
Contributions
Abstract: PB2422
Type: Publication Only
Background
Melphalan and Carmustine (BCNU) are key components of the gold standard conditioning regimen (BEAM) for autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (AHCT) in Hodgkin (HL) and Non-Hodgkin (NHL) lymphoma patients. However, given their limited availability over the last decade, we have administered alternative conditioning regimens including intravenous Busulfan (BuEM) instead of BCNU and then, Cyclophosphamide (BEAC) instead of Melphalan. Although BuEM has been well tolerated and highly efficacious compared to the gold standard BEAM regimen, BEAC has not been extensively studied.
Aims
We aimed to determine the safety, toxicity and efficacy of BEAC in AHCT for lymphoma.
Methods
We enrolled consecutive lymphoma patients that received BEAC (Carmustine 300 mg/m2, Etoposide 800 mg/m2, Cytarabine 800 mg/m2, and Cyclophosphamide 140 mg/kg) between 2016 and 2017. As a control group, we studied consecutive lymphoma patients that had been transplanted using BuEM (Busilvex 9.6 mg/kg, Etoposide 800mg/m2 and Melphalan 140mg/m2) in our center between 2011 and 2013.
Results
In total, 33 patients received BEAC and 67 BuEM with no significant difference in baseline characteristics (Table).
| BEAC | BuEM | p-value | |
| Age (years) | 42 (17-64) | 34 (18-65) | 0.146 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma (%) | 64 | 61 | 0.813 |
| Relapsed/refractory disease (%) | 21 | 21 | 0.998 |
| Chemosensitive disease (%) | 69 | 52 | 0.140 |
| Infused CD34 (x106/kg) | 6.3±3.7 | 6.4±3.4 | 0.900 |
Days of neutrophil (p=0.657) and platelet (p=0.572) engraftment or transfusion needs (p=0.114 for red blood cell units and p=0.135 for platelets transfused) were also similar between BEAC and BuEM patients. BEAC resulted in significantly lower toxicity regarding infection rate (51.5% versus 91%, p<0.001) and WHO grade 3-4 mucositis (p<0.001), gastrointestinal (p=0.025) and liver toxicity (p=0.013).
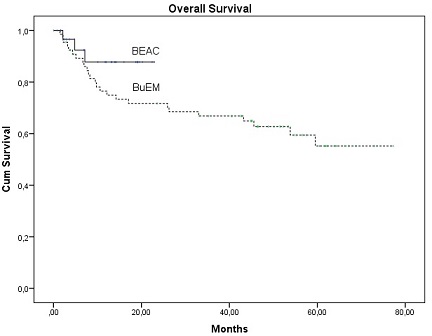
Regarding outcomes, there was no difference in disease status at +100 or at last follow-up. Furthermore, no significant difference was found in the percentage of patients receiving adjuvant therapy post-transplant (p=0.492). Among them, BuEM patients received only radiation; whereas 6 BEAC patients received also adjuvant therapy with brentuximab according to current indications. With a median follow-up of 7.2 (0.8-22.9) months for BEAC and 44.9 (2.3-77.1) for BuEM, relapse mortality was similar between regimens (p=0.626). 1-year overall survival (OS) was 92.4% and 87.6% respectively (Figure, p=0.186). In the multivariate model, OS was significantly associated with diagnosis of HL (p=0.001) and chemosensitive disease (p=0.005).
Conclusion
BEAC resulted in lower toxicity and similar outcomes compared to BuEM regimen in lymphoma patients with similar pre-transplant characteristics. Outcomes were also comparable to our previously published experience with the gold standard BEAM regimen. Therefore, BEAC emerges as a feasible alternative conditioning regimen in AHCT for lymphoma.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Autologous bone marrow transplant, Conditioning, Lymphoma therapy
Abstract: PB2422
Type: Publication Only
Background
Melphalan and Carmustine (BCNU) are key components of the gold standard conditioning regimen (BEAM) for autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (AHCT) in Hodgkin (HL) and Non-Hodgkin (NHL) lymphoma patients. However, given their limited availability over the last decade, we have administered alternative conditioning regimens including intravenous Busulfan (BuEM) instead of BCNU and then, Cyclophosphamide (BEAC) instead of Melphalan. Although BuEM has been well tolerated and highly efficacious compared to the gold standard BEAM regimen, BEAC has not been extensively studied.
Aims
We aimed to determine the safety, toxicity and efficacy of BEAC in AHCT for lymphoma.
Methods
We enrolled consecutive lymphoma patients that received BEAC (Carmustine 300 mg/m2, Etoposide 800 mg/m2, Cytarabine 800 mg/m2, and Cyclophosphamide 140 mg/kg) between 2016 and 2017. As a control group, we studied consecutive lymphoma patients that had been transplanted using BuEM (Busilvex 9.6 mg/kg, Etoposide 800mg/m2 and Melphalan 140mg/m2) in our center between 2011 and 2013.
Results
In total, 33 patients received BEAC and 67 BuEM with no significant difference in baseline characteristics (Table).
| BEAC | BuEM | p-value | |
| Age (years) | 42 (17-64) | 34 (18-65) | 0.146 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma (%) | 64 | 61 | 0.813 |
| Relapsed/refractory disease (%) | 21 | 21 | 0.998 |
| Chemosensitive disease (%) | 69 | 52 | 0.140 |
| Infused CD34 (x106/kg) | 6.3±3.7 | 6.4±3.4 | 0.900 |
Days of neutrophil (p=0.657) and platelet (p=0.572) engraftment or transfusion needs (p=0.114 for red blood cell units and p=0.135 for platelets transfused) were also similar between BEAC and BuEM patients. BEAC resulted in significantly lower toxicity regarding infection rate (51.5% versus 91%, p<0.001) and WHO grade 3-4 mucositis (p<0.001), gastrointestinal (p=0.025) and liver toxicity (p=0.013).
Regarding outcomes, there was no difference in disease status at +100 or at last follow-up. Furthermore, no significant difference was found in the percentage of patients receiving adjuvant therapy post-transplant (p=0.492). Among them, BuEM patients received only radiation; whereas 6 BEAC patients received also adjuvant therapy with brentuximab according to current indications. With a median follow-up of 7.2 (0.8-22.9) months for BEAC and 44.9 (2.3-77.1) for BuEM, relapse mortality was similar between regimens (p=0.626). 1-year overall survival (OS) was 92.4% and 87.6% respectively (Figure, p=0.186). In the multivariate model, OS was significantly associated with diagnosis of HL (p=0.001) and chemosensitive disease (p=0.005).

Conclusion
BEAC resulted in lower toxicity and similar outcomes compared to BuEM regimen in lymphoma patients with similar pre-transplant characteristics. Outcomes were also comparable to our previously published experience with the gold standard BEAM regimen. Therefore, BEAC emerges as a feasible alternative conditioning regimen in AHCT for lymphoma.
Session topic: 23. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Autologous bone marrow transplant, Conditioning, Lymphoma therapy


