
Contributions
Abstract: PB2030
Type: Publication Only
Background
Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia (WM) is a rare lymphoid disorder that represents 1-2% of hematological neoplasms. There is no standard frontline therapy for WM although Rituximab and an alkylating agent are recommended (Buske, Ann Oncol 2013). Bendamustine plus Rituximab (BR) is an effective regimen for relapsed WM (Tedeschi, Leukemia Lymphoma 2015 ; Rummel, Lancet 2013) and is routinely used in our center since 2010.
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy of BR regimen in Wladentrom's Macroglubulinemia compared to RCD
Methods
We conducted a retrospective, monocentric study from January 2010 to January 2018 to assess the efficacy and safety of the BR regimen. Twenty-six patients (pts) ≥ 18 years were analyzed and 23 of them had previously been treated including 13 pts who received the RCD regimen (Rituximab+Cyclophosphomide+Dexamethasone). BR regimen consisted in 375 mg/m2 of rituximab on day 1 and 90 mg/m2 of Bendamustine on days 1 and 2 every 4 weeks, with a maximum of 6 cycles. All patients were considered for response as well as short and long-term complications. Only pts who received BR as salvage treatment were analyzed for survival.
Results
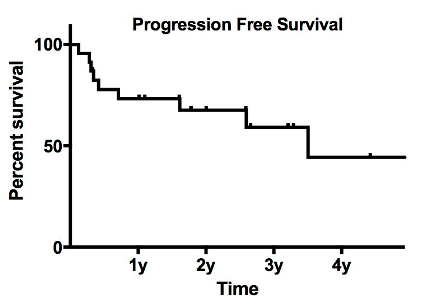
Median age at initiation of BR was 68 (54-84) and 16 pts (62%) were male. At BR initiation, patients were classified according to the IPSSWM score as low (16%) intermediate (42%) and high risk (42%). Treatment criteria for BR therapy were anemia (42%), high tumor burden (30%), thrombocytopenia (19%), B-symptoms (11%), hyper viscosity (7%), neuropathy (3%), and renal failure (3%). Twenty two (84 %) patients completed the planned 6 courses and 89% of them received the full doses. Four patients had to stop for progressive disease (n=1), toxicity (n=2) and death from multi-organ failure 45 days after the first cycle (n=1). Among patients evaluable for response (n=25), the overall response rate (ORR) was 61% including complete response (CR, 19%) and partial response (PR, 42%). When focusing only on patients who received BR as salvage therapy (n = 23), 22 pts were evaluable for response with an ORR of 56% (CR=22%, PR=34%). With a median follow-up of 32 months, median progression free survival (PFS) was 40 months (Fig. 1). Apart from the patient who died early after the first cycle, 3 patients died from progressive disease after 3, 7 and 8 months after the end of treatment. Among patients who received previously RCD, median PFS was 31, 5 months and 23 months for BR and RCD respectively (not statistically significant).
Hematologic and gastrointestinal (mainly nausea) toxicities were the most frequent adverse events with 23% grade 3-4 neutropenia, 22% grade 2 febrile neutropenia, 11% grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia and 3% grade 3-4 anemia. Six patients (23%) had grade 1 nausea. Twenty six percent of pts had prolonged lymphopenia and 15% had hypogammaglobulinemia with infectious complications leading to gammaglobulin infusions. Only 1 pts had prolonged neutropenia 6 months after the completion of BR regimen.
Conclusion
BR regimen is efficient in patients previously treated for WM. Although not significant, there is a trend for longer PFS among patients who received previously RCD. BR regimen is well-tolerated even in elderly patients but frequently involved in long-lasting cytopenias which increases the risk of infection and supports prophylactic measures.
Session topic: 20. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – Clinical
Keyword(s): bendamustine, Rituximab, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Abstract: PB2030
Type: Publication Only
Background
Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia (WM) is a rare lymphoid disorder that represents 1-2% of hematological neoplasms. There is no standard frontline therapy for WM although Rituximab and an alkylating agent are recommended (Buske, Ann Oncol 2013). Bendamustine plus Rituximab (BR) is an effective regimen for relapsed WM (Tedeschi, Leukemia Lymphoma 2015 ; Rummel, Lancet 2013) and is routinely used in our center since 2010.
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy of BR regimen in Wladentrom's Macroglubulinemia compared to RCD
Methods
We conducted a retrospective, monocentric study from January 2010 to January 2018 to assess the efficacy and safety of the BR regimen. Twenty-six patients (pts) ≥ 18 years were analyzed and 23 of them had previously been treated including 13 pts who received the RCD regimen (Rituximab+Cyclophosphomide+Dexamethasone). BR regimen consisted in 375 mg/m2 of rituximab on day 1 and 90 mg/m2 of Bendamustine on days 1 and 2 every 4 weeks, with a maximum of 6 cycles. All patients were considered for response as well as short and long-term complications. Only pts who received BR as salvage treatment were analyzed for survival.
Results
Median age at initiation of BR was 68 (54-84) and 16 pts (62%) were male. At BR initiation, patients were classified according to the IPSSWM score as low (16%) intermediate (42%) and high risk (42%). Treatment criteria for BR therapy were anemia (42%), high tumor burden (30%), thrombocytopenia (19%), B-symptoms (11%), hyper viscosity (7%), neuropathy (3%), and renal failure (3%). Twenty two (84 %) patients completed the planned 6 courses and 89% of them received the full doses. Four patients had to stop for progressive disease (n=1), toxicity (n=2) and death from multi-organ failure 45 days after the first cycle (n=1). Among patients evaluable for response (n=25), the overall response rate (ORR) was 61% including complete response (CR, 19%) and partial response (PR, 42%). When focusing only on patients who received BR as salvage therapy (n = 23), 22 pts were evaluable for response with an ORR of 56% (CR=22%, PR=34%). With a median follow-up of 32 months, median progression free survival (PFS) was 40 months (Fig. 1). Apart from the patient who died early after the first cycle, 3 patients died from progressive disease after 3, 7 and 8 months after the end of treatment. Among patients who received previously RCD, median PFS was 31, 5 months and 23 months for BR and RCD respectively (not statistically significant).
Hematologic and gastrointestinal (mainly nausea) toxicities were the most frequent adverse events with 23% grade 3-4 neutropenia, 22% grade 2 febrile neutropenia, 11% grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia and 3% grade 3-4 anemia. Six patients (23%) had grade 1 nausea. Twenty six percent of pts had prolonged lymphopenia and 15% had hypogammaglobulinemia with infectious complications leading to gammaglobulin infusions. Only 1 pts had prolonged neutropenia 6 months after the completion of BR regimen.

Conclusion
BR regimen is efficient in patients previously treated for WM. Although not significant, there is a trend for longer PFS among patients who received previously RCD. BR regimen is well-tolerated even in elderly patients but frequently involved in long-lasting cytopenias which increases the risk of infection and supports prophylactic measures.
Session topic: 20. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – Clinical
Keyword(s): bendamustine, Rituximab, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia


