
Contributions
Abstract: PB1843
Type: Publication Only
Background
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is an indolent B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Several prognostic factors such as IGHV mutation status and chromosomal aberrations as trisomy 12, del11q, del13q or del17p have been detected so far. More recent genetic mutations such as BIRC3, SF3B1, NOTCH1 and TP53 stratifies the prognosis and outcome in CLL patients (pts). However all data above reported, because of expensive techniques and experience typical of big laboratories, are not available to all medical centers. Data concerning the presence of IgM, IgG paraprotein and their impact on natural history of CLL pts are controversial and contradictory while more certain seem to be the ones concerning hypogamma/CLL pts.
Aims
The aim of the study is to evaluate the prevalence and the outcome of monoclonal IgM/CLL, IgG/CLL and hypogammaglobulinemia compared with CLL pts with normal immunoglobulin (Ig) levels.
Methods
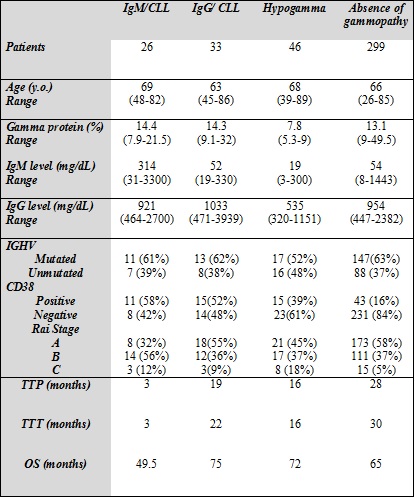
Our center collected from our CLL database 404 pts diagnosed from 1999 to 2017 with a baseline assessment of serum Ig, immunofixation, immunophenotype, chromosomal aberrations and clinical features evaluating time to progression (TTP), time to treatment (TTT) and overall survival (OS).
Results
Among 404 pts who met eligibility criteria, 26 pts had IgM/CLL, 33 pts had IgG/CLL, 46 pts had hypogamma/CLL and 299 showed no evidence of paraprotein. Median IgM level was 314 mg/dL in IgM/CLL, median IgG level was 1033 mg/dL in IgG/CLL, median gamma globulin was 7.8% in hypogamma/CLL. Median age was similar in all the groups. The worst time-dependent parameters such as TTP, TTT and OS were identified in the IgM/CLL group. These data probably reflect a more aggressive disease with more than 68% of pts in an advanced stage at diagnosis (Rai B/C).
Conclusion
This study highlights the frequency of clonal IgM, IgG and hypogammaglobulinemia in CLL patients. Among the 4 groups, IgM/CLL group seems to have the worst outcome which proved to be a negative prognostic marker in newly diagnosed CLL patients.
Session topic: 5. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Immunoglobulin, Monoclonal gammopathy
Abstract: PB1843
Type: Publication Only
Background
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is an indolent B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Several prognostic factors such as IGHV mutation status and chromosomal aberrations as trisomy 12, del11q, del13q or del17p have been detected so far. More recent genetic mutations such as BIRC3, SF3B1, NOTCH1 and TP53 stratifies the prognosis and outcome in CLL patients (pts). However all data above reported, because of expensive techniques and experience typical of big laboratories, are not available to all medical centers. Data concerning the presence of IgM, IgG paraprotein and their impact on natural history of CLL pts are controversial and contradictory while more certain seem to be the ones concerning hypogamma/CLL pts.
Aims
The aim of the study is to evaluate the prevalence and the outcome of monoclonal IgM/CLL, IgG/CLL and hypogammaglobulinemia compared with CLL pts with normal immunoglobulin (Ig) levels.
Methods
Our center collected from our CLL database 404 pts diagnosed from 1999 to 2017 with a baseline assessment of serum Ig, immunofixation, immunophenotype, chromosomal aberrations and clinical features evaluating time to progression (TTP), time to treatment (TTT) and overall survival (OS).
Results
Among 404 pts who met eligibility criteria, 26 pts had IgM/CLL, 33 pts had IgG/CLL, 46 pts had hypogamma/CLL and 299 showed no evidence of paraprotein. Median IgM level was 314 mg/dL in IgM/CLL, median IgG level was 1033 mg/dL in IgG/CLL, median gamma globulin was 7.8% in hypogamma/CLL. Median age was similar in all the groups. The worst time-dependent parameters such as TTP, TTT and OS were identified in the IgM/CLL group. These data probably reflect a more aggressive disease with more than 68% of pts in an advanced stage at diagnosis (Rai B/C).

Conclusion
This study highlights the frequency of clonal IgM, IgG and hypogammaglobulinemia in CLL patients. Among the 4 groups, IgM/CLL group seems to have the worst outcome which proved to be a negative prognostic marker in newly diagnosed CLL patients.
Session topic: 5. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Immunoglobulin, Monoclonal gammopathy


