
Contributions
Abstract: PB1618
Type: Publication Only
Background
Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) is a master transcriptional factor of regulatory T-cells (Tregs). Recent studies have shown that FOXP3 expression is associated with growth inhibition of various solid tumor cells such as gastric cancer and ovarian cancer. However, the role of FOXP3 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells is not known. It was also reported that NOTCH signaling promoted the expression of FOXP3 in Tregs. However, little is known about the effects of FOXP3 expression on NOTCH expression in T-ALL cells.
Aims
To elucidate the effect of FOXP3 knockdown on the proliferation and NOTCH expression of T-ALL cells.
Methods
The two T-ALL cell lines Jurkat and KOPT-K1, harboring an activating NOTCH1 mutation, were transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA) against FOXP3 or control siRNA using an electroporation system. Cell growth was assessed in five-day cultures with a colorimetric assay. The relative cell number was determined based on optical density measured using an ELISA plate reader and expressed as the percentage of the mean absorbance value normalized to that of control cells. Cell morphology was examined in cytospin preparations from the cells cultured for 6 hours. They were stained with Wright’s stain and observed under a microscope. The effects of FOXP3 knockdown on mRNA expression were examined by quantitative RT-PCR.
Results
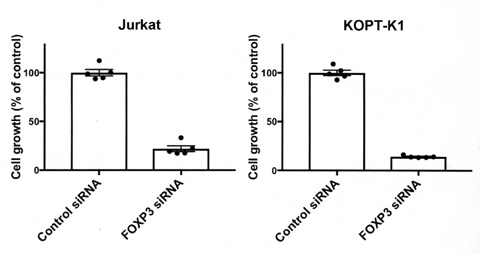
Transfection with FOXP3 siRNA significantly reduced the FOXP3 expression to 29% and 45% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. By FOXP3 knockdown, cell growth was significantly suppressed to 22% and 14% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. Observation of cytospin preparations indicated that apoptotic cells with nuclear condensation and apoptotic bodies appeared in both cells. The expression of NOTCH1 was significantly reduced to 56% and 60% compared with that of control in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. HES1 expression was significantly reduced to 52% and 34% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively.
Conclusion
FOXP3 knockdown suppressed the growth and induced apoptosis of the two T-ALL cell lines. This suggests that FOXP3 supports the growth of T-ALL cells although this can not be generalized in T-ALL because we just examined only two cell lines. We think that the role of FOXP3 on cell growth can diverge in different types of cancer. FOXP3 knockdown downregulated NOTCH1 expression in T-ALL cells. The observed growth suppression can be partly related to the downregulation of NOTCH1 signaling because NOTCH1 plays a role in the growth of some T-ALL cells. The underlying molecular mechanisms and the biological significance of the effect need to be further elucidated. Then, FOXP3 may be a potential therapeutic target in T-ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Notch, RNA interference (RNAi)
Abstract: PB1618
Type: Publication Only
Background
Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) is a master transcriptional factor of regulatory T-cells (Tregs). Recent studies have shown that FOXP3 expression is associated with growth inhibition of various solid tumor cells such as gastric cancer and ovarian cancer. However, the role of FOXP3 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells is not known. It was also reported that NOTCH signaling promoted the expression of FOXP3 in Tregs. However, little is known about the effects of FOXP3 expression on NOTCH expression in T-ALL cells.
Aims
To elucidate the effect of FOXP3 knockdown on the proliferation and NOTCH expression of T-ALL cells.
Methods
The two T-ALL cell lines Jurkat and KOPT-K1, harboring an activating NOTCH1 mutation, were transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA) against FOXP3 or control siRNA using an electroporation system. Cell growth was assessed in five-day cultures with a colorimetric assay. The relative cell number was determined based on optical density measured using an ELISA plate reader and expressed as the percentage of the mean absorbance value normalized to that of control cells. Cell morphology was examined in cytospin preparations from the cells cultured for 6 hours. They were stained with Wright’s stain and observed under a microscope. The effects of FOXP3 knockdown on mRNA expression were examined by quantitative RT-PCR.
Results
Transfection with FOXP3 siRNA significantly reduced the FOXP3 expression to 29% and 45% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. By FOXP3 knockdown, cell growth was significantly suppressed to 22% and 14% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. Observation of cytospin preparations indicated that apoptotic cells with nuclear condensation and apoptotic bodies appeared in both cells. The expression of NOTCH1 was significantly reduced to 56% and 60% compared with that of control in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively. HES1 expression was significantly reduced to 52% and 34% in Jurkat and KOPT-K1 cells, respectively.

Conclusion
FOXP3 knockdown suppressed the growth and induced apoptosis of the two T-ALL cell lines. This suggests that FOXP3 supports the growth of T-ALL cells although this can not be generalized in T-ALL because we just examined only two cell lines. We think that the role of FOXP3 on cell growth can diverge in different types of cancer. FOXP3 knockdown downregulated NOTCH1 expression in T-ALL cells. The observed growth suppression can be partly related to the downregulation of NOTCH1 signaling because NOTCH1 plays a role in the growth of some T-ALL cells. The underlying molecular mechanisms and the biological significance of the effect need to be further elucidated. Then, FOXP3 may be a potential therapeutic target in T-ALL.
Session topic: 1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Notch, RNA interference (RNAi)


