
Contributions
Abstract: S1576
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:15 - 08:30
Location: Room A7
Background
The development of precision medicine requires powerful biomarkers mainly based on the mechanism of drug action to predict and improve response to treatment. Although genomic technologies have significantly increased the numbers of potential biomarkers in MM, most of them have not been subsequently validated at protein level. The low protein concentration obtained after CD138+ selection has limited the quantification of proteins in MM so far. We have recently reported the usefulness of a new technique based on capillary nanoimmunoassay (CNIA) for protein expression quantification from purified CD138+ plasma cells (PC).
Aims
To investigate the prognostic impact of the expression of proteins involved in the anti-myeloma mechanism of bortezomib (V), lenalidomide (R) and dexamethasone (D), together with the expression of cyclin D1 and D2 in a large cohort of CD138+ PC samples from MM patients treated with VRD.
Methods
Bone marrow aspirates from 213 newly diagnosed MM patients treated according to the Spanish clinical trial VRD-GEM followed by ASCT conditioned with Mel-200 vs BuMel, were included in the study. Plasma cells were purified by anti-CD138 magnetic microbeads using the AutoMACs separation system (purity was above 85%) and next, were stored in RLT+ buffer at -800C. Proteins were extracted by a method previously reported by our group. Total protein quantification and protein expression were analyzed by the CNIA methodology (ProteinSimple, WES™ system). Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated for each protein. Survival curves were plotted by means of the Kaplan-Meier method and statistical significance was tested using the log-rank test. The Cutoff Finder software was used to obtain the optimal cutoff.
Results
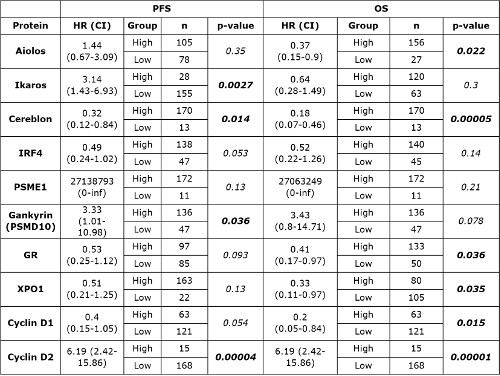
After the analysis of total protein content, 194 MM samples of 213 (91%) fulfilled the quantity and quality requirements. Among the 10 proteins analyzed the expression of aiolos, cereblon, ikaros, gankyrin, proteasome activator subunit 1 (PSME1), glucocorticoid receptor (GR), exportin 1 (XPO1) and interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) were detected in about 90% of MM samples. On the contrary, cyclin D1 and cyclin D2 proteins were detected in only 43% and 25% of MM samples, respectively. Regarding cytogenetic risk, IRF4, PSME1 GR and XPO1 proteins were significantly upregulated in low risk MM patients, while cyclin D2 was upregulated in high risk MM (p<0.05). At the time of study, the median follow-up for survivors was 25.5 months (range, 14.1-42.1). Kaplan-Meier survival analyses showed that high levels of ikaros and gankyrin were associated with shorter PFS (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively), while high level of cereblon was associated with longer PFS (p < 0.05). Regarding OS, high protein levels of aiolos, cereblon, GR and XPO1 were associated with better prognosis (see table below). Interestingly, patients with high cyclin D2 protein levels had a significantly shorter PFS and OS (p < 0.0001), while those with high level of cyclin D1 exhibited longer OS (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
The expression level of proteins involved in the mechanism of action of bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone, discriminate prognosis in MM patients.
High level of cyclin D2 protein identified MM patients with poor outcome.
The quantification of protein expression by CNIA platform can be a useful tool for biomarker identification in the era of precision medicine.
Funding: This study has been funded by ISCIII, project “PI16/01074” (co-funded by FEDER), and the GRS grant “GRS1654/A/17”.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Prediction, Protein Expression
Abstract: S1576
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:15 - 08:30
Location: Room A7
Background
The development of precision medicine requires powerful biomarkers mainly based on the mechanism of drug action to predict and improve response to treatment. Although genomic technologies have significantly increased the numbers of potential biomarkers in MM, most of them have not been subsequently validated at protein level. The low protein concentration obtained after CD138+ selection has limited the quantification of proteins in MM so far. We have recently reported the usefulness of a new technique based on capillary nanoimmunoassay (CNIA) for protein expression quantification from purified CD138+ plasma cells (PC).
Aims
To investigate the prognostic impact of the expression of proteins involved in the anti-myeloma mechanism of bortezomib (V), lenalidomide (R) and dexamethasone (D), together with the expression of cyclin D1 and D2 in a large cohort of CD138+ PC samples from MM patients treated with VRD.
Methods
Bone marrow aspirates from 213 newly diagnosed MM patients treated according to the Spanish clinical trial VRD-GEM followed by ASCT conditioned with Mel-200 vs BuMel, were included in the study. Plasma cells were purified by anti-CD138 magnetic microbeads using the AutoMACs separation system (purity was above 85%) and next, were stored in RLT+ buffer at -800C. Proteins were extracted by a method previously reported by our group. Total protein quantification and protein expression were analyzed by the CNIA methodology (ProteinSimple, WES™ system). Progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated for each protein. Survival curves were plotted by means of the Kaplan-Meier method and statistical significance was tested using the log-rank test. The Cutoff Finder software was used to obtain the optimal cutoff.
Results
After the analysis of total protein content, 194 MM samples of 213 (91%) fulfilled the quantity and quality requirements. Among the 10 proteins analyzed the expression of aiolos, cereblon, ikaros, gankyrin, proteasome activator subunit 1 (PSME1), glucocorticoid receptor (GR), exportin 1 (XPO1) and interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) were detected in about 90% of MM samples. On the contrary, cyclin D1 and cyclin D2 proteins were detected in only 43% and 25% of MM samples, respectively. Regarding cytogenetic risk, IRF4, PSME1 GR and XPO1 proteins were significantly upregulated in low risk MM patients, while cyclin D2 was upregulated in high risk MM (p<0.05). At the time of study, the median follow-up for survivors was 25.5 months (range, 14.1-42.1). Kaplan-Meier survival analyses showed that high levels of ikaros and gankyrin were associated with shorter PFS (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively), while high level of cereblon was associated with longer PFS (p < 0.05). Regarding OS, high protein levels of aiolos, cereblon, GR and XPO1 were associated with better prognosis (see table below). Interestingly, patients with high cyclin D2 protein levels had a significantly shorter PFS and OS (p < 0.0001), while those with high level of cyclin D1 exhibited longer OS (p < 0.05).

Conclusion
The expression level of proteins involved in the mechanism of action of bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone, discriminate prognosis in MM patients.
High level of cyclin D2 protein identified MM patients with poor outcome.
The quantification of protein expression by CNIA platform can be a useful tool for biomarker identification in the era of precision medicine.
Funding: This study has been funded by ISCIII, project “PI16/01074” (co-funded by FEDER), and the GRS grant “GRS1654/A/17”.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): Myeloma, Prediction, Protein Expression


