
Contributions
Abstract: PB2342
Type: Publication Only
Background
Flow-cytometric assessment on lymph node biopsies has been reported to be useful in the diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common form of B-NHL among adults. The forward-scatter is a useful flow-cytometric parameter to study the lymphoma cell size.
Aims
The aim of the present study was to assess the diagnostic relevance of forward-scatter in identification of DLBCL on lymph node suspension samples.
Methods
Lymph node suspensions were prepared from biopsies obtained by surgical resection or by ultrasound-guided endoscopic core biopsies. We used the Medimachine system (BD Biosciences) for mechanical disaggregation of the solid tissue. The screening panel included CD19, CD20, CD10, Kappa, Lambda, CD5, CD3, CD4 and CD8. For B-cells the normal range of Kappa/Lambda ratio was >0.8 or <3.0. A clear clonality, CD10+ or CD5+ expression on B cell populations or absence of surface immunoglobulin light chain were suggestive of B-NHL. The Forward-scatter Area (FSC-A) was evaluated on B- and T-cells of lymph node suspensions and expressed as median value. Data were acquired on BD FACSCantoII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed by BD FACSDiva software (BD Biosciences). We defined the ratio between FSC-A of the pathological B-cell population and the FCS-A of CD3+ T-cells as FSC ratio.
Results
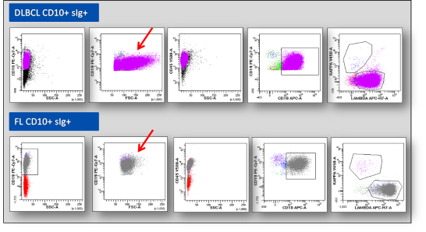
In this study we included 41 lymph node suspensions with a pathological B cell population. Immunohistochemical diagnosis was DLBCL in 23 patients, follicular lymphoma (FL) in 12 patients, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in 3 patients, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in 2 patients and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in 1 patients. Subsequent immunohistochemical analysis proved that all B-NHL were correctly identified (100% sensitivity) by flow-cytometry analysis. B-cell pathological populations were CD19 and CD20 positive and presented a clear clonal light chain restriction in 33/41 cases, while 8/41 (6 DLBCL, 1 FL, 1 MZL) did not show any light chain expression. CD10 was expressed in all FL cases and in 4/23 DLBCL. CD5 was present in the patients with MCL and in 1 case of DLBCL. DLBCL cases showed a higher FSC ratio (see fig. 1) compared to other B-NHL (1.60 vs 1.04, P < 0.001). By calculating the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, the best cut-off for FSC ratio was 1.23, with an AUC = 0.94 (95% CI 0.85 to 1.00). This cut-off value provided a sensitivity of 96%, a specificity of 79%. The positive predictive value was 86% and a negative predictive value of 96%.
Conclusion
The FSC ratio between the pathological B lymphoma cell population to the normal CD3+ T cells is a simple parameter, that is routinely acquired during flow cytometry and can be helpful in discerning between DLBCL and low-grade lymphomas and mantle cell lymphoma. This information may be helpful to direct the immunohistochemical work-up.
Session topic: 19. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): DLBCL, flow cytometry
Abstract: PB2342
Type: Publication Only
Background
Flow-cytometric assessment on lymph node biopsies has been reported to be useful in the diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common form of B-NHL among adults. The forward-scatter is a useful flow-cytometric parameter to study the lymphoma cell size.
Aims
The aim of the present study was to assess the diagnostic relevance of forward-scatter in identification of DLBCL on lymph node suspension samples.
Methods
Lymph node suspensions were prepared from biopsies obtained by surgical resection or by ultrasound-guided endoscopic core biopsies. We used the Medimachine system (BD Biosciences) for mechanical disaggregation of the solid tissue. The screening panel included CD19, CD20, CD10, Kappa, Lambda, CD5, CD3, CD4 and CD8. For B-cells the normal range of Kappa/Lambda ratio was >0.8 or <3.0. A clear clonality, CD10+ or CD5+ expression on B cell populations or absence of surface immunoglobulin light chain were suggestive of B-NHL. The Forward-scatter Area (FSC-A) was evaluated on B- and T-cells of lymph node suspensions and expressed as median value. Data were acquired on BD FACSCantoII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed by BD FACSDiva software (BD Biosciences). We defined the ratio between FSC-A of the pathological B-cell population and the FCS-A of CD3+ T-cells as FSC ratio.
Results
In this study we included 41 lymph node suspensions with a pathological B cell population. Immunohistochemical diagnosis was DLBCL in 23 patients, follicular lymphoma (FL) in 12 patients, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in 3 patients, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in 2 patients and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in 1 patients. Subsequent immunohistochemical analysis proved that all B-NHL were correctly identified (100% sensitivity) by flow-cytometry analysis. B-cell pathological populations were CD19 and CD20 positive and presented a clear clonal light chain restriction in 33/41 cases, while 8/41 (6 DLBCL, 1 FL, 1 MZL) did not show any light chain expression. CD10 was expressed in all FL cases and in 4/23 DLBCL. CD5 was present in the patients with MCL and in 1 case of DLBCL. DLBCL cases showed a higher FSC ratio (see fig. 1) compared to other B-NHL (1.60 vs 1.04, P < 0.001). By calculating the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, the best cut-off for FSC ratio was 1.23, with an AUC = 0.94 (95% CI 0.85 to 1.00). This cut-off value provided a sensitivity of 96%, a specificity of 79%. The positive predictive value was 86% and a negative predictive value of 96%.

Conclusion
The FSC ratio between the pathological B lymphoma cell population to the normal CD3+ T cells is a simple parameter, that is routinely acquired during flow cytometry and can be helpful in discerning between DLBCL and low-grade lymphomas and mantle cell lymphoma. This information may be helpful to direct the immunohistochemical work-up.
Session topic: 19. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): DLBCL, flow cytometry


