
Contributions
Abstract: PB1673
Type: Publication Only
Background
PPM1D (wild-type p53-inducible protein phosphatase, WIP1) is a serine hreonine phosphatase involved in negative regulation of cellular stress response pathways, leading to the suppression of p53. PPM1D mutations appeared to have oncogenic properties in many solid cancers, but their role is still unknown in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Aims
The aim of this study is to investigate whether the inhibition of WIP1 (GSK2830371, WIP1i) could increase the sensitivity to MDM2 inhibitor (Nutlin-3a) in order to restore p53 activity and obtain a novel therapeutic strategy for AML patients.
Methods
In vitro WST-1 cell-viability and Annexin V-PI apoptosis assays were performed on AML cell lines (MOLM-13, MV-4-11) and AML primary cells. The number of primary samples’ viable cells was detected by Trypan Blue Exclusion Dye (Sigma-Aldrich). Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and targeted Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) were performed to investigate the mutational state of PPM1D in newly diagnosed AML patients.
Results
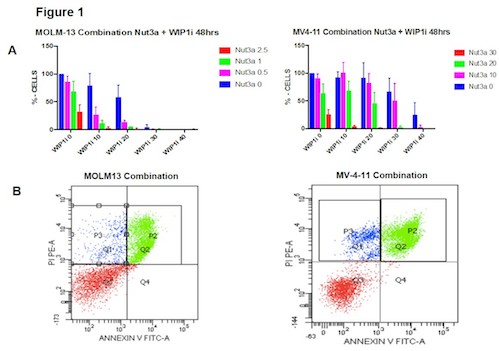
WIP1i and Nut-3a reduced the cell viability as single agent in all the treated cells in a time and dosage-dependent manner. The IC50 values in TP53-wild type (wt) cells showed that MOLM-13 (10 mM) are more sensitive than MV-4-11 (20 mM) to WIP1i. Combination index analyses by WST1-proliferation assay confirmed that WIP1i and Nut-3a had a synergistic effect (C.I.<1) in both cell lines (Figure 1 A). Annexin V/PI staining performed after treatment with different concentration of Nut-3a (0.5 mM for MOLM-13, 15 mM for MV4-11) and WIP1i (10 mM for MOLM-13, 20 mM for MV4-11) demonstrated that the combination significantly increased the number of apoptotic cells in comparison to single agents. In particular, after 48 hours of incubation with Nut-3a and WIP1i as single agents, the percentage of apoptotic cells was 34.4% and 21.4% for MOLM-13 and 17% and 18% for MV-4-11, respectively; while the combination induced 53.1% and 62.3% of apoptotic cells (Figure 1B).
Moreover, we observed a decrease of G2/M phase cells induced by single agents, enhanced by the combination of drugs in both cell lines and, in particular, MV-4-11 were characterized by an increasing percentage of S phase cells allowing us to hypothesize that the apoptotic death induced by the combination of drugs occurs when cells are blocked in S phase.
AML primary cells were also tested by Tripan Blue: we detected that the powerful combination of drugs on bone marrow AML samples at diagnosis was 5 mM of Nut3a plus 20 mM of Wip1i leading to life/death ratio of 0.77 versus 1.5 of single agents. Finally, by WES and targeted-NGS, 7 mutations have been detected in 2/37 and 4/96 patients at diagnosis. One patient harbored a truncating mutation on exon 6 (S468X), confirmed to be gain of function by Western Blot (WB), thus increasing the inhibition of p53; while mutations affecting exon 1 did not reveal any protein overexpression.
Conclusion
We hypothesize for the first time that the pharmacological inhibition of WIP1 could potentiate the sensitivity to MDM2 inhibitors (Nut-3a, e.g. Idasanutlin) in AML patients, suggesting an important role of PPM1D in leukemia. Further studies will help to confirm these preliminary data: in particular, Gene Expression Profiling and WB will identify the proteins playing roles in the biological alterations induced by WIP1i alone and in cooperation with Nut-3a.
