
Contributions
Abstract: PB1944
Type: Publication Only
Background
The arrival of the second-generation (2ndG) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) improved a significant percentage of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) after imatinib resistance or intolerance, increasing disease survival.
Aims
The primary endpoint of this open study was to determine complete cytigenetic response (CCyR) and major molecular response (MMR) rate in patients treated with nilotinib, at 6 and 12 months respectively. Secondary objectives were to determine the OS, PFS, and EFS, as well as establishing nilotinib safety profile.
Methods
A prospective, open label, single-center study was undertaken to examine the clinical characteristics, cytogenetic and molecular response rates, overall survival, progression-free survival, and event-free survival of patients with CML-CP treated with nilotinib as a second or third-line therapy at “La Raza” National Medical Center.
Results
Of the 161 CML-CP patients included in this analysis, 98.47% were imatinib resistant and 1.53% were imatinib intolerant. The median age of the individuals was 46 years, with a median CML duration of 76 months, and a median duration of prior imatinib therapy of 29.5 months. Overall, 81% of the patients treated with nilotinib achieved a durable complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), which dropped to 71% by excluding patients who had a CCyR at baseline cytogenetic analysis. Moreover, 62% of the individuals achieved a major molecular response (MMR) at 18 months. Among the 161 nilotinib-treated patients; 88.2% were alive and 11.8% died. The median duration of nilotinib therapy for all treated patients was 46 months. The overall survival at 48 months was 92%. Adverse events were mostly moderate, transitory, and manageable.
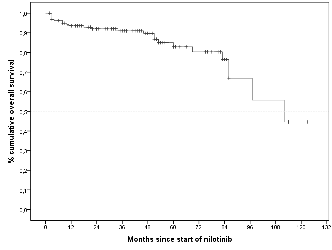
Conclusion
This study shows that nilotinib is effective and can provide favorable long-term benefits for CML-CP patients who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Furthermore, nilotinib had a manageable safety profile.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Therapy, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract: PB1944
Type: Publication Only
Background
The arrival of the second-generation (2ndG) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) improved a significant percentage of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) after imatinib resistance or intolerance, increasing disease survival.
Aims
The primary endpoint of this open study was to determine complete cytigenetic response (CCyR) and major molecular response (MMR) rate in patients treated with nilotinib, at 6 and 12 months respectively. Secondary objectives were to determine the OS, PFS, and EFS, as well as establishing nilotinib safety profile.
Methods
A prospective, open label, single-center study was undertaken to examine the clinical characteristics, cytogenetic and molecular response rates, overall survival, progression-free survival, and event-free survival of patients with CML-CP treated with nilotinib as a second or third-line therapy at “La Raza” National Medical Center.
Results
Of the 161 CML-CP patients included in this analysis, 98.47% were imatinib resistant and 1.53% were imatinib intolerant. The median age of the individuals was 46 years, with a median CML duration of 76 months, and a median duration of prior imatinib therapy of 29.5 months. Overall, 81% of the patients treated with nilotinib achieved a durable complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), which dropped to 71% by excluding patients who had a CCyR at baseline cytogenetic analysis. Moreover, 62% of the individuals achieved a major molecular response (MMR) at 18 months. Among the 161 nilotinib-treated patients; 88.2% were alive and 11.8% died. The median duration of nilotinib therapy for all treated patients was 46 months. The overall survival at 48 months was 92%. Adverse events were mostly moderate, transitory, and manageable.

Conclusion
This study shows that nilotinib is effective and can provide favorable long-term benefits for CML-CP patients who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Furthermore, nilotinib had a manageable safety profile.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Therapy, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor


