
Contributions
Abstract: PB1626
Type: Publication Only
Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a frequent disease in childhood. An analysis of the efficacy of standard programs chemotherapy for ALL treatment is an important part of introducing new methods for treatment in the future.
Aims
Analysis of the results of 25 years treatment period of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children.
Methods
The results of the treatment from February 1993 to January 2018 according to the standard chemotherapy programs ALL-BFM'90/95, ALL IC-BFM2002, ALL IC-BFM2009, INTERFANT’99/06 were analyzed in 370 patients with ALL at the age from 0 to 18 years. The program "Statistica for Windows 8.0" (Statsoft, USA) was used for the above mentioned analysis. The function event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) from the first diagnosis to death for any reason is calculated by the Kaplan-Mayer method. Comparison of survival between groups − by using the Cox's-F-test.
Results
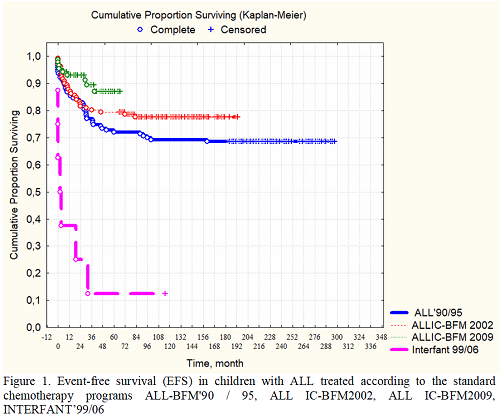
From February 1993 to October 2002 143 (38,65%) patients received treatment based on programs ALL-BFM'90/95 (group 1); from November 2002 to June 2012-131 (35,41%) patients - ALLIC-BFM2002 (group 2); from June 2012-88 (23.78%) patients − ALLIC-BFM2009 (group 3) correspondingly. Children under the age of 1 year (8 persons) from August 2008 were treated according to INTERFANT’99/06 programs (group 4). EFS in group 1 is 68,0% with a median observation time (MO) for 219 months, in group 2 − 77,6% with MO 110 months, in group 3 - 85,2% with MO 38 months, in group 4 − 12,5% of MO 12,5 months (Figure 1). The sstatistically significant improvement of EFS indexes in group 3, the worst results in children under 1 y.o. (p <0,05) was found. The EFS for middle-risk group (MR) patients in the 1st group was 71,0%, in the 2nd group – 83,7%, and in the 3rd group – 90,5%. The EFS for the high-risk group (HR) patients in the 1st group was 50,0%, in the 2nd −55,6% and in the 3rd group – 73,9%. The OS in the entire sample is 78,2%. The relapse of ALL was diagnosed in 53 (14,32%) persons. 34 (9,19%) children died, of which 11 patients (32,35%) – from septic complications before achieving remission of ALL, 19 children (55,88%) – from septic complications in the 1st remission during intensive chemotherapy, 1 HR-group patient - from post-transplant complications, 1 patient in long-lasting remission (160 months) - from the fulminant course of viral hepatitis B, two patients (5,88%) of secondary tumors. Secondary malignancy has been reported in 5 (1,35%) children. Astrocytoma, meningioma, secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have been successfully treated, oligodendroglioma and secondary myelodysplastic syndrome with transformation in to AML was a reason of lethal consequence. 8 persons from the HR-group in the 1st remission had allo-ВМТ (abroad), including 2 patients – for whom allo-BMT was a second therapeutic line for treatment of secondary AML.
Conclusion
The BFM international group's treatment programs of ALL show constantly increasing high effectiveness. Results of treatment in children of the first year of life are unsatisfactory and require improvement of therapeutic approaches. A rare, remote consequence of the treatment of ALL in children is secondary neoplasms, which should be kapt in mind by first-contact doctors and specialists.
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Children
Abstract: PB1626
Type: Publication Only
Background
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a frequent disease in childhood. An analysis of the efficacy of standard programs chemotherapy for ALL treatment is an important part of introducing new methods for treatment in the future.
Aims
Analysis of the results of 25 years treatment period of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children.
Methods
The results of the treatment from February 1993 to January 2018 according to the standard chemotherapy programs ALL-BFM'90/95, ALL IC-BFM2002, ALL IC-BFM2009, INTERFANT’99/06 were analyzed in 370 patients with ALL at the age from 0 to 18 years. The program "Statistica for Windows 8.0" (Statsoft, USA) was used for the above mentioned analysis. The function event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) from the first diagnosis to death for any reason is calculated by the Kaplan-Mayer method. Comparison of survival between groups − by using the Cox's-F-test.
Results
From February 1993 to October 2002 143 (38,65%) patients received treatment based on programs ALL-BFM'90/95 (group 1); from November 2002 to June 2012-131 (35,41%) patients - ALLIC-BFM2002 (group 2); from June 2012-88 (23.78%) patients − ALLIC-BFM2009 (group 3) correspondingly. Children under the age of 1 year (8 persons) from August 2008 were treated according to INTERFANT’99/06 programs (group 4). EFS in group 1 is 68,0% with a median observation time (MO) for 219 months, in group 2 − 77,6% with MO 110 months, in group 3 - 85,2% with MO 38 months, in group 4 − 12,5% of MO 12,5 months (Figure 1). The sstatistically significant improvement of EFS indexes in group 3, the worst results in children under 1 y.o. (p <0,05) was found. The EFS for middle-risk group (MR) patients in the 1st group was 71,0%, in the 2nd group – 83,7%, and in the 3rd group – 90,5%. The EFS for the high-risk group (HR) patients in the 1st group was 50,0%, in the 2nd −55,6% and in the 3rd group – 73,9%. The OS in the entire sample is 78,2%. The relapse of ALL was diagnosed in 53 (14,32%) persons. 34 (9,19%) children died, of which 11 patients (32,35%) – from septic complications before achieving remission of ALL, 19 children (55,88%) – from septic complications in the 1st remission during intensive chemotherapy, 1 HR-group patient - from post-transplant complications, 1 patient in long-lasting remission (160 months) - from the fulminant course of viral hepatitis B, two patients (5,88%) of secondary tumors. Secondary malignancy has been reported in 5 (1,35%) children. Astrocytoma, meningioma, secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have been successfully treated, oligodendroglioma and secondary myelodysplastic syndrome with transformation in to AML was a reason of lethal consequence. 8 persons from the HR-group in the 1st remission had allo-ВМТ (abroad), including 2 patients – for whom allo-BMT was a second therapeutic line for treatment of secondary AML.

Conclusion
The BFM international group's treatment programs of ALL show constantly increasing high effectiveness. Results of treatment in children of the first year of life are unsatisfactory and require improvement of therapeutic approaches. A rare, remote consequence of the treatment of ALL in children is secondary neoplasms, which should be kapt in mind by first-contact doctors and specialists.
Session topic: 2. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia - Clinical
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Children