Supported by: ELN, AIL, AIRC, project Regione-Università 2010-12 (L. Bolondi), FP7 NGS-PTL project, HARMONY project, Fondazione del Monte BO e RA project.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Drug sensitivity, P53
Abstract: PB1673
Type: Publication Only
Background
PPM1D (wild-type p53-inducible protein phosphatase, WIP1) is a serine hreonine phosphatase involved in negative regulation of cellular stress response pathways, leading to the suppression of p53. PPM1D mutations appeared to have oncogenic properties in many solid cancers, but their role is still unknown in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Aims
The aim of this study is to investigate whether the inhibition of WIP1 (GSK2830371, WIP1i) could increase the sensitivity to MDM2 inhibitor (Nutlin-3a) in order to restore p53 activity and obtain a novel therapeutic strategy for AML patients.
Methods
In vitro WST-1 cell-viability and Annexin V-PI apoptosis assays were performed on AML cell lines (MOLM-13, MV-4-11) and AML primary cells. The number of primary samples’ viable cells was detected by Trypan Blue Exclusion Dye (Sigma-Aldrich). Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and targeted Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) were performed to investigate the mutational state of PPM1D in newly diagnosed AML patients.
Results
WIP1i and Nut-3a reduced the cell viability as single agent in all the treated cells in a time and dosage-dependent manner. The IC50 values in TP53-wild type (wt) cells showed that MOLM-13 (10 mM) are more sensitive than MV-4-11 (20 mM) to WIP1i. Combination index analyses by WST1-proliferation assay confirmed that WIP1i and Nut-3a had a synergistic effect (C.I.<1) in both cell lines (Figure 1 A). Annexin V/PI staining performed after treatment with different concentration of Nut-3a (0.5 mM for MOLM-13, 15 mM for MV4-11) and WIP1i (10 mM for MOLM-13, 20 mM for MV4-11) demonstrated that the combination significantly increased the number of apoptotic cells in comparison to single agents. In particular, after 48 hours of incubation with Nut-3a and WIP1i as single agents, the percentage of apoptotic cells was 34.4% and 21.4% for MOLM-13 and 17% and 18% for MV-4-11, respectively; while the combination induced 53.1% and 62.3% of apoptotic cells (Figure 1B).
Moreover, we observed a decrease of G2/M phase cells induced by single agents, enhanced by the combination of drugs in both cell lines and, in particular, MV-4-11 were characterized by an increasing percentage of S phase cells allowing us to hypothesize that the apoptotic death induced by the combination of drugs occurs when cells are blocked in S phase.
AML primary cells were also tested by Tripan Blue: we detected that the powerful combination of drugs on bone marrow AML samples at diagnosis was 5 mM of Nut3a plus 20 mM of Wip1i leading to life/death ratio of 0.77 versus 1.5 of single agents. Finally, by WES and targeted-NGS, 7 mutations have been detected in 2/37 and 4/96 patients at diagnosis. One patient harbored a truncating mutation on exon 6 (S468X), confirmed to be gain of function by Western Blot (WB), thus increasing the inhibition of p53; while mutations affecting exon 1 did not reveal any protein overexpression.

Conclusion
We hypothesize for the first time that the pharmacological inhibition of WIP1 could potentiate the sensitivity to MDM2 inhibitors (Nut-3a, e.g. Idasanutlin) in AML patients, suggesting an important role of PPM1D in leukemia. Further studies will help to confirm these preliminary data: in particular, Gene Expression Profiling and WB will identify the proteins playing roles in the biological alterations induced by WIP1i alone and in cooperation with Nut-3a.
Supported by: ELN, AIL, AIRC, project Regione-Università 2010-12 (L. Bolondi), FP7 NGS-PTL project, HARMONY project, Fondazione del Monte BO e RA project.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Drug sensitivity, P53


