
Contributions
Abstract: S855
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 16:45 - 17:00
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
Patients (pts) with relapsed, refractory (R/R) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a typical survival of 2 years despite the recent approval of active novel agents including lenalidomide, ibrutinib and acalabrutinib. Although ibrutinib monotherapy provides impressive efficacy (overall response rate (ORR) 68% (complete response (CR) 21%)) and tolerability in R/R MCL, primary resistance (i.e. lack of response) occurs in 30% and most pts ultimately relapse, representing a cohort with clear unmet need. Documented responses post-ibrutinib are seen in <1/3 of patients and median overall survival (OS) following cessation of ibrutinib 4 months. Venetoclax is a potent, selective and orally bioavailable BCL2 inhibitor. A phase 1 first-in-human trial of venetoclax (n=106) included 28 Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi)-naïve MCL pts; toxicity was minimal and an impressive ORR 75% (21% CR) was demonstrated.
Aims
There are no data regarding venetoclax efficacy in R/R MCL outside these initial data and none available in the post-BTKi setting. We provide data from the UK compassionate use programme.
Methods
20 R/R MCL pts who had failed BTKi received venetoclax monotherapy in UK and Ireland between 03/2016-02/2018. Data at diagnosis and relapse were collected from hospital records by the treating physician. Response to and duration of BTKi and reasons for stopping BTKi were collected. Baseline data collected prior to venetoclax included LDH, performance status, extranodal disease/sites, stage, histological subtype, and KI67%.
Results
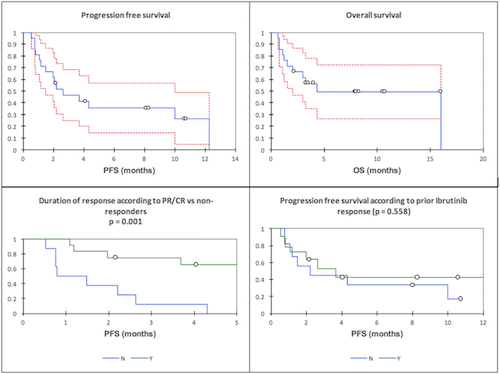
The median age was 69 years (range 43-84) with 86% male gender. Pts received a median of 3 prior lines (range 2-5). 38% received a Rituximab(R)-Maxi-CHOP/Ara-C-based induction, and 29% were consolidated with ASCT in 1st remission. Others pts received chemotherapy (fludarabine or CHOP-based) +/- R 1st line. At relapse (2nd or subsequent line), all but 1 pt received BTKi (ibrutinib (n=17), ibrutinib with DLI (n=1), tirabrutinib (n=2)). The ORR to BTKi was 55% (CR 15%), with a median progression free survival (PFS) of 4.8 months (95% CI 3.1-29.3 months). 9/20 pts did not respond to BKTi. 18 pts stopped BTKi due to disease progression and 2 for toxicity. Following BTKi, 4 pts relapsed with documented blastoid MCL and the median Ki67% was 45% (n=11). ECOG PS 0-1 (n=11) and PS 2-3 (n=9) were noted. LDH was raised in 75%. ORR to venetoclax monotherapy in the 20 BKTi exposure pts was 60% (20% CR). The median PFS was 2.6 months (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.5-9.9 months) and the median OS was 4.3 months (95% CI 2.1-16.0 months). The median duration of response was not reached (FIG). Although the ORR to venetoclax varied according to prior BTKi response (primary resistance to BKTi (n=9): ORR 44.4% vs response to prior BTKi (n=11): ORR 72.7%) differed (p=0.198)), this did not translate to an improved PFS. (FIG). There were no cases of clinical tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) and 5 asymptomatic biochemical TLS. Venetoclax was otherwise well tolerated. 3 pts required dose reductions (800 mg to 600 mg od) due to adverse events (AEs) (Grade (G) 2 fatigue (n=1), G2 diarrhoea (n=2)). There were 13 AEs reported including pneumonia (G3; n=3), sepsis (G4; n=2), fatigue (G2; n=2) and diarrhoea (G2; n=2). 11 pts have died; 9 from PD and 2 from the combination of PD and infection.
