
Contributions
Abstract: PB1672
Type: Publication Only
Background
The tumor suppressor TP53 is in average mutated in about 50% of solid cancers, however, over 90% of newly diagnosed AML patients express wild type TP53. This could indicate different levels of dysfunctionality of the p53 protein in AML, dependent on mutational status and genetics. At least 12 different protein isoforms of p53 have been described and we have previously reported that the p53 isoforms p53β and p53γ influence full-length p53 (FLp53) function and therapy response in AML. We found that FLT3-ITD, a poor prognostic marker for survival in AML, correlated with expression of FLp53. In contrast, mutated NPM1, a prognostic marker for longer survival, correlated with p53 isoforms β and γ expression. Chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) is the sole nuclear exporter for several tumor suppressor proteins including p53. CRM1 is frequently overexpressed in AML associated with poor survival. Karyopharm Therapeutics has developed several selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) of proteins dependent of CRM1 for nuclear export, including KPT-330, Selinexor; currently in clinical trials for treatment of AML.
Aims
To study the effect of KPT-330 on FLp53 and p53 isoforms in AML cells.
Methods
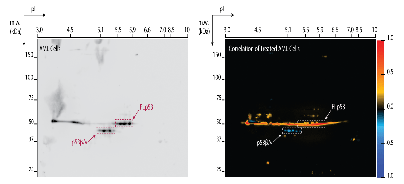
The effect of KPT-330 on p53 isoform protein expression was studied in p53 wild type AML cell lines. The p53 expression patterns were analysed using 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) followed by image analysis using Gel2de software which apply pixel-by-pixel Spearman rank correlation between pixel intensity and external biological parameters. In addition 1-dimensional immunoblot (1D), quantitative PCR (qPCR), immunofluorescence and flow cytometry was performed.
Results
The OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and MV4-11 p53 wild type cell lines were characterized for p53 mRNA isoform profile (FLp53, p53β, p53γ and p53Δ133) by qPCR with the p53 null cell line HL-60 as a negative control. KPT-330 treatment for 24h of OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and MV4-11 increased total p53 protein expression as demonstrated by 1D immunoblotting. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis immunoblotting followed by Gel2de correlation analysis to increasing dosage of KPT-330 resulted in positive correlation to FLp53 expression and negative correlation to p53β/γ isoform expression. However, no significant changes were found on the FLp53 or p53 isoform mRNA levels by qPCR. We found that the p53β protein is degraded following KPT-330 treatment through the proteosomal pathway. We are currently investigating the effect of KPT-330 on the p53Δ133 isoforms and the p53 isoform profile following cellular differentiation caused by 72h KPT-330 treatment, including changes in subcellular localization. Finally, the p53 isoform profiles of primary AML cells before and after KPT-330 in vitro treatment will be studied and correlated towards mutational status and drug sensitivity.
Conclusion
Treatment with KPT-330 influences the p53 isoform expression profile at the protein level, where FLp53 increase and the p53β/γ decreases where p53β is degraded through the proteasome. The response of AML patients towards KPT-330 treatment could be dependent on the p53 isoform profile and be closely related to p53 dysfunction.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): AML, Drug sensitivity, P53
Abstract: PB1672
Type: Publication Only
Background
The tumor suppressor TP53 is in average mutated in about 50% of solid cancers, however, over 90% of newly diagnosed AML patients express wild type TP53. This could indicate different levels of dysfunctionality of the p53 protein in AML, dependent on mutational status and genetics. At least 12 different protein isoforms of p53 have been described and we have previously reported that the p53 isoforms p53β and p53γ influence full-length p53 (FLp53) function and therapy response in AML. We found that FLT3-ITD, a poor prognostic marker for survival in AML, correlated with expression of FLp53. In contrast, mutated NPM1, a prognostic marker for longer survival, correlated with p53 isoforms β and γ expression. Chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) is the sole nuclear exporter for several tumor suppressor proteins including p53. CRM1 is frequently overexpressed in AML associated with poor survival. Karyopharm Therapeutics has developed several selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) of proteins dependent of CRM1 for nuclear export, including KPT-330, Selinexor; currently in clinical trials for treatment of AML.
Aims
To study the effect of KPT-330 on FLp53 and p53 isoforms in AML cells.
Methods
The effect of KPT-330 on p53 isoform protein expression was studied in p53 wild type AML cell lines. The p53 expression patterns were analysed using 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) followed by image analysis using Gel2de software which apply pixel-by-pixel Spearman rank correlation between pixel intensity and external biological parameters. In addition 1-dimensional immunoblot (1D), quantitative PCR (qPCR), immunofluorescence and flow cytometry was performed.
Results
The OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and MV4-11 p53 wild type cell lines were characterized for p53 mRNA isoform profile (FLp53, p53β, p53γ and p53Δ133) by qPCR with the p53 null cell line HL-60 as a negative control. KPT-330 treatment for 24h of OCI-AML3, MOLM-13 and MV4-11 increased total p53 protein expression as demonstrated by 1D immunoblotting. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis immunoblotting followed by Gel2de correlation analysis to increasing dosage of KPT-330 resulted in positive correlation to FLp53 expression and negative correlation to p53β/γ isoform expression. However, no significant changes were found on the FLp53 or p53 isoform mRNA levels by qPCR. We found that the p53β protein is degraded following KPT-330 treatment through the proteosomal pathway. We are currently investigating the effect of KPT-330 on the p53Δ133 isoforms and the p53 isoform profile following cellular differentiation caused by 72h KPT-330 treatment, including changes in subcellular localization. Finally, the p53 isoform profiles of primary AML cells before and after KPT-330 in vitro treatment will be studied and correlated towards mutational status and drug sensitivity.

Conclusion
Treatment with KPT-330 influences the p53 isoform expression profile at the protein level, where FLp53 increase and the p53β/γ decreases where p53β is degraded through the proteasome. The response of AML patients towards KPT-330 treatment could be dependent on the p53 isoform profile and be closely related to p53 dysfunction.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): AML, Drug sensitivity, P53


