
Contributions
Abstract: PB2166
Type: Publication Only
Background
In patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma, carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd56) was superior to bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) in the randomized, phase 3 ENDEAVOR trial for progression-free survival (PFS) (hazard ratio [HR] 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.44–0.65; P<0.0001). In ENDEAVOR, both Kd56 and Vd were planned to be administered until disease progression, while in other clinical trials, e.g., the randomized, phase 3 CASTOR trial comparing Vd with or without daratumumab, Vd was administered for up to 8 cycles (6 months) according to its EU label.
Aims
To estimate how efficacy and safety results for Kd56 vs Vd would have differed if Vd had been given for up to 8 cycles only.
Methods
For the efficacy analysis, published PFS data from the ENDEAVOR (Dimopoulos et al., Lancet Oncol 2017) and CASTOR (Spencer et al., ASH 2017) trials were used in three steps. First, ENDEAVOR Vd patients were matched to average characteristics of CASTOR Vd patients using matching-adjusted indirect comparison methodology. Then, a piecewise Cox regression model was fitted to the matched ENDEAVOR Vd data and re-constructed virtual patient-level CASTOR Vd data that allowed assessing the increased PFS risk due to stopping Vd treatment after 8 cycles vs continuing Vd treatment beyond 8 cycles till progression. Finally, the PFS HR for Kd56 vs Vd from ENDEAVOR was adjusted according to the increased PFS risk for the period beyond 8 cycles. The presented modeling approach has been previously accepted by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the UK (Technology Appraisal Guidance TA457, 2017). For the safety analyses, using most recent data on file, only adverse events (AEs) that occurred during the first 8 cycles plus 30 days of follow-up after the last dose were considered for patients in the Vd arm of the ENDEAVOR trial. Besides the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of grade 3 or more (Gr3+) for Vd 8 cycles, Kd56/Vd 8 cycles exposure-adjusted risk ratios were estimated for Gr3+ TEAEs.
Results
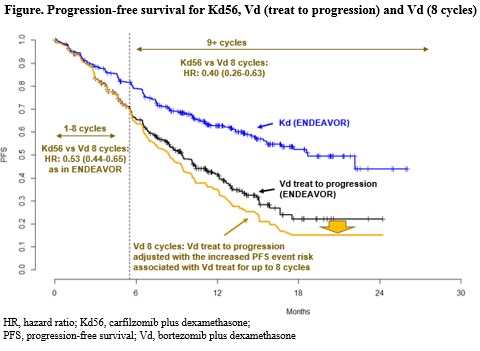
During the first 8 cycles, the risk reduction in PFS for Kd56 vs Vd 8 cycles was equal to that estimated for Kd56 vs Vd in ENDEAVOR. For Vd patients, the increase in PFS risk associated with stopping Vd beyond 8 cycles was estimated to be 32% (HR: 1.32, 95% CI 0.89-1.96, P=0.17). This corresponds to a 60% risk reduction in PFS for Kd56 vs Vd (HR: 0.40; 95% CI 0.26-0.63; P<0.0001) beyond 8 cycles (Figure). The frequency of Gr3+ TEAEs was 81.9% for Kd56, 71.1% for Vd, and was estimated to be 64.5% for Vd 8 cycles. Incidence of Gr3+ peripheral neuropathy was 2.4%, 9.6%, and 8.6% for Kd56, Vd, and Vd 8 cycles, respectively. The exposure-adjusted risk ratios of Kd56 vs Vd 8 cycles were estimated to be 0.61 (95% CI 0.53-0.71) for all Gr3+ TEAEs and 0.08 (95% CI 0.04-0.17) for Gr3+ peripheral neuropathy.