Conclusion
In summary, venetoclax monotherapy provided an ORR of 60% with 20% CR in a poor-risk R/R BTKi-resistant MCL. Venetoclax was relatively non-toxic and provides scope for rational novel combination therapies in this setting.
Session topic: 20. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – Clinical
Keyword(s): BCL2, Mantle cell lymphoma
Abstract: S855
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 16:45 - 17:00
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
Patients (pts) with relapsed, refractory (R/R) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a typical survival of 2 years despite the recent approval of active novel agents including lenalidomide, ibrutinib and acalabrutinib. Although ibrutinib monotherapy provides impressive efficacy (overall response rate (ORR) 68% (complete response (CR) 21%)) and tolerability in R/R MCL, primary resistance (i.e. lack of response) occurs in 30% and most pts ultimately relapse, representing a cohort with clear unmet need. Documented responses post-ibrutinib are seen in <1/3 of patients and median overall survival (OS) following cessation of ibrutinib 4 months. Venetoclax is a potent, selective and orally bioavailable BCL2 inhibitor. A phase 1 first-in-human trial of venetoclax (n=106) included 28 Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi)-naïve MCL pts; toxicity was minimal and an impressive ORR 75% (21% CR) was demonstrated.
Aims
There are no data regarding venetoclax efficacy in R/R MCL outside these initial data and none available in the post-BTKi setting. We provide data from the UK compassionate use programme.
Methods
20 R/R MCL pts who had failed BTKi received venetoclax monotherapy in UK and Ireland between 03/2016-02/2018. Data at diagnosis and relapse were collected from hospital records by the treating physician. Response to and duration of BTKi and reasons for stopping BTKi were collected. Baseline data collected prior to venetoclax included LDH, performance status, extranodal disease/sites, stage, histological subtype, and KI67%.
Results
The median age was 69 years (range 43-84) with 86% male gender. Pts received a median of 3 prior lines (range 2-5). 38% received a Rituximab(R)-Maxi-CHOP/Ara-C-based induction, and 29% were consolidated with ASCT in 1st remission. Others pts received chemotherapy (fludarabine or CHOP-based) +/- R 1st line. At relapse (2nd or subsequent line), all but 1 pt received BTKi (ibrutinib (n=17), ibrutinib with DLI (n=1), tirabrutinib (n=2)). The ORR to BTKi was 55% (CR 15%), with a median progression free survival (PFS) of 4.8 months (95% CI 3.1-29.3 months). 9/20 pts did not respond to BKTi. 18 pts stopped BTKi due to disease progression and 2 for toxicity. Following BTKi, 4 pts relapsed with documented blastoid MCL and the median Ki67% was 45% (n=11). ECOG PS 0-1 (n=11) and PS 2-3 (n=9) were noted. LDH was raised in 75%. ORR to venetoclax monotherapy in the 20 BKTi exposure pts was 60% (20% CR). The median PFS was 2.6 months (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.5-9.9 months) and the median OS was 4.3 months (95% CI 2.1-16.0 months). The median duration of response was not reached (FIG). Although the ORR to venetoclax varied according to prior BTKi response (primary resistance to BKTi (n=9): ORR 44.4% vs response to prior BTKi (n=11): ORR 72.7%) differed (p=0.198)), this did not translate to an improved PFS. (FIG). There were no cases of clinical tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) and 5 asymptomatic biochemical TLS. Venetoclax was otherwise well tolerated. 3 pts required dose reductions (800 mg to 600 mg od) due to adverse events (AEs) (Grade (G) 2 fatigue (n=1), G2 diarrhoea (n=2)). There were 13 AEs reported including pneumonia (G3; n=3), sepsis (G4; n=2), fatigue (G2; n=2) and diarrhoea (G2; n=2). 11 pts have died; 9 from PD and 2 from the combination of PD and infection.

Conclusion
In summary, venetoclax monotherapy provided an ORR of 60% with 20% CR in a poor-risk R/R BTKi-resistant MCL. Venetoclax was relatively non-toxic and provides scope for rational novel combination therapies in this setting.
Session topic: 20. Indolent Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – Clinical
Keyword(s): BCL2, Mantle cell lymphoma


