
Contributions
Abstract: PB2466
Type: Publication Only
Background
Approximately half of patients who develop acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) after an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant will respond to first-line corticosteroid therapy. Steroid-refractory (SR)-aGvHD has high 6‑month mortality rates of up to 80%, particularly when there is gastrointestinal (GI) involvement. There are no approved treatments for SR-aGvHD and success with off-label interventions has been limited and variably reported. There is a high degree of heterogeneity among studies regarding the definitions of SR disease, treatment response, and the timing of assessment of responses. Considering these limitations and the high burden of morbidity in SR-aGvHD, it is important to evaluate the efficacy of treatments currently used in clinical practice, to better understand the factors that may influence clinical outcomes.
Aims
To assess the clinical outcomes of interventions used off-label to treat SR-aGvHD.
Methods
A systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted using MEDLINE and Embase databases to identify studies published in English from January 2006 to August 2017, describing overall survival (OS) or treatment response rates in patients with SR-aGvHD. Any pharmacological intervention(s), including best supportive care, were included; non-pharmacological interventions such as extracorporeal photopheresis and stem cell infusions were excluded.
Results
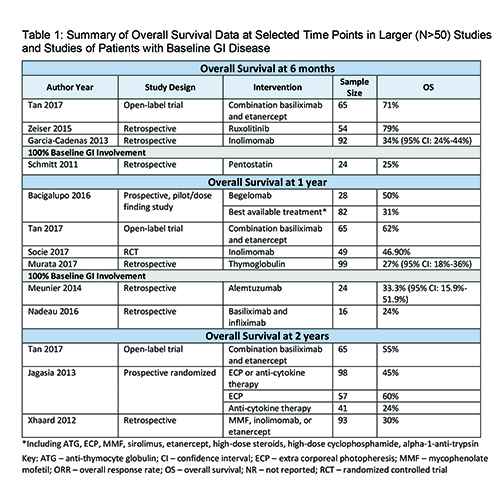
Sixty-one publications describing treatment of patients with SR-aGvHD and reporting relevant clinical outcomes data were included in the SLR. Interventions utilized in these studies included monoclonal antibodies originally licensed in autoimmune disease such as alemtuzumab, basiliximab, infliximab, tocilizumab, vedolizumab, and combinations thereof, as well as other immunosuppressive agents such as etanercept, mycophenolate mofetil, pentostatin, and ruxolitinib. There was a high degree of heterogeneity in study design, patient population and size, and length of follow-up reported among the publications included in the SLR. Most studies were retrospective chart reviews, and all but 3 were conducted in a single country, most frequently the United States. Most studies focused on patients with Grade II-IV SR-aGvHD, but some investigations included patients with less severe disease, and the proportion of patients with GI involvement reported at baseline was heterogeneous. Data for OS were highly variable across the included publications. Among larger (N>50) studies reporting 1-year OS, rates ranged from 27% in patients treated with thymoglobulin to 62% among those given basiliximab and etanercept in combination. OS rates for patients with GI involvement at baseline, described in a few studies with smaller numbers of patients, were generally lower than for the overall population, 25% versus 34%>79% at 6 months, and only 24%>33% at 1 year. Due to limited publications, small numbers of included patients, variability in study designs, and limited reporting of outcomes, no other clear trends for OS could be identified.
Conclusion
A considerable number of potential off-label treatments has been reported for use in patients with SR-aGvHD. Results are highly variable for clinical outcomes including OS, and long-term survival rates remain disappointingly low, particularly for patients with GI involvement. There remains a need for further research to identify effective treatments for patients with SR-aGvHD.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Monoclonal antibody, Survival, Systematic review, Acute graft-versus-host disease
Abstract: PB2466
Type: Publication Only
Background
Approximately half of patients who develop acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) after an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant will respond to first-line corticosteroid therapy. Steroid-refractory (SR)-aGvHD has high 6‑month mortality rates of up to 80%, particularly when there is gastrointestinal (GI) involvement. There are no approved treatments for SR-aGvHD and success with off-label interventions has been limited and variably reported. There is a high degree of heterogeneity among studies regarding the definitions of SR disease, treatment response, and the timing of assessment of responses. Considering these limitations and the high burden of morbidity in SR-aGvHD, it is important to evaluate the efficacy of treatments currently used in clinical practice, to better understand the factors that may influence clinical outcomes.
Aims
To assess the clinical outcomes of interventions used off-label to treat SR-aGvHD.
Methods
A systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted using MEDLINE and Embase databases to identify studies published in English from January 2006 to August 2017, describing overall survival (OS) or treatment response rates in patients with SR-aGvHD. Any pharmacological intervention(s), including best supportive care, were included; non-pharmacological interventions such as extracorporeal photopheresis and stem cell infusions were excluded.
Results
Sixty-one publications describing treatment of patients with SR-aGvHD and reporting relevant clinical outcomes data were included in the SLR. Interventions utilized in these studies included monoclonal antibodies originally licensed in autoimmune disease such as alemtuzumab, basiliximab, infliximab, tocilizumab, vedolizumab, and combinations thereof, as well as other immunosuppressive agents such as etanercept, mycophenolate mofetil, pentostatin, and ruxolitinib. There was a high degree of heterogeneity in study design, patient population and size, and length of follow-up reported among the publications included in the SLR. Most studies were retrospective chart reviews, and all but 3 were conducted in a single country, most frequently the United States. Most studies focused on patients with Grade II-IV SR-aGvHD, but some investigations included patients with less severe disease, and the proportion of patients with GI involvement reported at baseline was heterogeneous. Data for OS were highly variable across the included publications. Among larger (N>50) studies reporting 1-year OS, rates ranged from 27% in patients treated with thymoglobulin to 62% among those given basiliximab and etanercept in combination. OS rates for patients with GI involvement at baseline, described in a few studies with smaller numbers of patients, were generally lower than for the overall population, 25% versus 34%>79% at 6 months, and only 24%>33% at 1 year. Due to limited publications, small numbers of included patients, variability in study designs, and limited reporting of outcomes, no other clear trends for OS could be identified.

Conclusion
A considerable number of potential off-label treatments has been reported for use in patients with SR-aGvHD. Results are highly variable for clinical outcomes including OS, and long-term survival rates remain disappointingly low, particularly for patients with GI involvement. There remains a need for further research to identify effective treatments for patients with SR-aGvHD.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Monoclonal antibody, Survival, Systematic review, Acute graft-versus-host disease


