
Contributions
Abstract: PB1955
Type: Publication Only
Background
Monitoring BCR-ABL transcript levels in peripheral whole blood (WB) of patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is standard of care in the management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). A successful RT-qPCR reaction requires isolation of high quality RNA and optimization of the input quantity for the conversion of RNA to cDNA for accurate quantification. GeneXpert® BCR-ABL V2¥¥ or Xpert® BCR-ABL Ultra (Ultra), a cartridge-based assay for use on the GeneXpert Instrument system, automates and standardizes the process in less than 2 hours. The Ultra calibration and quantification are standardized by monitoring the input RNA quality and quantity based on the cycle threshold (Ct) of the control gene ABL, which is highly correlated to the input white blood cell (WBC) number in whole blood (WB). Using a lysate prepared from 4mL WB, resulting in an effective WB input volume of 600µL, Ultra reproducibly achieves molecular response (MR) sensitivity to 4.5 logs below baseline (MR 4.5, defined as BCR-ABL1 IS ≤ 0.0032%) per the WHO International Scale (IS). There are, however, clinical situations where the total RNA isolated from high numbers of WBC circulating in the patient’s blood or in bone marrow (BM) samples can overload the Ultra cartridge and other quantitative BCR-ABL assays, requiring subsequent dilution of the sample and retesting.
Aims
In this set of experiments, we sought to define the WBC input limits for Ultra that would predict cartridge overload, and thereby provide guidance regarding when to dilute the patient’s sample in the presence of high WBC.
Methods
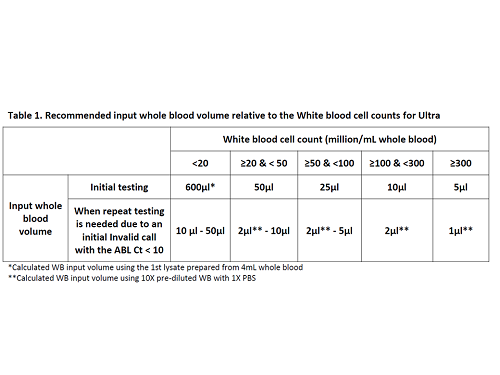
Serial dilutions of high or normal WBC counts (WBCCs) specimens were tested in Ultra to determine the upper and lower WBC input limits corresponded to the valid ABL Ct cutoffs of 10 and 18, respectively. Sample prep procedures were developed to allow using 50µL or lower input volume from WB, BM, or their 1st lysate with or without the WBCCs information, , and validated by testing in CML specimens with various WB or BM input volume, compared to the Qiagen® BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR assay (IS-MMR) (Table 1).
Results
The WBC input number of ~20 million cells/mL WB corresponded to the upper limit, and ~150K cells/mL WB corresponded to the lower limit of the valid ABL Ct range for Ultra, respectively. For CML specimens with WBCCs <20 million cells/mL WB, the standard initial 4mL WB sample input yielded ABL Ct results within acceptable limits. For the WBCCs ≥20 million cells/mL WB, reaching as high as >500 million, sample prep procedures were developed to use 50µL or lower input volume (Table 1). When the WBCC information is not available but with suspicion of high WBC yielding a very viscous 1st lysate that is hard to pipette, a 1st lysate dilution procedure was developed to allow for testing with 50µL or lower WB or BM input volume. However, for the situation where a low input sample volume, for example 50µL, was used but still yielded ABL Ct <10, then an even lower input sample volume (10µL or lower) might be used to re-test the sample (Table 1). This was validated in Ultra by testing CML specimens with various WB or BM input volume and showed high concordance when compared to the Qiagen® IS-MMR.
Conclusion
In summary, sample prep procedures were developed in cases where high WBCC is known, or is suspected, or when repeat testing is needed for Invalids with ABL Ct <10, allowing the use of Ultra with various input sample volume for WB or BM in a wide variety of clinical situations.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Quantitative RT-PCR, Tyrosine kinase
Abstract: PB1955
Type: Publication Only
Background
Monitoring BCR-ABL transcript levels in peripheral whole blood (WB) of patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is standard of care in the management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). A successful RT-qPCR reaction requires isolation of high quality RNA and optimization of the input quantity for the conversion of RNA to cDNA for accurate quantification. GeneXpert® BCR-ABL V2¥¥ or Xpert® BCR-ABL Ultra (Ultra), a cartridge-based assay for use on the GeneXpert Instrument system, automates and standardizes the process in less than 2 hours. The Ultra calibration and quantification are standardized by monitoring the input RNA quality and quantity based on the cycle threshold (Ct) of the control gene ABL, which is highly correlated to the input white blood cell (WBC) number in whole blood (WB). Using a lysate prepared from 4mL WB, resulting in an effective WB input volume of 600µL, Ultra reproducibly achieves molecular response (MR) sensitivity to 4.5 logs below baseline (MR 4.5, defined as BCR-ABL1 IS ≤ 0.0032%) per the WHO International Scale (IS). There are, however, clinical situations where the total RNA isolated from high numbers of WBC circulating in the patient’s blood or in bone marrow (BM) samples can overload the Ultra cartridge and other quantitative BCR-ABL assays, requiring subsequent dilution of the sample and retesting.
Aims
In this set of experiments, we sought to define the WBC input limits for Ultra that would predict cartridge overload, and thereby provide guidance regarding when to dilute the patient’s sample in the presence of high WBC.
Methods
Serial dilutions of high or normal WBC counts (WBCCs) specimens were tested in Ultra to determine the upper and lower WBC input limits corresponded to the valid ABL Ct cutoffs of 10 and 18, respectively. Sample prep procedures were developed to allow using 50µL or lower input volume from WB, BM, or their 1st lysate with or without the WBCCs information, , and validated by testing in CML specimens with various WB or BM input volume, compared to the Qiagen® BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR assay (IS-MMR) (Table 1).
Results
The WBC input number of ~20 million cells/mL WB corresponded to the upper limit, and ~150K cells/mL WB corresponded to the lower limit of the valid ABL Ct range for Ultra, respectively. For CML specimens with WBCCs <20 million cells/mL WB, the standard initial 4mL WB sample input yielded ABL Ct results within acceptable limits. For the WBCCs ≥20 million cells/mL WB, reaching as high as >500 million, sample prep procedures were developed to use 50µL or lower input volume (Table 1). When the WBCC information is not available but with suspicion of high WBC yielding a very viscous 1st lysate that is hard to pipette, a 1st lysate dilution procedure was developed to allow for testing with 50µL or lower WB or BM input volume. However, for the situation where a low input sample volume, for example 50µL, was used but still yielded ABL Ct <10, then an even lower input sample volume (10µL or lower) might be used to re-test the sample (Table 1). This was validated in Ultra by testing CML specimens with various WB or BM input volume and showed high concordance when compared to the Qiagen® IS-MMR.

Conclusion
In summary, sample prep procedures were developed in cases where high WBCC is known, or is suspected, or when repeat testing is needed for Invalids with ABL Ct <10, allowing the use of Ultra with various input sample volume for WB or BM in a wide variety of clinical situations.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Quantitative RT-PCR, Tyrosine kinase


