
Contributions
Abstract: PB2083
Type: Publication Only
Background
The importance of the identification of somatic mutations in myeloid neoplasms has increased dramatically in the last ten years. The study of these mutations has improved the understanding of bone marrow (BM) clonal expansion that occurs in these malignancies. Mutations in genes participating in the mechanism of splicing and epigenetics are found in patients with clonal cytopenia of undetermined significance (CCUS), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS/MPN) and acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The evaluation of somatic mutations profiles in the Brazilian population has clinical relevance due to the great ethnic differences found in our population as compared to the North American and European populations, where the vast majority of these studies were conducted.
Aims
Evaluation of the frequency of somatic mutations in genes: SF3B1, TET2, U2AF1, IDH1/2, tp53 in patients from the city of Salvador, Bahia, Brazil, with diagnoses of CCUS, MDS, MDS/MPN and AML-MRC.
Methods
In this observational study, 50 untreated patients ≥ 18 years were analyzed. Blood counts, cytogenetic and BM analysis were performed. DNA was isolated from BM and PCR analyzes was performed. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
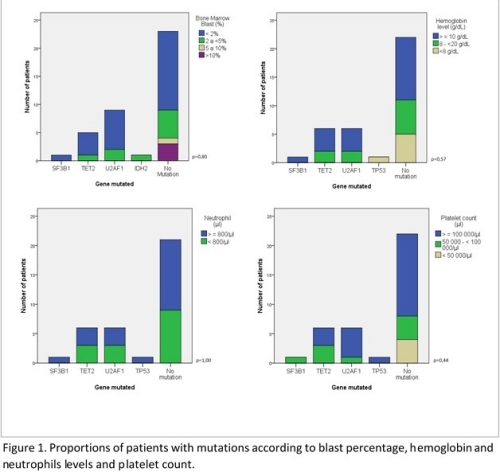
From the 50 patients analyzed, 24 were diagnosed with cytopenias (48%), 18 with MDS (36%), 5 with MDS/MPN (10%) and 3 with AML (6%). Overall, 29 patients were female (58%) and 21 were male (42%). The mean age was 60.5 years (range 22 – 84). Mutated genes were found in 19 patients (38%). Ten patients showed mutations in U2AF1 gene (20%), 6 (12%) in TET2, one (2%) in SF3B1, one (2%) in IDH2 and one (2%) in TP53 mutated. The coexisting mutations were found in four patients, as follows: IDH2 + SF3B1, SF3B1 + TET2, U2AF1 + IDH2 and U2AF1 + TET2. Eleven patients (45,8%) presented mutations in the cytopenias group. From these, 7 cases showed mutations in U2AF1 and the remaining four cases had mutations in SF3B1, TET2, IDH2 and TP53. All the coexisting mutations found were in this group. In the MDS group, TET2 mutations were found in four (38,9%) patients and U2AF1 mutations were found in 16,7% (n=3). No mutations were observed in the AML group and one patient (20%) presented mutation in TET2 gene in the group MDS/MPN (p=0,66). From the 27 patients < 60 years of age, 9 (40,9%) showed mutations: four had U2AF1 mutated, two patients presented mutation in TET2 and three presented mutations in SF3B1, IDH2 and TP53. From the 27 patients > 60 years of age, 10 (37%) presented mutations: 6 in U2AF1 and four in TET2 (p=0,66). All of the patients with coexisting mutations were < 60y. Mutations were not differentially associated with sex. Of 21 male patients, 9 (42,9%) had one or more mutations. Of the 29 female patients, 10 (34,5%) had mutations (p=0,55). The majority of patients analyzed had <2% blasts in the BM, hemoglobin levels ≥ 10g / dL, neutrophils ≥ 800/μL and platelets ≥ 100,000/μL (Figure 1).
Conclusion
Differently from literature data, the main gene mutated was U2AF1, found in 20% of cases here, as opposed to ~ 8% found in other studies. The cytopenias group presented the highest number of cases with mutations. Moreover, the number of coexisting mutations was higher in this group and the same were found only in patients <60y. This is a preliminary study, that is under development to increase the number of enrolled individuals and might be added to other Brazilian studies, aiming to define the mutation profile of myeloid neoplasms in Brazil.
Session topic: 9. Myelodysplastic syndromes – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Myeloid malignancies, Population, Somatic mutation
Abstract: PB2083
Type: Publication Only
Background
The importance of the identification of somatic mutations in myeloid neoplasms has increased dramatically in the last ten years. The study of these mutations has improved the understanding of bone marrow (BM) clonal expansion that occurs in these malignancies. Mutations in genes participating in the mechanism of splicing and epigenetics are found in patients with clonal cytopenia of undetermined significance (CCUS), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS/MPN) and acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The evaluation of somatic mutations profiles in the Brazilian population has clinical relevance due to the great ethnic differences found in our population as compared to the North American and European populations, where the vast majority of these studies were conducted.
Aims
Evaluation of the frequency of somatic mutations in genes: SF3B1, TET2, U2AF1, IDH1/2, tp53 in patients from the city of Salvador, Bahia, Brazil, with diagnoses of CCUS, MDS, MDS/MPN and AML-MRC.
Methods
In this observational study, 50 untreated patients ≥ 18 years were analyzed. Blood counts, cytogenetic and BM analysis were performed. DNA was isolated from BM and PCR analyzes was performed. All patients provided informed consent.
Results
From the 50 patients analyzed, 24 were diagnosed with cytopenias (48%), 18 with MDS (36%), 5 with MDS/MPN (10%) and 3 with AML (6%). Overall, 29 patients were female (58%) and 21 were male (42%). The mean age was 60.5 years (range 22 – 84). Mutated genes were found in 19 patients (38%). Ten patients showed mutations in U2AF1 gene (20%), 6 (12%) in TET2, one (2%) in SF3B1, one (2%) in IDH2 and one (2%) in TP53 mutated. The coexisting mutations were found in four patients, as follows: IDH2 + SF3B1, SF3B1 + TET2, U2AF1 + IDH2 and U2AF1 + TET2. Eleven patients (45,8%) presented mutations in the cytopenias group. From these, 7 cases showed mutations in U2AF1 and the remaining four cases had mutations in SF3B1, TET2, IDH2 and TP53. All the coexisting mutations found were in this group. In the MDS group, TET2 mutations were found in four (38,9%) patients and U2AF1 mutations were found in 16,7% (n=3). No mutations were observed in the AML group and one patient (20%) presented mutation in TET2 gene in the group MDS/MPN (p=0,66). From the 27 patients < 60 years of age, 9 (40,9%) showed mutations: four had U2AF1 mutated, two patients presented mutation in TET2 and three presented mutations in SF3B1, IDH2 and TP53. From the 27 patients > 60 years of age, 10 (37%) presented mutations: 6 in U2AF1 and four in TET2 (p=0,66). All of the patients with coexisting mutations were < 60y. Mutations were not differentially associated with sex. Of 21 male patients, 9 (42,9%) had one or more mutations. Of the 29 female patients, 10 (34,5%) had mutations (p=0,55). The majority of patients analyzed had <2% blasts in the BM, hemoglobin levels ≥ 10g / dL, neutrophils ≥ 800/μL and platelets ≥ 100,000/μL (Figure 1).

Conclusion
Differently from literature data, the main gene mutated was U2AF1, found in 20% of cases here, as opposed to ~ 8% found in other studies. The cytopenias group presented the highest number of cases with mutations. Moreover, the number of coexisting mutations was higher in this group and the same were found only in patients <60y. This is a preliminary study, that is under development to increase the number of enrolled individuals and might be added to other Brazilian studies, aiming to define the mutation profile of myeloid neoplasms in Brazil.
Session topic: 9. Myelodysplastic syndromes – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Myeloid malignancies, Population, Somatic mutation


