
Contributions
Abstract: S105
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 11:30 - 11:45
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
The phase 3 GIMEMA-MMY-3006 study comparing bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone (VTD) versus thalidomide-dexamethasone (TD) as induction therapy before, and consolidation after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) provided demonstration of prolonged PFS, but not OS, for patients randomized to the VTD arm (Cavo M et al, Lancet 2010; Blood 2012). Based on superior rates of high quality response and PFS, a bortezomib-based triplet is currently considered as the standard induction therapy for ASCT-eligible MM patients. However, no data from prospective phase 3 trials have so far shown an OS benefit from incorporation of bortezomib and an immunomodulatory into ASCT.
Aims
The current analysis was aimed at evaluating long term results of the GIMEMA-MMY-3006 study.
Methods
Overall, 474 patients were included in the trial, and of these 236 were randomized to VTD and 238 to the TD arm. Median follow-up for surviving patients was 92.8 months (IQR: 59.6-123.0). Analyses were performed on an intention-to-treat basis.
Results
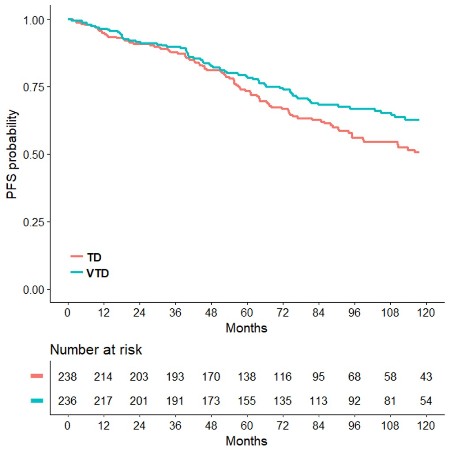
Median PFS was 56.5 months for patients randomly assigned to the VTD arm, and 41.3 months for those in the TD group (HR=0.66, p<0.001). PFS benefit with VTD was seen for patients with ISS stage II-III (HR=0.68, p=0.007) and ISS stage I (HR=0.60, p=0.005), as well as for those with t(4;14) and/or del(17p) positivity (HR=0.45, p<0.001) and negativity (HR=0.66, p=0.003). Median OS was not yet reached in the VTD arm and was 118.6 months in the TD arm (HR=0.71, p=0.024), representing a 29% reduction in the risk of death with incorporation of VTD into double ASCT (Figure 1). Estimated rates of OS at 93 months were 67.6% and 58.5%, respectively. Superior OS benefit with VTD over TD was retained across prespecified subgroups of patients with both high-risk and low-risk disease, including those with ISS stages III (HR=0.52, p=0.056), ISS stage I (HR=0.56, p=0.033) and cytogenetics by FISH. In particular, VTD significantly prolonged the OS of patients with both t(4;14) and/or del(17p) positivity (HR=0.57, p=0.031) and negativity (HR=0.66, p=0.034). On multivariate Cox regression analysis, randomization to VTD was an independent factor predicting for prolonged PFS (HR=0.62, p<0.001) and OS (HR=0.61, p=0.001). Additional disease-related variables with a favorable impact on PFS and OS were absence of t(4;14) and/or del(17p) (HR=0.50, p<0.001; HR=0.49, p<0.001), and β2-microglobulin <3.5 mg/L (HR=0.60, p<0.001; HR=0.51, p<0.001). Further analyses of PFS2, time to second anti-MM therapy, and second primary malignancies will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusion
With an extended median follow-up of 7.6 years, a persistent PFS benefit with incorporation of VTD into ASCT was confirmed. Moreover, a longer OS from primary randomization to VTD versus TD was demonstrated in the overall population, as well as in subgroups of patients with high risk and low risk MM.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, bortezomib, Myeloma
Abstract: S105
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Friday, June 15, 2018 from 11:30 - 11:45
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
The phase 3 GIMEMA-MMY-3006 study comparing bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone (VTD) versus thalidomide-dexamethasone (TD) as induction therapy before, and consolidation after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) provided demonstration of prolonged PFS, but not OS, for patients randomized to the VTD arm (Cavo M et al, Lancet 2010; Blood 2012). Based on superior rates of high quality response and PFS, a bortezomib-based triplet is currently considered as the standard induction therapy for ASCT-eligible MM patients. However, no data from prospective phase 3 trials have so far shown an OS benefit from incorporation of bortezomib and an immunomodulatory into ASCT.
Aims
The current analysis was aimed at evaluating long term results of the GIMEMA-MMY-3006 study.
Methods
Overall, 474 patients were included in the trial, and of these 236 were randomized to VTD and 238 to the TD arm. Median follow-up for surviving patients was 92.8 months (IQR: 59.6-123.0). Analyses were performed on an intention-to-treat basis.
Results
Median PFS was 56.5 months for patients randomly assigned to the VTD arm, and 41.3 months for those in the TD group (HR=0.66, p<0.001). PFS benefit with VTD was seen for patients with ISS stage II-III (HR=0.68, p=0.007) and ISS stage I (HR=0.60, p=0.005), as well as for those with t(4;14) and/or del(17p) positivity (HR=0.45, p<0.001) and negativity (HR=0.66, p=0.003). Median OS was not yet reached in the VTD arm and was 118.6 months in the TD arm (HR=0.71, p=0.024), representing a 29% reduction in the risk of death with incorporation of VTD into double ASCT (Figure 1). Estimated rates of OS at 93 months were 67.6% and 58.5%, respectively. Superior OS benefit with VTD over TD was retained across prespecified subgroups of patients with both high-risk and low-risk disease, including those with ISS stages III (HR=0.52, p=0.056), ISS stage I (HR=0.56, p=0.033) and cytogenetics by FISH. In particular, VTD significantly prolonged the OS of patients with both t(4;14) and/or del(17p) positivity (HR=0.57, p=0.031) and negativity (HR=0.66, p=0.034). On multivariate Cox regression analysis, randomization to VTD was an independent factor predicting for prolonged PFS (HR=0.62, p<0.001) and OS (HR=0.61, p=0.001). Additional disease-related variables with a favorable impact on PFS and OS were absence of t(4;14) and/or del(17p) (HR=0.50, p<0.001; HR=0.49, p<0.001), and β2-microglobulin <3.5 mg/L (HR=0.60, p<0.001; HR=0.51, p<0.001). Further analyses of PFS2, time to second anti-MM therapy, and second primary malignancies will be presented at the meeting.

Conclusion
With an extended median follow-up of 7.6 years, a persistent PFS benefit with incorporation of VTD into ASCT was confirmed. Moreover, a longer OS from primary randomization to VTD versus TD was demonstrated in the overall population, as well as in subgroups of patients with high risk and low risk MM.
Session topic: 14. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Keyword(s): Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, bortezomib, Myeloma


