
Contributions
Abstract: S133
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Room A7
Background
JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib (rux) reduces spleen size and myelofibrosis (MF)-related symptoms and improves survival, but nearly half of responders relapse within 5 years. Treatment options for MF after failure of rux are scant. Inhibition of PI3Kδ and AKT signaling reduces proliferation and clonogenic potential of JAK2-mutated cell lines, and synergizes with rux in patient samples. Umbralisib, a novel next-generation PI3K inhibitor highly selective for the delta isoform was well-tolerated in clinical trials in lymphoid malignancies. We tested the combination of umbralisib and rux in previously rux-treated MF.
Aims
1. To assess safety of the combination of umbralisib + ruxolitinib
2. To evaluate preliminary efficacy of the combination in MF
Methods
This study has three stages. In Escalation Stage (ES) 1, 12 MF subjects, on a stable ruxolitinib dose for ≥8 weeks with a suboptimal or lost response at the highest tolerated dose were treated with once daily doses of umbralisib in a 3+3 design. In ES2, 4 additional MF patients were treated with the umbralisib dose from ES1 and escalating rux doses to complete the safety analysis. In the Expansion Stage, 7 additional MF patients continued their stable dose of rux, and umbralisib was added at the ES1 recommended dose. Adverse events (AEs) were graded by NCI-CTCAE v4.03. Efficacy was assessed by IWG-MRT consensus response criteria. Symptoms were assessed by the MPN symptom assessment form total symptom score (MPN-SAF TSS).
Results
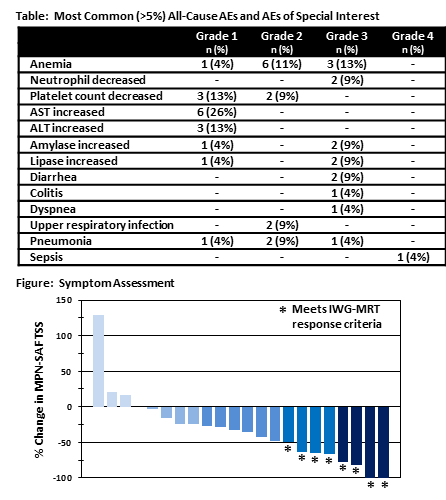
All 23 subjects enrolled as of the data cutoff on December 31, 2017 were included in safety analyses. Median number of cycles was 5 (range 1-29). Median age at study entry was 67 years; 61% were male; 91% had ECOG PS<2. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of asymptomatic pancreatic enzyme elevation were experienced by one subject each treated with 10mg or 15mg rux + 800mg umbralisib in ES1. No DLTs were seen in subjects at lower umbralisib doses. Thus, all subsequently enrolled subjects were treated with 600mg umbralisib. The most common Gr3/4 AE was anemia reported by 3 patients (see Table). Two patients each experienced Gr 3 diarrhea, neutropenia, and elevations in serum amylase and lipase. There was one case of colitis in a patient with chronic intermittent diarrhea. Three subjects were removed from study due to AEs, 1 to pursue HSCT; 10 remained on study. Of 23 response-evaluable rux-experienced MF subjects, 2 achieved CR after 5 and 15 cycles. An additional 11 met IWG-MRT criteria for clinical improvement based on anemia, spleen and/or symptoms responses. Mean improvement in hemoglobin was 1.2g/dL (range 0-3.7g/dL). Mean reduction in TSS was 33% (see Figure).