Conclusion
Results from the matched-efficacy analysis indicated that the duration of Vd treatment has a significant impact. If Vd had been given for 8 cycles, the relative decrease in PFS risk with Kd56 would have been larger than that observed in ENDEAVOR where Vd treatment was continued beyond 8 cycles till progression. The approach used in this study adjusts for differences in trial design such as Vd treatment duration, allows to reduce bias, and is a robust methodology. In contrast, indirect treatment comparisons including network meta-analyses that do not adjust for differences in trial design and/or patient populations are susceptible to greater bias.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Multiple Myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor
Abstract: PB2166
Type: Publication Only
Background
In patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma, carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd56) was superior to bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) in the randomized, phase 3 ENDEAVOR trial for progression-free survival (PFS) (hazard ratio [HR] 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.44–0.65; P<0.0001). In ENDEAVOR, both Kd56 and Vd were planned to be administered until disease progression, while in other clinical trials, e.g., the randomized, phase 3 CASTOR trial comparing Vd with or without daratumumab, Vd was administered for up to 8 cycles (6 months) according to its EU label.
Aims
To estimate how efficacy and safety results for Kd56 vs Vd would have differed if Vd had been given for up to 8 cycles only.
Methods
For the efficacy analysis, published PFS data from the ENDEAVOR (Dimopoulos et al., Lancet Oncol 2017) and CASTOR (Spencer et al., ASH 2017) trials were used in three steps. First, ENDEAVOR Vd patients were matched to average characteristics of CASTOR Vd patients using matching-adjusted indirect comparison methodology. Then, a piecewise Cox regression model was fitted to the matched ENDEAVOR Vd data and re-constructed virtual patient-level CASTOR Vd data that allowed assessing the increased PFS risk due to stopping Vd treatment after 8 cycles vs continuing Vd treatment beyond 8 cycles till progression. Finally, the PFS HR for Kd56 vs Vd from ENDEAVOR was adjusted according to the increased PFS risk for the period beyond 8 cycles. The presented modeling approach has been previously accepted by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the UK (Technology Appraisal Guidance TA457, 2017). For the safety analyses, using most recent data on file, only adverse events (AEs) that occurred during the first 8 cycles plus 30 days of follow-up after the last dose were considered for patients in the Vd arm of the ENDEAVOR trial. Besides the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of grade 3 or more (Gr3+) for Vd 8 cycles, Kd56/Vd 8 cycles exposure-adjusted risk ratios were estimated for Gr3+ TEAEs.
Results
During the first 8 cycles, the risk reduction in PFS for Kd56 vs Vd 8 cycles was equal to that estimated for Kd56 vs Vd in ENDEAVOR. For Vd patients, the increase in PFS risk associated with stopping Vd beyond 8 cycles was estimated to be 32% (HR: 1.32, 95% CI 0.89-1.96, P=0.17). This corresponds to a 60% risk reduction in PFS for Kd56 vs Vd (HR: 0.40; 95% CI 0.26-0.63; P<0.0001) beyond 8 cycles (Figure). The frequency of Gr3+ TEAEs was 81.9% for Kd56, 71.1% for Vd, and was estimated to be 64.5% for Vd 8 cycles. Incidence of Gr3+ peripheral neuropathy was 2.4%, 9.6%, and 8.6% for Kd56, Vd, and Vd 8 cycles, respectively. The exposure-adjusted risk ratios of Kd56 vs Vd 8 cycles were estimated to be 0.61 (95% CI 0.53-0.71) for all Gr3+ TEAEs and 0.08 (95% CI 0.04-0.17) for Gr3+ peripheral neuropathy.

Conclusion
Results from the matched-efficacy analysis indicated that the duration of Vd treatment has a significant impact. If Vd had been given for 8 cycles, the relative decrease in PFS risk with Kd56 would have been larger than that observed in ENDEAVOR where Vd treatment was continued beyond 8 cycles till progression. The approach used in this study adjusts for differences in trial design such as Vd treatment duration, allows to reduce bias, and is a robust methodology. In contrast, indirect treatment comparisons including network meta-analyses that do not adjust for differences in trial design and/or patient populations are susceptible to greater bias.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Multiple Myeloma, Proteasome inhibitor


