
Contributions
Abstract: PB1804
Type: Publication Only
Background
Plasmablastic lymphoma (PB) is a low incidence subtype of lymphoma with special clinical features, which is mainly seen in patients with HIV, but not exclusively. Currently, there is no standard of care and prognosis remains poor. Besides, little is known about its clinical behavior in HIV-negative patients.
Aims
Describe the cases of PB in a single center in order to find diferences between HIV-negative and HIV-positive patients.
Methods
9 patients were diagnosed between 2011-2016. Clinical features, treatment and overall survival (OS) were analized both in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients.
Results
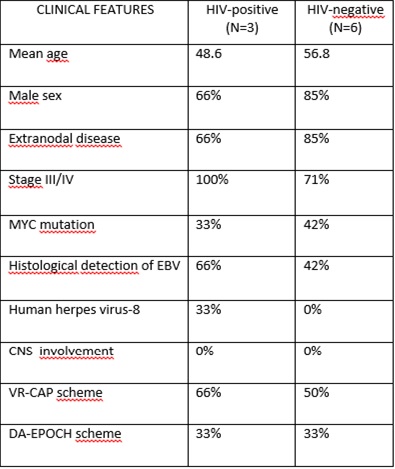
The main clinical features in the group HIV-positive vs. HIV-negative are described in table 1. Median follow-up was 7.23 months. In the HIV-negative group, 3 patients (50%) had a post-transplantation PB (2 patients after bone marrow transplant, and 1 after liver transplant). Most of patients received treatments based on bortezomib added to standard doses of chemotherapy (VR-CAP scheme) or an intensified protocol (DA-EPOCH scheme). Other protocol (Rituximab monotherapy) was used in only one HIV-negative patient with stage II PB. The median OS in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients was 3.5 and 25.3 months respectively. All HIV-positive patients died during the first year, whilst HIV-negative patients had a survival rate of 66% at 1 year and 50% at 2 years.
Conclusion
Among the patients with PB, HIV-negative group tends to share the same clinical features than HIV-positive group, but has a better prognosis in terms of OS even in the post-transplant setting. Both treatments (standard vs. intensified) show to be effective, but it is necessary further studies to determine an optimal treatment protocol. On the other hand, outcome in HIV patients with PB is dismal despite bortezomib based or intensified protocols.
Session topic: 21. Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Abstract: PB1804
Type: Publication Only
Background
Plasmablastic lymphoma (PB) is a low incidence subtype of lymphoma with special clinical features, which is mainly seen in patients with HIV, but not exclusively. Currently, there is no standard of care and prognosis remains poor. Besides, little is known about its clinical behavior in HIV-negative patients.
Aims
Describe the cases of PB in a single center in order to find diferences between HIV-negative and HIV-positive patients.
Methods
9 patients were diagnosed between 2011-2016. Clinical features, treatment and overall survival (OS) were analized both in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients.
Results
The main clinical features in the group HIV-positive vs. HIV-negative are described in table 1. Median follow-up was 7.23 months. In the HIV-negative group, 3 patients (50%) had a post-transplantation PB (2 patients after bone marrow transplant, and 1 after liver transplant). Most of patients received treatments based on bortezomib added to standard doses of chemotherapy (VR-CAP scheme) or an intensified protocol (DA-EPOCH scheme). Other protocol (Rituximab monotherapy) was used in only one HIV-negative patient with stage II PB. The median OS in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients was 3.5 and 25.3 months respectively. All HIV-positive patients died during the first year, whilst HIV-negative patients had a survival rate of 66% at 1 year and 50% at 2 years.

Conclusion
Among the patients with PB, HIV-negative group tends to share the same clinical features than HIV-positive group, but has a better prognosis in terms of OS even in the post-transplant setting. Both treatments (standard vs. intensified) show to be effective, but it is necessary further studies to determine an optimal treatment protocol. On the other hand, outcome in HIV patients with PB is dismal despite bortezomib based or intensified protocols.
Session topic: 21. Aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - Clinical
Keyword(s): Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma


