
Contributions
Abstract: PB1956
Type: Publication Only
Background
The European treatment and outcome study (EUTOS), a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) prognostic score based only on the percentage of basophils in the blood and on spleen size, was formulated and shown to have improved predictive power. The EUTOS score marks a significant advance because it provides better positive predictive values than those obtained with either of the previous scores ( Sokal and Hasford) and its easy application. Moreover, it is specifically based on Imatinib-treated patients, and does not need the use of the other factors that have not been found to affect the response to Imatinib. Serum alpha/beta tryptase 1 is a novel biomarker with a prognostic significance that can be used to differentiate clonal from non clonal causes of basophilia that may affect EUTOS score sensitivity.
Aims
Testing EUTOS score in newly diagnosed CML in chrnoic phase and evaluating the addition of serum alpha beta tryptase one on the score sensitivity in correlation with the established prognostic scores (Sokal and Hasford) and molecular milestones.
Methods
Results
| EUTOST | ||
| rs | P | |
| BCR-ABL at 3 | 0.736* | <0.001* |
| BCR-ABL at 6 | 0.830* | <0.001* |
| Sokal | 0.829* | <0.001* |
| Hasford | 0.715* | <0.001* |
| EUTOS | 0.972* | <0.001* |
The results show the EUTOS score has lower sensitivity and specificity at the cut off 87 compared to 154 suggesting the higher splenic meaurements and basophilia in our study, when applying the higher cut off better predictive power was seen. With the addition of serum tryptase (EUTOST) there is a noticed increase in the sensitivity and specificity compared to EUTOS score ( increased area under ROC curve). This may be explained by higher prevalence of liver disease in our sample (5 schistomiasis and 7 chronic HCV cases).
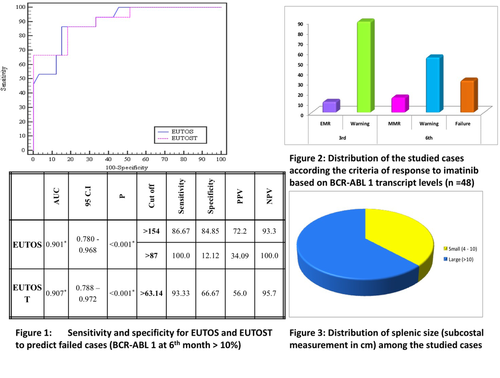
Conclusion
EUTOS score showed high sensitivity when used with a higher cut off value 154 suggesting that the non clonal causes of basophilia and splenomegaly in the Egyptian population play a role in high risk prognostication. Besides identifying the non clonal causes of high EUTOS risk prognostication, applying serum tryptase level has improved its prognostic significance and predictive power.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Molecular
Abstract: PB1956
Type: Publication Only
Background
The European treatment and outcome study (EUTOS), a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) prognostic score based only on the percentage of basophils in the blood and on spleen size, was formulated and shown to have improved predictive power. The EUTOS score marks a significant advance because it provides better positive predictive values than those obtained with either of the previous scores ( Sokal and Hasford) and its easy application. Moreover, it is specifically based on Imatinib-treated patients, and does not need the use of the other factors that have not been found to affect the response to Imatinib. Serum alpha/beta tryptase 1 is a novel biomarker with a prognostic significance that can be used to differentiate clonal from non clonal causes of basophilia that may affect EUTOS score sensitivity.
Aims
Testing EUTOS score in newly diagnosed CML in chrnoic phase and evaluating the addition of serum alpha beta tryptase one on the score sensitivity in correlation with the established prognostic scores (Sokal and Hasford) and molecular milestones.
Methods
Results
| EUTOST | ||
| rs | P | |
| BCR-ABL at 3 | 0.736* | <0.001* |
| BCR-ABL at 6 | 0.830* | <0.001* |
| Sokal | 0.829* | <0.001* |
| Hasford | 0.715* | <0.001* |
| EUTOS | 0.972* | <0.001* |
The results show the EUTOS score has lower sensitivity and specificity at the cut off 87 compared to 154 suggesting the higher splenic meaurements and basophilia in our study, when applying the higher cut off better predictive power was seen. With the addition of serum tryptase (EUTOST) there is a noticed increase in the sensitivity and specificity compared to EUTOS score ( increased area under ROC curve). This may be explained by higher prevalence of liver disease in our sample (5 schistomiasis and 7 chronic HCV cases).

Conclusion
EUTOS score showed high sensitivity when used with a higher cut off value 154 suggesting that the non clonal causes of basophilia and splenomegaly in the Egyptian population play a role in high risk prognostication. Besides identifying the non clonal causes of high EUTOS risk prognostication, applying serum tryptase level has improved its prognostic significance and predictive power.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic myeloid leukemia, Molecular


