
Contributions
Abstract: PB1703
Type: Publication Only
Background
AML is a heterogeneous disease in whom cytogenetic (CG) and ages at the moment of diagnosis are the best prognostic variables and both of them are the basis for adapted therapy protocols. However, the morphologic response and MRD status by MFC after chemotherapy are too powerful variables.
Aims
To compare, retrospectively, the powerful of the CG at the moment of diagnosis, morphologic status after induction and changes in mRNA levels of genes WT1 and BAALC between diagnosis and post induction
Methods
We design a retrospective study with AML patients and intermediate CG (ELN 2010 criteria) treated with at least one cycle of intensive chemotherapy and morphologic status evaluated. Patients with all other CG or exitus in induction were excluded. Patients treated in Hospital Dr Negrín between 2004-17 and Hospital Insular Gran Canaria 2010-2016 were included. Morphological response was according to Cheson's criteria with a dichotomous approach: Complete response (CR) or not. Gene expression levels were studied in bone marrow specimen at the diagnosis and after first induction cycle. The study was performed with real time qPCR with Light Cycler 480. The changes in expression level was considered for each patient and was selected a cut-off point of 95% decrease between the two study moments.
Results
Our series consisted of 112 patients, 60.7% males and 39.3% females. Median age was 58 (R 16-77). The overall survival (OS) of the entire cohort hat a median of 26 months (CI95% 19.8-32.3). Distribution for intensification treatment approaches: Allogenic transplant (Alo) 35.8%, high dose chemotherapy, including auto transplant (Chemo) 35.8%, not receive or hipomethilating agents 28.4%, with a median OS: NR, 24 m and 12 m respectively with p <0.001.
Global rate CR after first cycle was 62.5%. Median OS according to morphologic response was 38 m for CR (CI95% 4.8-71.1) and 16 m for non CR group (CI95% 8.4-23.5) with p=0.005
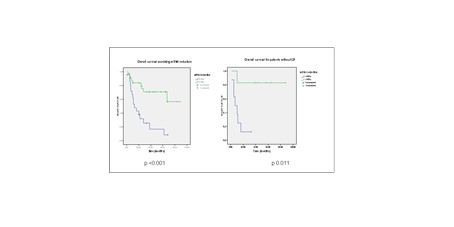
Total number of patients with gene expression study between diagnosis and post induction was 54 with 58 lost cases. Of valid cases, 60% achieved a decrease greater than 95% in their levels of expression. Median OS was 13 m (CI95% 6.2-19.7) and Non reached (NR) for those with better response with p <0.001. In patients without CR, the gene expression study was available for 14 cases. However 43% achieved a greater than 95% reduction in their levels. The median OS for those patients was NR and 7 m (CI95% 0.7-13.9) for low decliners with p=0.011. Considering intensification treatment, patients with greater decrease in expression, the median OS was NR for Alo and Chemo group, without significant difference, meanwhile in those with low decrease in gene expression the median OS for Alo group was 38 m (CI95% 17.1-58,8) and 11 m (CI95% 8.4-13.5) for chemo but without significance.
Conclusion
1) A decrease greater 95% in expression levels of genes WT1 or BAALC between diagnosis and post induction chemotherapy, was able to identify patients with greater probability of survival than the morphological response achieved after induction and the CG at diagnosis. Even in patients without CR, was able to separate patients into groups with significant survivals difference.
2) A decrease greater 95% in expression levels of genes WT1 or BAALC allowed identify patients with a good sensibility to chemotherapy and special good prognosis (>65% OS) in whom intensification with Alo would not provide benefit.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Gene expression, Minimal residual disease (MRD)
Abstract: PB1703
Type: Publication Only
Background
AML is a heterogeneous disease in whom cytogenetic (CG) and ages at the moment of diagnosis are the best prognostic variables and both of them are the basis for adapted therapy protocols. However, the morphologic response and MRD status by MFC after chemotherapy are too powerful variables.
Aims
To compare, retrospectively, the powerful of the CG at the moment of diagnosis, morphologic status after induction and changes in mRNA levels of genes WT1 and BAALC between diagnosis and post induction
Methods
We design a retrospective study with AML patients and intermediate CG (ELN 2010 criteria) treated with at least one cycle of intensive chemotherapy and morphologic status evaluated. Patients with all other CG or exitus in induction were excluded. Patients treated in Hospital Dr Negrín between 2004-17 and Hospital Insular Gran Canaria 2010-2016 were included. Morphological response was according to Cheson's criteria with a dichotomous approach: Complete response (CR) or not. Gene expression levels were studied in bone marrow specimen at the diagnosis and after first induction cycle. The study was performed with real time qPCR with Light Cycler 480. The changes in expression level was considered for each patient and was selected a cut-off point of 95% decrease between the two study moments.
Results
Our series consisted of 112 patients, 60.7% males and 39.3% females. Median age was 58 (R 16-77). The overall survival (OS) of the entire cohort hat a median of 26 months (CI95% 19.8-32.3). Distribution for intensification treatment approaches: Allogenic transplant (Alo) 35.8%, high dose chemotherapy, including auto transplant (Chemo) 35.8%, not receive or hipomethilating agents 28.4%, with a median OS: NR, 24 m and 12 m respectively with p <0.001.
Global rate CR after first cycle was 62.5%. Median OS according to morphologic response was 38 m for CR (CI95% 4.8-71.1) and 16 m for non CR group (CI95% 8.4-23.5) with p=0.005
Total number of patients with gene expression study between diagnosis and post induction was 54 with 58 lost cases. Of valid cases, 60% achieved a decrease greater than 95% in their levels of expression. Median OS was 13 m (CI95% 6.2-19.7) and Non reached (NR) for those with better response with p <0.001. In patients without CR, the gene expression study was available for 14 cases. However 43% achieved a greater than 95% reduction in their levels. The median OS for those patients was NR and 7 m (CI95% 0.7-13.9) for low decliners with p=0.011. Considering intensification treatment, patients with greater decrease in expression, the median OS was NR for Alo and Chemo group, without significant difference, meanwhile in those with low decrease in gene expression the median OS for Alo group was 38 m (CI95% 17.1-58,8) and 11 m (CI95% 8.4-13.5) for chemo but without significance.

Conclusion
1) A decrease greater 95% in expression levels of genes WT1 or BAALC between diagnosis and post induction chemotherapy, was able to identify patients with greater probability of survival than the morphological response achieved after induction and the CG at diagnosis. Even in patients without CR, was able to separate patients into groups with significant survivals difference.
2) A decrease greater 95% in expression levels of genes WT1 or BAALC allowed identify patients with a good sensibility to chemotherapy and special good prognosis (>65% OS) in whom intensification with Alo would not provide benefit.
Session topic: 3. Acute myeloid leukemia - Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Gene expression, Minimal residual disease (MRD)


