
Contributions
Abstract: PB1685
Type: Publication Only
Background
The high expression of brain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (BAALC) and ETS-related gene (ERG) has been associated with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) but due to limited prospective studies, their role as prognostic factors is still unclear. We had presented the BAALC & ERG expression data and its impact on survival during the ASH 2017 meeting at San Diego. In that study, the median value was taken as a cut-off to distinguish between high & low BAALC/ERG expressers. So far, there are no standard methods or tools to decide the optimal cut-off points. In this analysis of the same cohort of patients, we generated threshold values for BAALC & ERG cut-off points through P-chain procedure (Bhattacharjee et al. 2017). In brief, BAALC & ERG expression values were measured as continuous variable at baseline, post-induction and post-consolidation blood/marrow samples. Further, lists of p-values were generated from arbitrarily defined threshold values of BAALC & ERG. The lowest p-value was defined as maximum survival difference among these patients to decide the cut-off point for threshold values of BAALC & ERG
Aims
To determine the optimal threshold values of BAALC & ERG expression as a cut-off point to predict the survival outcome
Methods
All patients included in this prospective study (N=149) between March 2012 & February 2015 underwent following investigations: (i) Cytogenetic analyses- by standard techniques of chromosome banding & FISH (ii) Mutation profiling of NPM1, FLT3-ITD and CEBPA by capillary electrophoresis & direct DNA sequencing. Long-range PCR was done to establish MLL-PTD (iii) BAALC & ERG expressions by quantitative real-time PCR assays. Patients received standard induction chemotherapy with daunorubicin 60 mg/m2 for 3 days and cytosine arabinoside 100 mg/m2 for 7 days. Marrow was done 21-28 days after start of chemotherapy. If marrow was in remission, then patients received 3 courses of consolidation therapy with 12-18 gm/m2 of cytosine arabinoside (HiDAC). The statistical analysis was done using R 3.4.0 version
Results
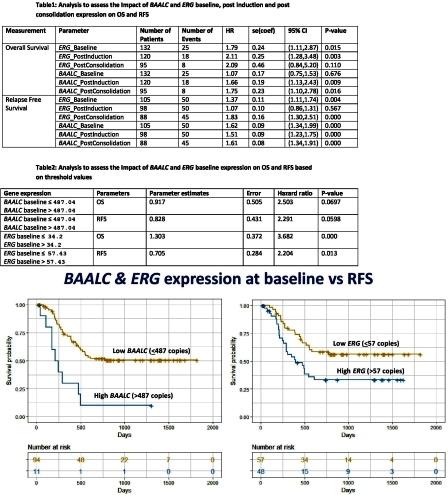
A total of 149 patients were accrued. Of 149 patients, 105 achieved CR after 1 or 2 cycles of chemotherapy. Twenty-seven patients were refractory of which 18 were lost to follow up and hence excluded from OS analysis. Seventeen patients died during induction. The follow-up samples included post induction (N=120) and post-consolidation (N=95) bone marrow. The OS of 132 patients was 36.5% at 2 years. The OS & RFS of 105 patients who achieved CR was 54% and 43.8% respectively. The threshold value (487 BAALC copies/ABL [on OS and RFS], 34 ERG copies/ABL[on OS] and 57 ERG copies/ABL[on RFS]) was used to distinguish high expressers from low expressers. Initially, the baseline, post induction and post-consolidation expression values of BAALC & ERG were observed for their influence on OS & RFS using univariate Cox proportional hazards analyses & results are reported in Table 1. The data revealed that higher BAALC & ERG expression values were significantly hazardous for OS & RFS. Furthermore, threshold values of BAALC & ERG at baseline were calculated and results are reported in Table 2. The RFS of high BAALC vs low BAALC expressers at 2 years was 9% vs 51% (p=0.059), while RFS of high ERG vs low ERG expressers at 2 years was 31% vs 59% (p=0.013) (Figure 1)
Conclusion
This study established the optimal threshold values of BAALC & ERG expression as cut-off points to predict the outcome. The data suggest that high BAALC & ERG expression adversely affects prognosis of AML patients
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Gene expression, Real time PCR, Survival prediction
Abstract: PB1685
Type: Publication Only
Background
The high expression of brain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (BAALC) and ETS-related gene (ERG) has been associated with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) but due to limited prospective studies, their role as prognostic factors is still unclear. We had presented the BAALC & ERG expression data and its impact on survival during the ASH 2017 meeting at San Diego. In that study, the median value was taken as a cut-off to distinguish between high & low BAALC/ERG expressers. So far, there are no standard methods or tools to decide the optimal cut-off points. In this analysis of the same cohort of patients, we generated threshold values for BAALC & ERG cut-off points through P-chain procedure (Bhattacharjee et al. 2017). In brief, BAALC & ERG expression values were measured as continuous variable at baseline, post-induction and post-consolidation blood/marrow samples. Further, lists of p-values were generated from arbitrarily defined threshold values of BAALC & ERG. The lowest p-value was defined as maximum survival difference among these patients to decide the cut-off point for threshold values of BAALC & ERG
Aims
To determine the optimal threshold values of BAALC & ERG expression as a cut-off point to predict the survival outcome
Methods
All patients included in this prospective study (N=149) between March 2012 & February 2015 underwent following investigations: (i) Cytogenetic analyses- by standard techniques of chromosome banding & FISH (ii) Mutation profiling of NPM1, FLT3-ITD and CEBPA by capillary electrophoresis & direct DNA sequencing. Long-range PCR was done to establish MLL-PTD (iii) BAALC & ERG expressions by quantitative real-time PCR assays. Patients received standard induction chemotherapy with daunorubicin 60 mg/m2 for 3 days and cytosine arabinoside 100 mg/m2 for 7 days. Marrow was done 21-28 days after start of chemotherapy. If marrow was in remission, then patients received 3 courses of consolidation therapy with 12-18 gm/m2 of cytosine arabinoside (HiDAC). The statistical analysis was done using R 3.4.0 version
Results
A total of 149 patients were accrued. Of 149 patients, 105 achieved CR after 1 or 2 cycles of chemotherapy. Twenty-seven patients were refractory of which 18 were lost to follow up and hence excluded from OS analysis. Seventeen patients died during induction. The follow-up samples included post induction (N=120) and post-consolidation (N=95) bone marrow. The OS of 132 patients was 36.5% at 2 years. The OS & RFS of 105 patients who achieved CR was 54% and 43.8% respectively. The threshold value (487 BAALC copies/ABL [on OS and RFS], 34 ERG copies/ABL[on OS] and 57 ERG copies/ABL[on RFS]) was used to distinguish high expressers from low expressers. Initially, the baseline, post induction and post-consolidation expression values of BAALC & ERG were observed for their influence on OS & RFS using univariate Cox proportional hazards analyses & results are reported in Table 1. The data revealed that higher BAALC & ERG expression values were significantly hazardous for OS & RFS. Furthermore, threshold values of BAALC & ERG at baseline were calculated and results are reported in Table 2. The RFS of high BAALC vs low BAALC expressers at 2 years was 9% vs 51% (p=0.059), while RFS of high ERG vs low ERG expressers at 2 years was 31% vs 59% (p=0.013) (Figure 1)

Conclusion
This study established the optimal threshold values of BAALC & ERG expression as cut-off points to predict the outcome. The data suggest that high BAALC & ERG expression adversely affects prognosis of AML patients
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Gene expression, Real time PCR, Survival prediction


