
Contributions
Abstract: PB1607
Type: Publication Only
Background
ALL remains one of the most challenging adult malignancies with a high recurrence rate and a low cure rate. The main causes of ALL relapse is a severe disturbance of apoptotic pathways occurs.It was reported that mir-21 is significantly increased in patients with B-ALL, however, the biological function of miR‑21 in B‑ALL remains poorly understood.Cell cycle disorders play an important role in the development of tumor, We used miRanda software to look for possible downstream target genes for miR-21, and found that the cell cycle protein TLK2 3 '-UTR region has a sequence that can be combined with the miR-21 seed region, as well as we found in the Oncomine database that TLK2 has differential expression in B-ALL patients and normal human bone marrow.
Aims
In this study, we detected miR-21 levels in B-ALL cell line (nalm-6) to investigate the mechanism of its oncogenic function
Methods
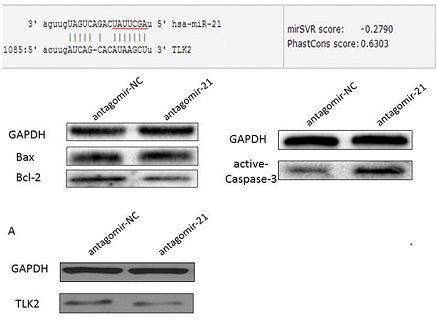
First, we compared miR-21 levels of bone marrow mononuclear cells between patients (n=28) and normal control (n=15),Then, to investigate the miR-21expression in vitro, we detected the miR-21 levels in BCP-ALL cell lines Nalm-6 cells. To evaluate whether miR-21 influence the function of Nalm-6 cells, antagomir-21 was used to knockdown miR-21 and antagomir-NC was used as a control. After incubating antagomir-21or antagomir-NC with Nalm-6 cells for 24h, 48h and 72h, we detected the proliferation by Cell Counting Kit-8, and assessed the apoptosis and cell cycle by flow cytomete, western blot was performed to study the expression analysis of Bcl-2, Bax and active caspase-3 proteins.we used miRanda software looking for the downstream target genes of miR-21, and verified the relation of miR-21 and TLK-2, we detected the qPCR and western blot.
Results
The results showed that the relative expression of miR-21(3.328 ± 0.5156,N=18) in the bone marrow of B-ALL patients was significantly higher than that in normal control (1.174 + 0.1641, N=15), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The expression of miR-21 in nalm-6 cells was about 3.2 times (P<0.01) the control. The proliferation ability of the nalm-6 transfected with antagomir-21 was significantly inhibited.Compared with the antagomir-nc negative control group, the proliferation ability of nalm-6 decreased in 48 hours (16.5 + 0.09287)%, and decreased in 72 hours (18.4 + 0.01479)% (P<0.05 and P<0.001), and the apoptosis rate of nalm-6 cells in the antagomir-21 group was about 2.44 times that of the negative control group (P<0.05). The expression level of bcl-2 protein was positively correlated with miR-21 expression, and miR-21 had no significant effect on Bax expression level.Compared with the control group, the proportion of G1 phase cells (55.75 + + 3.748%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (44.635 + + 1.266%) (P<0.05), while the proportion of S phase cells decreased significantly (41.88 + 2.630) % and (53.675 + 0.8132) % (P<0.05).PCR results showed no significantlly change on TLK2 mRNA levels after transfection with antagomir-21 (P< 0.05), but western Blot results showed a significant decrease in TLK2 protein expression levels in transfected antagomir-21 group (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Overall, in this work ,For the first time, the novel mechanism of miR-21 regulating cycle was explored in the b-all cell line nalm6, and an interesting relationship between mi21 and cell cycle protein TLK2 was introduced initially, providing new ideas for the oncogene role of miR-21 in B‑ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): acute leukemia
Abstract: PB1607
Type: Publication Only
Background
ALL remains one of the most challenging adult malignancies with a high recurrence rate and a low cure rate. The main causes of ALL relapse is a severe disturbance of apoptotic pathways occurs.It was reported that mir-21 is significantly increased in patients with B-ALL, however, the biological function of miR‑21 in B‑ALL remains poorly understood.Cell cycle disorders play an important role in the development of tumor, We used miRanda software to look for possible downstream target genes for miR-21, and found that the cell cycle protein TLK2 3 '-UTR region has a sequence that can be combined with the miR-21 seed region, as well as we found in the Oncomine database that TLK2 has differential expression in B-ALL patients and normal human bone marrow.
Aims
In this study, we detected miR-21 levels in B-ALL cell line (nalm-6) to investigate the mechanism of its oncogenic function
Methods
First, we compared miR-21 levels of bone marrow mononuclear cells between patients (n=28) and normal control (n=15),Then, to investigate the miR-21expression in vitro, we detected the miR-21 levels in BCP-ALL cell lines Nalm-6 cells. To evaluate whether miR-21 influence the function of Nalm-6 cells, antagomir-21 was used to knockdown miR-21 and antagomir-NC was used as a control. After incubating antagomir-21or antagomir-NC with Nalm-6 cells for 24h, 48h and 72h, we detected the proliferation by Cell Counting Kit-8, and assessed the apoptosis and cell cycle by flow cytomete, western blot was performed to study the expression analysis of Bcl-2, Bax and active caspase-3 proteins.we used miRanda software looking for the downstream target genes of miR-21, and verified the relation of miR-21 and TLK-2, we detected the qPCR and western blot.
Results
The results showed that the relative expression of miR-21(3.328 ± 0.5156,N=18) in the bone marrow of B-ALL patients was significantly higher than that in normal control (1.174 + 0.1641, N=15), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The expression of miR-21 in nalm-6 cells was about 3.2 times (P<0.01) the control. The proliferation ability of the nalm-6 transfected with antagomir-21 was significantly inhibited.Compared with the antagomir-nc negative control group, the proliferation ability of nalm-6 decreased in 48 hours (16.5 + 0.09287)%, and decreased in 72 hours (18.4 + 0.01479)% (P<0.05 and P<0.001), and the apoptosis rate of nalm-6 cells in the antagomir-21 group was about 2.44 times that of the negative control group (P<0.05). The expression level of bcl-2 protein was positively correlated with miR-21 expression, and miR-21 had no significant effect on Bax expression level.Compared with the control group, the proportion of G1 phase cells (55.75 + + 3.748%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (44.635 + + 1.266%) (P<0.05), while the proportion of S phase cells decreased significantly (41.88 + 2.630) % and (53.675 + 0.8132) % (P<0.05).PCR results showed no significantlly change on TLK2 mRNA levels after transfection with antagomir-21 (P< 0.05), but western Blot results showed a significant decrease in TLK2 protein expression levels in transfected antagomir-21 group (P<0.05).

Conclusion
Overall, in this work ,For the first time, the novel mechanism of miR-21 regulating cycle was explored in the b-all cell line nalm6, and an interesting relationship between mi21 and cell cycle protein TLK2 was introduced initially, providing new ideas for the oncogene role of miR-21 in B‑ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): acute leukemia


