
Contributions
Abstract: PB2310
Type: Publication Only
Background
Though WHO criteria for the prefibrotic and overt fibrotic stages of primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is well established, diagnosis and management of this disease often remains a challenging problem. Pathogenesis of anemia or cytopenia, that accompanies PMF, or development of post MF acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is also frequently unclear.
Aims
Our aim was to reveal peculiarities of hematopoiesis and main reasons of cytopenia in patients with PMF.
Methods
We studied blood and bone marrow cell (BMC) cultures of 7 patients with PMF in fibrotic stage using the method worked out by us. This method enables to observe hematopoiesis and detect proliferating clone in patients with hematological malignances during 3-5-7-14-21-days of cultivation of BMC. In 3-day-blood leukocyte cultures we studied macrophage-lymphocyte rosettes (MLRos) formation that reflects immune reactivity of organism. Increase of the amount of MLRos in vitro points to immune sensitization or immune conflict, while its decrease points to low immune reactivity of organism.
Results
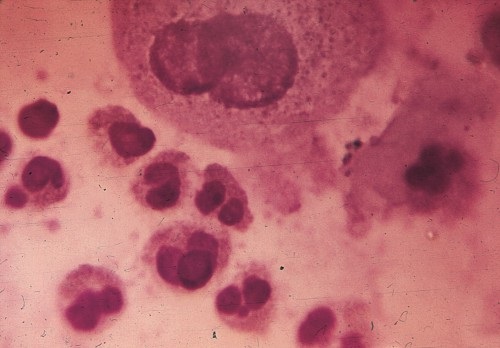
Patients age was in the range of 40-70, 4- men, 3- women, all had anemia with reticolocytosis, 4 had thrombocytopenia, 1- leukopenia, except the last patient leukocytes were in the range of 8-12x109/L with moderate neutrophil leukocytosis and left shift to myelocytes and promyelocytes. All patients had splenomegaly (from 5-7 up to 15-18 cm), 5 had hepatomegaly (up to 5cm). BM biopsy showed megakaryocytic proliferation with reticulin and collagen fibrosis grades 2 or 3. Spleen aspirate showed myeloid metaplasia. In 3-5-days BMC cultures poor growth of myeloid cells, atypical megacaryocytes with hypolobulated nuclei and decreased erythropoiesis was observed; In 7-14-21-day cultures mainly growth of reticular stromal cells was seen, besides in one case growth of eosinophilic cells was observed (Fig.1). In 5 cases anti-erythrocyte and in 3 cases antiplatelet antibodies were also detected. In blood cultures of all patients amount of MLRos was increased significantly up to 75-85%, showing autoimmune character of cytopenia, while in norm it equals 37,4±2,2%. As above mentioned patients didn’t have high leukocytosis and prominently progressive hepatosplenomegaly, they were effectively treated with prednisone 30-60mg/day. Because of frequent recurrence of cytopenia in 2 cases was done splenectomy. 1patient died after operation because of sepsis, second one was in remission for 5 years. 4 patients are alive more than 6 years and receive low dosage of steroids in case of cytopenia recurrence. 2 patients died because of disease progression. One of them developed post MF AML. Notable that in BMC culture of this patient proliferation of myeloid blast cells was revealed a month before clinical onset of AML.
Conclusion
Results of our data show that MLRos formation in vitro can be successfully applied for the detection of immune conflict in the pathogenesis of cytopenia in patients with PMF while use of BMC cultures is reasonable for observation and estimation of hematopoiesis in vitro that will help to precise diagnosis and hold tailored treatment in each case. Growth of eosinophilic cells in long-term culture confirm myeloproliferative nature of the PMF, while clonal expansion of blast cells in vitro predicts development of post MF AML.
Fig 1. Eosinophilic cells at the different stages of maturation. Hypolobulated megakaryocyte (above) sequestrating platelets. 21-day-culture of bone marrow aspirate of a patient with primary myelofibrosis.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Clonal expansion, Lymphocyte, Macrophage, Megakaryopoiesis
Abstract: PB2310
Type: Publication Only
Background
Though WHO criteria for the prefibrotic and overt fibrotic stages of primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is well established, diagnosis and management of this disease often remains a challenging problem. Pathogenesis of anemia or cytopenia, that accompanies PMF, or development of post MF acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is also frequently unclear.
Aims
Our aim was to reveal peculiarities of hematopoiesis and main reasons of cytopenia in patients with PMF.
Methods
We studied blood and bone marrow cell (BMC) cultures of 7 patients with PMF in fibrotic stage using the method worked out by us. This method enables to observe hematopoiesis and detect proliferating clone in patients with hematological malignances during 3-5-7-14-21-days of cultivation of BMC. In 3-day-blood leukocyte cultures we studied macrophage-lymphocyte rosettes (MLRos) formation that reflects immune reactivity of organism. Increase of the amount of MLRos in vitro points to immune sensitization or immune conflict, while its decrease points to low immune reactivity of organism.
Results
Patients age was in the range of 40-70, 4- men, 3- women, all had anemia with reticolocytosis, 4 had thrombocytopenia, 1- leukopenia, except the last patient leukocytes were in the range of 8-12x109/L with moderate neutrophil leukocytosis and left shift to myelocytes and promyelocytes. All patients had splenomegaly (from 5-7 up to 15-18 cm), 5 had hepatomegaly (up to 5cm). BM biopsy showed megakaryocytic proliferation with reticulin and collagen fibrosis grades 2 or 3. Spleen aspirate showed myeloid metaplasia. In 3-5-days BMC cultures poor growth of myeloid cells, atypical megacaryocytes with hypolobulated nuclei and decreased erythropoiesis was observed; In 7-14-21-day cultures mainly growth of reticular stromal cells was seen, besides in one case growth of eosinophilic cells was observed (Fig.1). In 5 cases anti-erythrocyte and in 3 cases antiplatelet antibodies were also detected. In blood cultures of all patients amount of MLRos was increased significantly up to 75-85%, showing autoimmune character of cytopenia, while in norm it equals 37,4±2,2%. As above mentioned patients didn’t have high leukocytosis and prominently progressive hepatosplenomegaly, they were effectively treated with prednisone 30-60mg/day. Because of frequent recurrence of cytopenia in 2 cases was done splenectomy. 1patient died after operation because of sepsis, second one was in remission for 5 years. 4 patients are alive more than 6 years and receive low dosage of steroids in case of cytopenia recurrence. 2 patients died because of disease progression. One of them developed post MF AML. Notable that in BMC culture of this patient proliferation of myeloid blast cells was revealed a month before clinical onset of AML.

Conclusion
Results of our data show that MLRos formation in vitro can be successfully applied for the detection of immune conflict in the pathogenesis of cytopenia in patients with PMF while use of BMC cultures is reasonable for observation and estimation of hematopoiesis in vitro that will help to precise diagnosis and hold tailored treatment in each case. Growth of eosinophilic cells in long-term culture confirm myeloproliferative nature of the PMF, while clonal expansion of blast cells in vitro predicts development of post MF AML.
Fig 1. Eosinophilic cells at the different stages of maturation. Hypolobulated megakaryocyte (above) sequestrating platelets. 21-day-culture of bone marrow aspirate of a patient with primary myelofibrosis.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Clonal expansion, Lymphocyte, Macrophage, Megakaryopoiesis


