
Contributions
Abstract: PB2321
Type: Publication Only
Background
The balance of the thiol-disulphide homeostasis shifted to reductive thiol side in
the Polycythemia Vera (PV).
Aims
This study aims to demonstrate in PV patients the thiol disulphide homeostasis which is known to play a role in cell proliferation, apoptosis and various steps of cell cycle.
Methods
Forty-two PV patients and 47 healthy controls were included in the
study. Serum total (–SH + –S–S–) and native (–SH) thiol levels were measured in all subjects.
The amount of dynamic disulphide bonds and, the ratio of (–S–S–) and (–S–S–) × 100/(–SH),
(–S–S–) × 100/(–SH + –S–S–), and –SH ×100/(–SH + –S–S–) were calculated with automatic
method. The data obtained from the patient group were compared with the control group.
Results
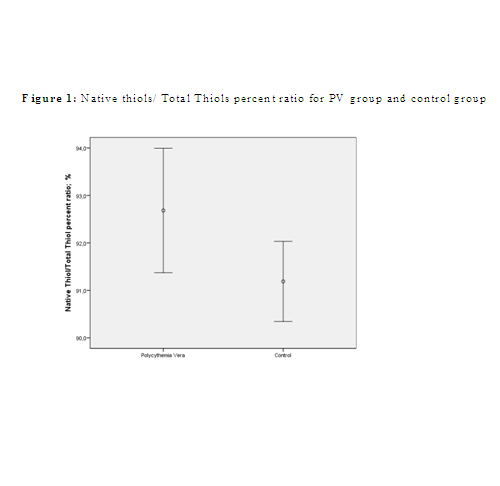
Both groups were similar in terms of age and gender distribution. Compared with the
control group, PV group had significantly higher native thiol, total thiol and nativ/total thiol
levels.
Conclusion
In accordance with the nature of the disease, thiol balance in PV patients was in
favor of proliferation. Increased total thiol (–SH + –S–S), native thiol (–SH) levels and native
thiol/total thiol ratio might be associated with uncontrolled proliferation. his change can provocate proliferation status of the disease and/or may be secondary to the disease.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, Polycythemia vera
Abstract: PB2321
Type: Publication Only
Background
The balance of the thiol-disulphide homeostasis shifted to reductive thiol side in
the Polycythemia Vera (PV).
Aims
This study aims to demonstrate in PV patients the thiol disulphide homeostasis which is known to play a role in cell proliferation, apoptosis and various steps of cell cycle.
Methods
Forty-two PV patients and 47 healthy controls were included in the
study. Serum total (–SH + –S–S–) and native (–SH) thiol levels were measured in all subjects.
The amount of dynamic disulphide bonds and, the ratio of (–S–S–) and (–S–S–) × 100/(–SH),
(–S–S–) × 100/(–SH + –S–S–), and –SH ×100/(–SH + –S–S–) were calculated with automatic
method. The data obtained from the patient group were compared with the control group.
Results
Both groups were similar in terms of age and gender distribution. Compared with the
control group, PV group had significantly higher native thiol, total thiol and nativ/total thiol
levels.

Conclusion
In accordance with the nature of the disease, thiol balance in PV patients was in
favor of proliferation. Increased total thiol (–SH + –S–S), native thiol (–SH) levels and native
thiol/total thiol ratio might be associated with uncontrolled proliferation. his change can provocate proliferation status of the disease and/or may be secondary to the disease.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myeloproliferative disorder, Polycythemia vera


