceptable toxicity profile. Especially in patients with high risk DLBCL (high IPI score, DEL and DHL) R-DA-EPOCH is an alternative to standard induction therapy which can be administered as an outpatient regimen in the majority of pts.
Session topic: 21. Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Lymphoma therapy, Outcome
Abstract: PB1775
Type: Publication Only
Background
R -CHOP still remains the standard of care for large B cell Lymphoma(LBCL) patients(pts) but it’s clearly unsatisfactory for about 30-40% of them, especially for pts characterized by high-risk molecular profile,carrying expression of MYC and BCL2 proteins (Double Expressor Lymphoma[DEL]) associated or not to the underlying translocation(Double Hit Lymphoma[DHL]).More intensive programs and in particular R-DA-EPOCH scheme obtained good results in retrospective studies. We report our prospective experience with this program.
Aims
to analyze the outcome in terms of response, Progression free survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), feasibility and toxicity of consecutive pts with Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma(DLBCL),High grade Lymphoma(HGL) or Primary mediastinal B cell Lymphoma(PMBCL) diagnosed in a single Italian hematological center and all treated with the R-DA-EPOCH, which was delivered either as an inpatient regimen or administered on an outpatient basis using ambulatory infusion pumps.
Methods
We reviewed chart data of 36 LBCL pts consecutively diagnosed from December 2014 to February 2018 at our center. For pts diagnosed since 2016 we introduced the new category of HGL according to WHO 2016.
Results
Median follow up of our pts is 533 days (42 -1154). Regarding pts characteristics 23/36 (63.9%) are male, 13/36 (36.1%) female. Response is available for 33/36 pts, 1 is waiting for restaging and 2 pts are still receiving therapy at time of analysis. Median age at diagnosis was 50 years(range 22-69). Considering histology 23/36 (63.9%) were DLBCL, 6/36(16.7%) HGL and 7/36 (19.4%) PMBCL. Median ki67% was 80% (range 50- >90). Regarding molecular profiles a total of 18/36 (50%) pts show bcl2 expression,28/36 (77,8%) are bcl6 and 7/36 (19,4%) myc positive. In our series 4/36(11,1%) pts were DEL (bcl2 and myc positive) but FISH data were available only for 2 pts and only 1 resulted DHL. Regarding the disease stage 17/36(47,2%) have IPI score 0-2 and 19/36 (52,8%) IPI score 3-5. Twenty out of 36 pts (55,6%) have an extra-nodal (EN) localization at diagnosis; 15/36 (41,7%) >1 EN localization. Of note 4/36 (11,1%) were HIV positive pts. Data regarding the feasibility of this approach are available for all pts: 28/36(77,8%) pts completed six planned cycles and 23/36(63,9%)received therapy on an outpatient basis (123 outpatient cycles administrated).Four pts didn’t complete 6 cycles because of disease progression. Dose escalation was possible in 23/36(63.9% [95% C.I. 57% - 85%]) pts, but rarely in pts >65 yrs (only in 2/36 [5,6%, 95% C.I. 1.7% - 17%]). The median dose level reached was 2 (range level -1 – 5). Grade4 neutropenia occurred in 36/36 (100%)pts, thrombocytopenia grade 4 in 8/36 pts (22,2%). A total of 15/36 (41,7%) pts had an infectious event and 10/36(27.8%) had therapy delay due to toxicities. Grade 3/4 non-hematological toxicities, especially neurotoxicity, were infrequent and manageable. We observed cardiotoxicity in 2/36 pts, which was related to tumor lysis syndrome and HIV infection. Among pts evaluable for response, 27/33(81,8%) obtained a complete remission (CR). A total of 6/36 pts died, all due to disease progression. PFS at 2 years was 74,7% (Figure 1). OS at 2 years 77%.

Conclusion
Our results confirm R-DA-EPOCH as a feasible program with promising response rate.This scheme allows to obtain CR in 81,8% of pts with an acceptable toxicity profile. Especially in patients with high risk DLBCL (high IPI score, DEL and DHL) R-DA-EPOCH is an alternative to standard induction therapy which can be administered as an outpatient regimen in the majority of pts.
Session topic: 21. Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Lymphoma therapy, Outcome


