
Contributions
Abstract: S820
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 12:00 - 12:15
Location: Room K1
Background
The interaction between hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and the bone marrow (BM) niche is best described for CXCR4 and its ligand, SDF-1/CXCL12. Therefore, CXCR4 antagonists like AMD3100 are used in the clinic for the collection of HSCs from patients who fail to mobilize HSCs in response to G-CSF. However, their effects are short-lived, limiting the collection time to only 4-6h and 30 % of the patients fail to collect the required amounts of CD34+ cells for autologous transplantation. We have previously demonstrated that the PIM1 kinase regulates CXCR4 receptor recycling and surface expression on HSCs. Consequently, deletion of Pim1 results in reduced migration of HSCs towards a CXCL12 gradient and reduced homing to the BM.
Aims
We aimed to improve HSC mobilization by combining CXCR4 and PIM inhibition and demonstrate that the mobilized stem cells are capable of homing to the bone marrow niche.
Methods
In order to study the mobilization efficiency in the murine model, mice were treated with AMD3100 alone or in combination with LGB321, a novel pan-PIM inhibitor. The mice were sacrificed at various timepoints and peripheral blood (PB) was isolated. The percentage of HSCs was then determined by flow cytometry and colony-formation assays. To rule out long-term effects of PIM inhibition on stem cell engraftment, we transplanted mobilized cells into lethally irradiated recipient mice. The mechanism of HSC mobilization was studied in isolated HSC and stroma populations by analyzing mRNA levels of Cxcl-12 and surface expression of CXCR4
Results
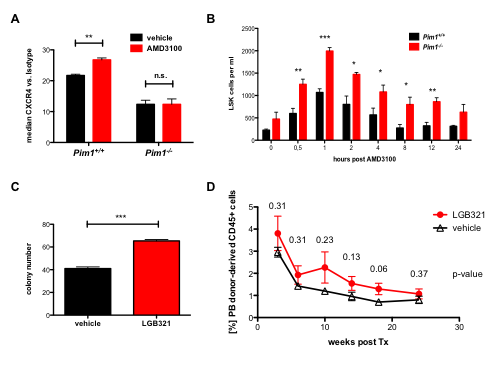
We found that CXCR4 inhibition using AMD3100 leads to a compensatory upregulation of CXCR4 surface expression on total BM cells as well as HSCs. This effect can be reverted by deficiency or inhibition of PIM1 (Figure 1A). As a consequence, HSC mobilization using AMD3100 is strongly enhanced and prolonged in Pim1-deficient mice compared to WT animals (Figure 1B). Likewise, treatment of WT animals with AMD3100 in combination with LGB321 leads to increased and prolonged HSC mobilization compared to animals treated only with AMD3100. Moreover, colony formation potential of LGB321/ AMD3100-mobilized LSKs was significantly elevated compared to AMD3100-only mobilized cells (Figure 1C). LSK cells mobilized with LGB321 and AMD3100 showed long-term engraftment (>1% donor-derived cells in 5/8 mice after week 18) after transplantation into lethally irradiated recipient mice. These cells even exhibited a strong trend towards higher repopulating capacity compared to LSK cells mobilized only with AMD3100 (Figure 1D). Besides the downregulation of CXCR4 on HSCs, we found that the Cxcl-12 expression as well as CXCR4 surface expression in CXCL12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells is dramatically decreased in Pim1-deficient mice, which even further increases the mobilization capacity of Pim1-deficient mice.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate, that PIM1 inhibition counteracts the compensatory upregulation of the CXCR4 receptor on HSCs after AMD3100 treatment and decreases CXCL12 levels within the bone marrow niche. Furthermore, PIM inhibition does not interfere with stem cell engraftment in the murine model. Therefore, targeting PIM kinases in combination with CXCR4 inhibition could improve the collection of stem cells in patients at risk for poor mobilization.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): AMD3100, HSC, Pim-1, Stem cell mobilization
Abstract: S820
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 12:00 - 12:15
Location: Room K1
Background
The interaction between hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and the bone marrow (BM) niche is best described for CXCR4 and its ligand, SDF-1/CXCL12. Therefore, CXCR4 antagonists like AMD3100 are used in the clinic for the collection of HSCs from patients who fail to mobilize HSCs in response to G-CSF. However, their effects are short-lived, limiting the collection time to only 4-6h and 30 % of the patients fail to collect the required amounts of CD34+ cells for autologous transplantation. We have previously demonstrated that the PIM1 kinase regulates CXCR4 receptor recycling and surface expression on HSCs. Consequently, deletion of Pim1 results in reduced migration of HSCs towards a CXCL12 gradient and reduced homing to the BM.
Aims
We aimed to improve HSC mobilization by combining CXCR4 and PIM inhibition and demonstrate that the mobilized stem cells are capable of homing to the bone marrow niche.
Methods
In order to study the mobilization efficiency in the murine model, mice were treated with AMD3100 alone or in combination with LGB321, a novel pan-PIM inhibitor. The mice were sacrificed at various timepoints and peripheral blood (PB) was isolated. The percentage of HSCs was then determined by flow cytometry and colony-formation assays. To rule out long-term effects of PIM inhibition on stem cell engraftment, we transplanted mobilized cells into lethally irradiated recipient mice. The mechanism of HSC mobilization was studied in isolated HSC and stroma populations by analyzing mRNA levels of Cxcl-12 and surface expression of CXCR4
Results
We found that CXCR4 inhibition using AMD3100 leads to a compensatory upregulation of CXCR4 surface expression on total BM cells as well as HSCs. This effect can be reverted by deficiency or inhibition of PIM1 (Figure 1A). As a consequence, HSC mobilization using AMD3100 is strongly enhanced and prolonged in Pim1-deficient mice compared to WT animals (Figure 1B). Likewise, treatment of WT animals with AMD3100 in combination with LGB321 leads to increased and prolonged HSC mobilization compared to animals treated only with AMD3100. Moreover, colony formation potential of LGB321/ AMD3100-mobilized LSKs was significantly elevated compared to AMD3100-only mobilized cells (Figure 1C). LSK cells mobilized with LGB321 and AMD3100 showed long-term engraftment (>1% donor-derived cells in 5/8 mice after week 18) after transplantation into lethally irradiated recipient mice. These cells even exhibited a strong trend towards higher repopulating capacity compared to LSK cells mobilized only with AMD3100 (Figure 1D). Besides the downregulation of CXCR4 on HSCs, we found that the Cxcl-12 expression as well as CXCR4 surface expression in CXCL12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells is dramatically decreased in Pim1-deficient mice, which even further increases the mobilization capacity of Pim1-deficient mice.

Conclusion
Our findings indicate, that PIM1 inhibition counteracts the compensatory upregulation of the CXCR4 receptor on HSCs after AMD3100 treatment and decreases CXCL12 levels within the bone marrow niche. Furthermore, PIM inhibition does not interfere with stem cell engraftment in the murine model. Therefore, targeting PIM kinases in combination with CXCR4 inhibition could improve the collection of stem cells in patients at risk for poor mobilization.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Experimental
Keyword(s): AMD3100, HSC, Pim-1, Stem cell mobilization