Conclusion
Enhancing suppression of pathologic JAK-STAT signaling with PI3Kδ inhibition represents a viable treatment strategy for MF patients with inadequate or lost response to ruxolitinib. The addition of umbralisib to rux was well-tolerated. Pancreatic enzyme elevation was not seen with doses of umbralisib <800mg. Significant LFT abnormalities were absent and colitis uncommon, distinguishing umbralisib from other PI3Kδ inhibitors. Hematologic AEs were largely unrelated to drug and occurred in the context of extensive marrow fibrosis and disease progression. An IWG-MRT response (CR, PR or CI) was observed in 56.5% of rux-experienced MF subjects. Two patients who had lost response after >1y of ruxolitinib monotherapy achieved CR on study, demonstrating that umbralisib can augment and resurrect a response in subjects with suboptimal or lost response to ruxolitinib alone.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myelofibrosis, Phase I, PI3K, Ruxolitinib
Abstract: S133
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 12:30 - 12:45
Location: Room A7
Background
JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib (rux) reduces spleen size and myelofibrosis (MF)-related symptoms and improves survival, but nearly half of responders relapse within 5 years. Treatment options for MF after failure of rux are scant. Inhibition of PI3Kδ and AKT signaling reduces proliferation and clonogenic potential of JAK2-mutated cell lines, and synergizes with rux in patient samples. Umbralisib, a novel next-generation PI3K inhibitor highly selective for the delta isoform was well-tolerated in clinical trials in lymphoid malignancies. We tested the combination of umbralisib and rux in previously rux-treated MF.
Aims
1. To assess safety of the combination of umbralisib + ruxolitinib
2. To evaluate preliminary efficacy of the combination in MF
Methods
This study has three stages. In Escalation Stage (ES) 1, 12 MF subjects, on a stable ruxolitinib dose for ≥8 weeks with a suboptimal or lost response at the highest tolerated dose were treated with once daily doses of umbralisib in a 3+3 design. In ES2, 4 additional MF patients were treated with the umbralisib dose from ES1 and escalating rux doses to complete the safety analysis. In the Expansion Stage, 7 additional MF patients continued their stable dose of rux, and umbralisib was added at the ES1 recommended dose. Adverse events (AEs) were graded by NCI-CTCAE v4.03. Efficacy was assessed by IWG-MRT consensus response criteria. Symptoms were assessed by the MPN symptom assessment form total symptom score (MPN-SAF TSS).
Results
All 23 subjects enrolled as of the data cutoff on December 31, 2017 were included in safety analyses. Median number of cycles was 5 (range 1-29). Median age at study entry was 67 years; 61% were male; 91% had ECOG PS<2. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of asymptomatic pancreatic enzyme elevation were experienced by one subject each treated with 10mg or 15mg rux + 800mg umbralisib in ES1. No DLTs were seen in subjects at lower umbralisib doses. Thus, all subsequently enrolled subjects were treated with 600mg umbralisib. The most common Gr3/4 AE was anemia reported by 3 patients (see Table). Two patients each experienced Gr 3 diarrhea, neutropenia, and elevations in serum amylase and lipase. There was one case of colitis in a patient with chronic intermittent diarrhea. Three subjects were removed from study due to AEs, 1 to pursue HSCT; 10 remained on study. Of 23 response-evaluable rux-experienced MF subjects, 2 achieved CR after 5 and 15 cycles. An additional 11 met IWG-MRT criteria for clinical improvement based on anemia, spleen and/or symptoms responses. Mean improvement in hemoglobin was 1.2g/dL (range 0-3.7g/dL). Mean reduction in TSS was 33% (see Figure).

Conclusion
Enhancing suppression of pathologic JAK-STAT signaling with PI3Kδ inhibition represents a viable treatment strategy for MF patients with inadequate or lost response to ruxolitinib. The addition of umbralisib to rux was well-tolerated. Pancreatic enzyme elevation was not seen with doses of umbralisib <800mg. Significant LFT abnormalities were absent and colitis uncommon, distinguishing umbralisib from other PI3Kδ inhibitors. Hematologic AEs were largely unrelated to drug and occurred in the context of extensive marrow fibrosis and disease progression. An IWG-MRT response (CR, PR or CI) was observed in 56.5% of rux-experienced MF subjects. Two patients who had lost response after >1y of ruxolitinib monotherapy achieved CR on study, demonstrating that umbralisib can augment and resurrect a response in subjects with suboptimal or lost response to ruxolitinib alone.
Session topic: 16. Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Keyword(s): Myelofibrosis, Phase I, PI3K, Ruxolitinib


