
Contributions
Abstract: PB2151
Type: Publication Only
Background
Multiple myelomas (MM) is characterized as the neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells producing a monoclonal immunoglobulin. Multiple myeloma is a heterogeneous disease. The prognosis of patients with MM is dependent on four factors: staging, patient factors, disease biology and response to therapy. The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance.
Aims
The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance. Accurate identification of high-risk and low-risk cytogenetic abnormalities plays a crucial role in predicting the response or resistance to the treatment. The aim of this paper is to report complex karyotype with novel translocation leading to a fatal clinical course in a patient with MM.
Methods
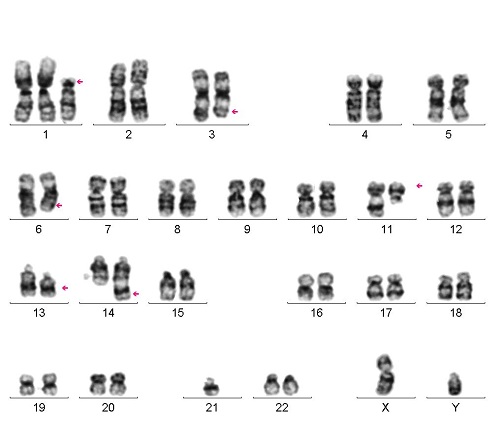
We report the case of a 48-year-old man presenting with black stool, bicytopenia, high creatinine level and hypercalcemia. The bone marrow aspiration of the patient showed diffuse neoplastic plasma cell infiltration and complex karyotype was detected in all of 20 metaphases on cytogenetic analyses. The karyotype of the patient was 46,XY,dic(1;21) (p11;p11), del(3) (q25;q29), del(6) (q24;q26), t(11;14) (q13;q32), del(13) (q14q21). The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time.
Results
The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time. Although the prognostic impact of this unique anomaly may be unclear. Regarding the very aggressive clinical presentation of the MM, cytogenetic abnormalities could be linked to poor prognosis.
Conclusion
Multiple myeloma is a heterogeneous disease. The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance. We report the case of complex karyotype was detected in all of 20 metaphases on cytogenetic analyses. The karyotype of the patient was 46,XY,dic(1;21) (p11;p11), del(3) (q25;q29), del(6) (q24;q26), t(11;14) (q13;q32), del(13) (q14q21). The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Chromosomal abnormality, Multiple Myeloma, Translocation
Abstract: PB2151
Type: Publication Only
Background
Multiple myelomas (MM) is characterized as the neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells producing a monoclonal immunoglobulin. Multiple myeloma is a heterogeneous disease. The prognosis of patients with MM is dependent on four factors: staging, patient factors, disease biology and response to therapy. The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance.
Aims
The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance. Accurate identification of high-risk and low-risk cytogenetic abnormalities plays a crucial role in predicting the response or resistance to the treatment. The aim of this paper is to report complex karyotype with novel translocation leading to a fatal clinical course in a patient with MM.
Methods
We report the case of a 48-year-old man presenting with black stool, bicytopenia, high creatinine level and hypercalcemia. The bone marrow aspiration of the patient showed diffuse neoplastic plasma cell infiltration and complex karyotype was detected in all of 20 metaphases on cytogenetic analyses. The karyotype of the patient was 46,XY,dic(1;21) (p11;p11), del(3) (q25;q29), del(6) (q24;q26), t(11;14) (q13;q32), del(13) (q14q21). The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time.
Results
The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time. Although the prognostic impact of this unique anomaly may be unclear. Regarding the very aggressive clinical presentation of the MM, cytogenetic abnormalities could be linked to poor prognosis.

Conclusion
Multiple myeloma is a heterogeneous disease. The cytogenetic anomalies of patients have prognostic significance. We report the case of complex karyotype was detected in all of 20 metaphases on cytogenetic analyses. The karyotype of the patient was 46,XY,dic(1;21) (p11;p11), del(3) (q25;q29), del(6) (q24;q26), t(11;14) (q13;q32), del(13) (q14q21). The anomaly of t (1; 21) (p11; p11), which we detected in this case and which has not been detected between these breaking points in any malignancies before, was detected in a case with MM for the first time.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Chromosomal abnormality, Multiple Myeloma, Translocation


