
Contributions
Abstract: PB1605
Type: Publication Only
Background
MRD-tailored therapy based on pediatric-inspired intensification is a back-bone of the majority of the European study groups in adult ALL. Up to 50-70% of patients from the high risk group defined by specific molecular markers and MRD persistence are being now transplanted from allogeneic donors. The aim of the RALL-study group was to create the protocol that could be easily reproduced in any regional center, to reduce toxicity with the preserving high efficacy. The Russian multicenter ALL-2009 trial defined as non-intensive but non-interruptive approach was conducted since Apr 2009 till Dec 2016 and included 330 Ph-negative ALL pts. OS and disease-free survival (DFS) at 7-years constituted 54,7% and 57% for BCP-ALL and 61% and 68% for T-ALL, respectively. Since Dec 2016 were started new protocol RALL-2016 that based on results of previously ALL-2009 protocol.
Aims
To evaluate the frequency of MRD-persistence and impact IKZF1/NRAS mutation status in patients with de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated by RALL-2016 protocol.
Methods
Taking in consideration the major pitfalls of RALL-2009 (high CR death rate, early CNS relapses in T-ALL, selection in autoHSCT vs chemotherapy comparison, absence of MRD monitoring) we developed a new RALL-2016 protocol. One day high-dose MTX and high-dose ARA-C blocks were eliminated and substituted by 2 months of non-interruptive therapy, L-asparaginase was scheduled for 1 year of treatment instead of 2,5y, 15 intrathecal injections were increased up to 21 mostly while consolidation phase, CR T-ALL pts were brought to randomization after the informed consent: autoHSCT vs no autoHSCT, with the similar further maintenance. All primary bone samples are collected and tested for cytogenetics and molecular markers, all included pts are MRD monitored by flow cytometry in a centralized lab.
Since Dec 2016 till Feb 2018 56 adult Ph-negative ALL pts from 5 centers were included in RALL-2016 protocol: median age 35 y (18-54) (BCP-ALL-34(62%) pts, T-ALL-19(34%), biphenotypic-2(4%)).
Results
Induction results are evaluable in 53 pts: 44(83%) achieved CR, 5 died during induction (9%), 4(8%) was resistant. 15 patients with T-ALL after CR achievement were randomized for chemotherapy or autoHSCT: 7 and 8 pts, respectively. So far 5 of 8 T-ALL pts were transplanted at a median time of 6 months of CR. Long-term results will come in some years.
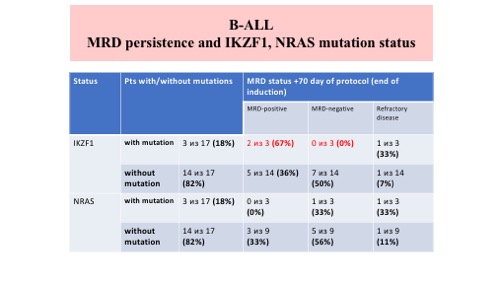
MRD was detected in 14 (48%) out of 29 B‐ALL pts, in 1 (8%) out of 13 T-ALL pts and in 1 out of 2 biphenotypic pts on +70 protocol day (end of induction). MRD testing was performed in 27 B‐ALL patients and 13 T‐ALL patients on +133 and +190 protocol day. All T‐ALL patients were MRD‐negative. 8 (30%) and 7(26%) out of 27 B‐ALL patients were MRD‐positive on +133 and +190 protocol day, respectively.We estimated IKZF1 and NRAS mutation status in 17 pts with B-ALL. We detected IKZF1 and NRAS mutations in 3 (18%) different pts for both. All 3 pts with IKZF1 mutations were MRD-positive on day +70 (2 in CR and 1 with refractory disease). Only 1 pts (with refractory disease) was MRD-positive on day +70 with NRAS mutation, another 2 pts with NRAS mutation were MRD-negative.
Conclusion
MRD was detected more often in B‐ALL pts than T‐ALL pts on +70, +133 and +190 days of RALL‐2016. Tumor clone decline was identified in B‐ALL MRD‐positive patients on +133 comparing to day +70 day. Pts with IKZF1 mutations were characterized MRD persistence after induction. Currently the group of analyzed pts is small and it seems to be reasonable to continue a study of MRD persistence and IKZF1 gene mutation status in pts with B-ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Ikaros, MRD, Treatment
Abstract: PB1605
Type: Publication Only
Background
MRD-tailored therapy based on pediatric-inspired intensification is a back-bone of the majority of the European study groups in adult ALL. Up to 50-70% of patients from the high risk group defined by specific molecular markers and MRD persistence are being now transplanted from allogeneic donors. The aim of the RALL-study group was to create the protocol that could be easily reproduced in any regional center, to reduce toxicity with the preserving high efficacy. The Russian multicenter ALL-2009 trial defined as non-intensive but non-interruptive approach was conducted since Apr 2009 till Dec 2016 and included 330 Ph-negative ALL pts. OS and disease-free survival (DFS) at 7-years constituted 54,7% and 57% for BCP-ALL and 61% and 68% for T-ALL, respectively. Since Dec 2016 were started new protocol RALL-2016 that based on results of previously ALL-2009 protocol.
Aims
To evaluate the frequency of MRD-persistence and impact IKZF1/NRAS mutation status in patients with de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated by RALL-2016 protocol.
Methods
Taking in consideration the major pitfalls of RALL-2009 (high CR death rate, early CNS relapses in T-ALL, selection in autoHSCT vs chemotherapy comparison, absence of MRD monitoring) we developed a new RALL-2016 protocol. One day high-dose MTX and high-dose ARA-C blocks were eliminated and substituted by 2 months of non-interruptive therapy, L-asparaginase was scheduled for 1 year of treatment instead of 2,5y, 15 intrathecal injections were increased up to 21 mostly while consolidation phase, CR T-ALL pts were brought to randomization after the informed consent: autoHSCT vs no autoHSCT, with the similar further maintenance. All primary bone samples are collected and tested for cytogenetics and molecular markers, all included pts are MRD monitored by flow cytometry in a centralized lab.
Since Dec 2016 till Feb 2018 56 adult Ph-negative ALL pts from 5 centers were included in RALL-2016 protocol: median age 35 y (18-54) (BCP-ALL-34(62%) pts, T-ALL-19(34%), biphenotypic-2(4%)).
Results
Induction results are evaluable in 53 pts: 44(83%) achieved CR, 5 died during induction (9%), 4(8%) was resistant. 15 patients with T-ALL after CR achievement were randomized for chemotherapy or autoHSCT: 7 and 8 pts, respectively. So far 5 of 8 T-ALL pts were transplanted at a median time of 6 months of CR. Long-term results will come in some years.
MRD was detected in 14 (48%) out of 29 B‐ALL pts, in 1 (8%) out of 13 T-ALL pts and in 1 out of 2 biphenotypic pts on +70 protocol day (end of induction). MRD testing was performed in 27 B‐ALL patients and 13 T‐ALL patients on +133 and +190 protocol day. All T‐ALL patients were MRD‐negative. 8 (30%) and 7(26%) out of 27 B‐ALL patients were MRD‐positive on +133 and +190 protocol day, respectively.We estimated IKZF1 and NRAS mutation status in 17 pts with B-ALL. We detected IKZF1 and NRAS mutations in 3 (18%) different pts for both. All 3 pts with IKZF1 mutations were MRD-positive on day +70 (2 in CR and 1 with refractory disease). Only 1 pts (with refractory disease) was MRD-positive on day +70 with NRAS mutation, another 2 pts with NRAS mutation were MRD-negative.

Conclusion
MRD was detected more often in B‐ALL pts than T‐ALL pts on +70, +133 and +190 days of RALL‐2016. Tumor clone decline was identified in B‐ALL MRD‐positive patients on +133 comparing to day +70 day. Pts with IKZF1 mutations were characterized MRD persistence after induction. Currently the group of analyzed pts is small and it seems to be reasonable to continue a study of MRD persistence and IKZF1 gene mutation status in pts with B-ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Ikaros, MRD, Treatment


