
Contributions
Abstract: PB1945
Type: Publication Only
Background
Monitoring BCR-ABL transcript levels in peripheral whole blood (WB) of patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is standard of care in the management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Xpert® BCR-ABL Ultra (Ultra) ¥, a cartridge-based assay for use on the GeneXpert Instrument system, automates and standardizes the RT-qPCR process by integrating RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, target amplification, detection and quantification directly from specimens in less than 2 hours. Using a lysate prepared from 4mL whole blood (WB) resulting in an effective WB input volume of 600µL, Ultra reproducibly achieves molecular response (MR) sensitivity to 4.5 logs below baseline (MR 4.5, defined as BCR-ABL1 IS ≤ 0.0032%) per the WHO International Scale (IS). Sample prep procedures were developed for cases where a high white blood cell count (WBCC) is known or is suspected, or when repeat testing is needed for Invalids with ABL Ct <10, allowing the use of Ultra with various input sample volume for WB or bone barrow (BM) in a wide variety of clinical situations.
Aims
We sought to evaluate the automated Ultra assay with various input sample volume. The Qiagen® psogen BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR manual real-time PCR assay (IS-MMR), a copy number based standardization assay, was compared with Ultra in terms of assay sensitivity, concordance and classification of molecular responses.
Methods
Thirty CML specimens with %BCR-ABL/ABL (IS) between 100% and 0% were evaluated in WB or BM. Based on the EUTOS criteria for method comparison, acceptable concordance between two assays is defined as achieving 2 out of 3 required benchmarks: 1) ≥50% of samples within 2-fold range, 2) ≥75% within 3-fold range, and/or 3) ≥90% within 5-fold range. A linear regression analysis and an overall reporting bias analysis using the Bland-Altman model were evaluated for comparison.
Results
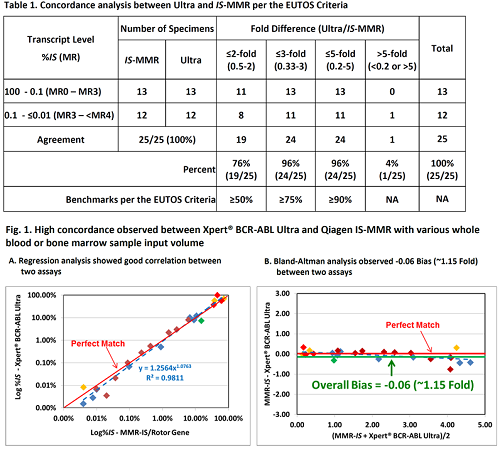
Among 30 CML specimens evaluated, 25 were detected by both assays with 13 identified between 100% IS and 0.1% IS, and 12 between 1% IS and ≤0.01% IS with 100% agreement to the IS-MMR assay (Table 1). Five specimens determined as negative by Ultra were also identified as negative by IS-MMR. The concordance analysis between the two assays exceeded the EUTOS criteria with 19/25 (76%), 24/25 (96%), and 24/25 (96%) falling within a 2-fold range, a 3-fold range and a 5-fold range, respectively (Table 1). Linear regression analysis showed good correlation between two assays (R2=0.9811; N=25) (Fig.1A). In addition, an overall bias of -0.06 (~1.15 fold) was derived using the Bland-Altman model, suggesting high concordance in % IS reporting between two assays across the assay dynamic range (Fig.1B).
Conclusion
Good concordance between Ultra and IS-MMR assays was achieved in WB and BM for all three benchmarks per the EUTOS criteria with good correlation observed in the linear regression analysis and using the Bland-Altman model. The Ultra assay demonstrated the ability to detect BCR-ABL1 transcripts in patients with MR 4.5 or greater reduction, thus achieving sufficient sensitivity for use in monitoring CML patients under TKI treatment.
¥CE-IVD; In vitro diagnostic medical device. May not be available in all countries. Not available in the United States.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Quantitative RT-PCR, Tyrosine kinase
Abstract: PB1945
Type: Publication Only
Background
Monitoring BCR-ABL transcript levels in peripheral whole blood (WB) of patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is standard of care in the management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Xpert® BCR-ABL Ultra (Ultra) ¥, a cartridge-based assay for use on the GeneXpert Instrument system, automates and standardizes the RT-qPCR process by integrating RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, target amplification, detection and quantification directly from specimens in less than 2 hours. Using a lysate prepared from 4mL whole blood (WB) resulting in an effective WB input volume of 600µL, Ultra reproducibly achieves molecular response (MR) sensitivity to 4.5 logs below baseline (MR 4.5, defined as BCR-ABL1 IS ≤ 0.0032%) per the WHO International Scale (IS). Sample prep procedures were developed for cases where a high white blood cell count (WBCC) is known or is suspected, or when repeat testing is needed for Invalids with ABL Ct <10, allowing the use of Ultra with various input sample volume for WB or bone barrow (BM) in a wide variety of clinical situations.
Aims
We sought to evaluate the automated Ultra assay with various input sample volume. The Qiagen® psogen BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR manual real-time PCR assay (IS-MMR), a copy number based standardization assay, was compared with Ultra in terms of assay sensitivity, concordance and classification of molecular responses.
Methods
Thirty CML specimens with %BCR-ABL/ABL (IS) between 100% and 0% were evaluated in WB or BM. Based on the EUTOS criteria for method comparison, acceptable concordance between two assays is defined as achieving 2 out of 3 required benchmarks: 1) ≥50% of samples within 2-fold range, 2) ≥75% within 3-fold range, and/or 3) ≥90% within 5-fold range. A linear regression analysis and an overall reporting bias analysis using the Bland-Altman model were evaluated for comparison.
Results
Among 30 CML specimens evaluated, 25 were detected by both assays with 13 identified between 100% IS and 0.1% IS, and 12 between 1% IS and ≤0.01% IS with 100% agreement to the IS-MMR assay (Table 1). Five specimens determined as negative by Ultra were also identified as negative by IS-MMR. The concordance analysis between the two assays exceeded the EUTOS criteria with 19/25 (76%), 24/25 (96%), and 24/25 (96%) falling within a 2-fold range, a 3-fold range and a 5-fold range, respectively (Table 1). Linear regression analysis showed good correlation between two assays (R2=0.9811; N=25) (Fig.1A). In addition, an overall bias of -0.06 (~1.15 fold) was derived using the Bland-Altman model, suggesting high concordance in % IS reporting between two assays across the assay dynamic range (Fig.1B).

Conclusion
Good concordance between Ultra and IS-MMR assays was achieved in WB and BM for all three benchmarks per the EUTOS criteria with good correlation observed in the linear regression analysis and using the Bland-Altman model. The Ultra assay demonstrated the ability to detect BCR-ABL1 transcripts in patients with MR 4.5 or greater reduction, thus achieving sufficient sensitivity for use in monitoring CML patients under TKI treatment.
¥CE-IVD; In vitro diagnostic medical device. May not be available in all countries. Not available in the United States.
Session topic: 8. Chronic myeloid leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): BCR-ABL, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Quantitative RT-PCR, Tyrosine kinase


